What is it about?
JPA 2 defines a typesafe Criteria API which allows Criteria queries
to be constructed in a strongly-typed manner, utilizing so called
static metamodel classes.
For developers it is important that the task of the metamodel generation
can be automated.
Hibernate Static Metamodel Generator is an annotation processor based on
JSR_269 with the task of creating JPA 2
static metamodel classes.
The following example shows two JPA 2 entities Order and Item, together
with the metamodel class Order_ and a typesafe query.
Order and Item@Entity
public class Order {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
Integer id;
@ManyToOne
Customer customer;
@OneToMany
Set<Item> items;
BigDecimal totalCost;
// standard setter/getter methods
...
}
@Entity
public class Item {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
Integer id;
int quantity;
@ManyToOne
Order order;
// standard setter/getter methods
...
}@StaticMetamodel(Order.class)
public class Order_ {
public static volatile SingularAttribute<Order, Integer> id;
public static volatile SingularAttribute<Order, Customer> customer;
public static volatile SetAttribute<Order, Item> items;
public static volatile SingularAttribute<Order, BigDecimal> totalCost;
}CriteriaBuilder cb = entityManager.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<Order> cq = cb.createQuery(Order.class);
SetJoin<Order, Item> itemNode = cq.from(Order.class).join(Order_.items);
cq.where( cb.equal(itemNode.get(Item_.id), 5 ) ).distinct(true);|
Hibernate Static Metamodel Generator also takes into consideration xml
configuration specified in <persistence-unit-metadata> <xml-mapping-metadata-complete/> </persistence-unit-metadata> |
Canonical Metamodel
The structure of the metamodel classes is described in the JPA 2 (JSR 317) specification, but for completeness the definition is repeated in the following paragraphs. Feel free to skip ahead to the usage chapter, if you are not interested into the gory details.
The annotation processor produces for every managed entity in the persistence unit a metamodel class based on these rules:
-
For each managed class X in package p, a metamodel class X_ in package p is created.
-
The name of the metamodel class is derived from the name of the managed class by appending "_" to the name of the managed class.
-
The metamodel class X_ must be annotated with the
javax.persistence.StaticMetamodelannotation. -
If class X extends another class S, where S is the most derived managed class (i.e., entity or mapped superclass) extended by X, then class X_ must extend class S_, where S_ is the metamodel class created for S.
-
For every persistent non-collection-valued attribute y declared by class X, where the type of y is Y, the metamodel class must contain a declaration as follows:
public static volatile SingularAttribute<X, Y> y;
-
For every persistent collection-valued attribute z declared by class X, where the element type of z is Z, the metamodel class must contain a declaration as follows:
-
if the collection type of z is java.util.Collection, then
public static volatile CollectionAttribute<X, Z> z;
-
if the collection type of z is java.util.Set, then
public static volatile SetAttribute<X, Z> z;
-
if the collection type of z is java.util.List, then
public static volatile ListAttribute<X, Z> z;
-
if the collection type of z is java.util.Map, then
public static volatile MapAttribute<X, K, Z> z;
where K is the type of the key of the map in class X
-
Import statements must be included for the needed javax.persistence.metamodel types as
appropriate and all classes X, Y, Z, and K.
Usage
The jar file for the annotation processor can be found in the Maven Central repository under:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-jpamodelgen</artifactId>
<version>5.4.33.Final</version>
</dependency>Alternatively, it can be found in the ORM distribution bundle on SourceForge.
In most cases the annotation processor will automatically run provided the processor jar is added to the build classpath. This happens due to Java’s Service Provider contract and the fact the Hibernate Static Metamodel Generator jar files contains the file javax.annotation.processing.Processor in the META-INF/services directory.
The fully qualified name of the processor itself is:
org.hibernate.jpamodelgen.JPAMetaModelEntityProcessor.
Usage from the command line
Usage with Ant
As mentioned above, the annotation processor will run automatically each time the Java compiler is called, provided the jar file is on the classpath. Sometimes, however, it is useful to control the annotation processing in more detail, for example if you exclusively want to run the processor without compiling any other source files. The Javac task configuration below shows how Ant can be configured to just run annotation processing.
<javac srcdir="${src.dir}"
destdir="${target.dir}"
failonerror="false"
fork="true"
classpath="${classpath}">
<compilerarg value="-proc:only"/>
</javac>The option -proc:only instructs the compiler to just run the annotation processing. You can also completely disable processing by specifying -proc:none.
|
Run |
Usage with Maven
There are several ways of running the annotation processor as part of a Maven build. Again, it will automatically run if you are compiling with a JDK >6. In case you have more than one annotation processor on your classpath you can explicitly pass the processor option to the compiler plugin:
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<compilerArguments>
<processor>org.hibernate.jpamodelgen.JPAMetaModelEntityProcessor</processor>
</compilerArguments>
</configuration>
</plugin>The maven-compiler-plugin approach has the disadvantage that the maven compiler plugin does currently not allow to specify multiple compiler arguments (MCOMPILER-62) and that messages from the Messenger API are suppressed (MCOMPILER-66). A better approach is to disable annotation processing for the compiler plugin as seen in below.
