 |
|
Temperature (sometimes called thermodynamic temperature) is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
a system. Adding heat to a system causes its temperature to rise. While there is no maximum theoretically
reachable temperature, there is a minimum temperature, known as absolute zero, at which all molecular motion
stops. Temperatures are commonly measured in the Kelvin or Celsius scales, with Fahrenheit still
in common use in the Unites States.
Temperature is an important quantity in thermodynamics and kinetic theory, appearing explicitly for example
in the ideal gas law
 |
(1) |
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, and R is the
universal gas constant. Thermodynamically, temperature is given by the Maxwell relation
 |
(2) |
where E is the energy, S is the entropy, and the partial derivative is taken at constant volume.
The quantity 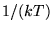 , where k is Boltzmann's constant, arising frequently in thermodynamics is
defined as , where k is Boltzmann's constant, arising frequently in thermodynamics is
defined as
 |
(3) |
a quantity sometimes known as thermodynamic beta.
 Absolute Temperature, Absolute Zero, Blackbody Temperature, Debye Temperature, Fahrenheit, Heat, Kelvin, Potential Temperature, Rankine, Temperature Wave Absolute Temperature, Absolute Zero, Blackbody Temperature, Debye Temperature, Fahrenheit, Heat, Kelvin, Potential Temperature, Rankine, Temperature Wave


© 1996-2007 Eric W. Weisstein
|