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<compilerArgument>-proc:none</compilerArgument>
</configuration>
</plugin>Once disabled, the maven-processor-plugin for annotation processing can be used:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.bsc.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-processor-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>process</id>
<goals>
<goal>process</goal>
</goals>
<phase>generate-sources</phase>
<configuration>
<processors>
<processor>org.hibernate.jpamodelgen.JPAMetaModelEntityProcessor</processor>
</processors>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-jpamodelgen</artifactId>
<version>5.4.33.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>Another possibility is to supply the dependency as an annotation processor path to the maven-compiler-plugin:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-jpamodelgen</artifactId>
<version>5.4.33.Final</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>Usage within the IDE
Of course you also want to have annotation processing available in your favorite IDE. The following paragraphs and screenshots show you how to enable the Hibernate Static Metamodel Generator within your IDE.
Idea
Intellij Idea contains from version 9.x onwards a specific configuration section for annotation processing under the project settings window. The screenshots show you how to configure the Hibernate Static Metamodel Generator.
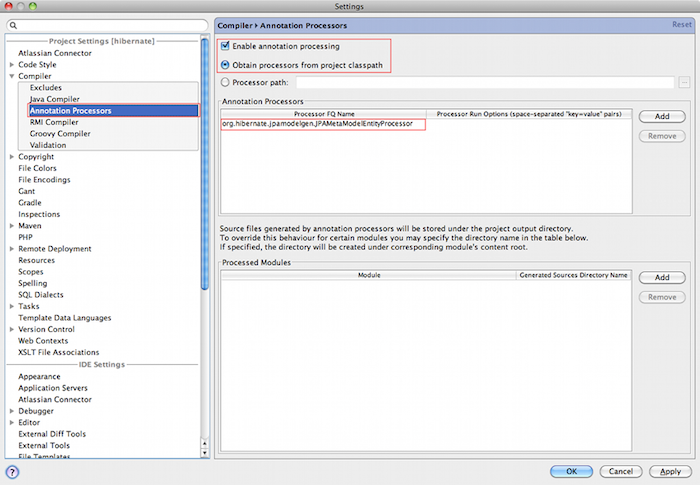
In the annotation processor configuration, enable annotation processing and select obtain
from project classpath.
Add the annotation processor name org.hibernate.jpamodelgen.JPAMetaModelEntityProcessor
(and optionally the annotation processor options).
Select the module(s) containing your entities.
If you have configured Maven as recommended, it is best to select the same output directory
for the generated classes.
At the time of writing, it is target/generated-sources/apt. That way, the generated
classes will be available in IntelliJ Idea.
Eclipse
In Eclipse exists also an additional configuration section under Java Compiler. There you can configure all kinds of aspects of annotation processing. Just check the "Enable annotation processing" option, configure the directory for the generated sources and finally add the Hibernate Static Metamodel Generator and JPA 2 jar files to the factory path.
If you use JDK 11+, you also need to add the javax.xml.bind:jaxb-api and
org.glassfish.jaxb:jaxb-runtime jars as JAXB is not included in the JDK anymore.
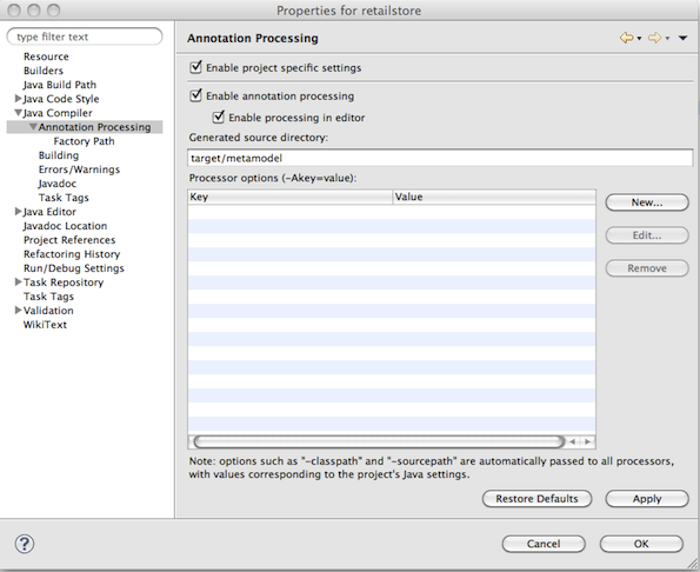
Processor specific options
The Hibernate Static Metamodel Generator accepts a series of custom
options which can be passed to the processor in the format: -A[property]=[value]
The supported properties can be found in the table below:
| Option name | Option value and usage |
|---|---|
debug |
If set to |
persistenceXml |
Per default the processor looks in /META-INF for persistence.xml. Specifying this option a persitence.xml file from a different location can be specified (has to be on the classpath) |
ormXml |
Allows to specify additional entity mapping files. The specified value for this option is a comma separated string of mapping file names. Even when this option is specified /META-INF/orm.xml is implicit. |
lazyXmlParsing |
Possible values are |
fullyAnnotationConfigured |
If set to |
addGeneratedAnnotation |
If set to |
addGenerationDate |
If set to true the generation date
of the metamodel class will be inserted in the
date parameter of the @Generated annotation.
The default is |
addSuppressWarningsAnnotation |
If set to |