Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
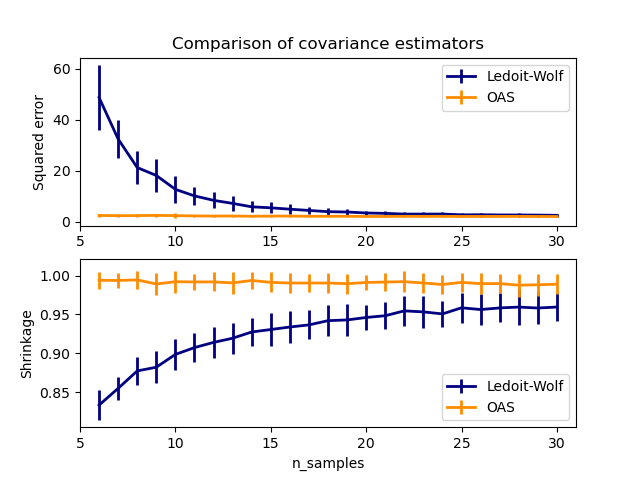
Ledoit-Wolf vs OAS estimation#
The usual covariance maximum likelihood estimate can be regularized using shrinkage. Ledoit and Wolf proposed a close formula to compute the asymptotically optimal shrinkage parameter (minimizing a MSE criterion), yielding the Ledoit-Wolf covariance estimate.
Chen et al. proposed an improvement of the Ledoit-Wolf shrinkage parameter, the OAS coefficient, whose convergence is significantly better under the assumption that the data are Gaussian.
This example, inspired from Chen’s publication [1], shows a comparison of the estimated MSE of the LW and OAS methods, using Gaussian distributed data.
[1] “Shrinkage Algorithms for MMSE Covariance Estimation” Chen et al., IEEE Trans. on Sign. Proc., Volume 58, Issue 10, October 2010.
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.linalg import cholesky, toeplitz
from sklearn.covariance import OAS, LedoitWolf
np.random.seed(0)
n_features = 100
# simulation covariance matrix (AR(1) process)
r = 0.1
real_cov = toeplitz(r ** np.arange(n_features))
coloring_matrix = cholesky(real_cov)
n_samples_range = np.arange(6, 31, 1)
repeat = 100
lw_mse = np.zeros((n_samples_range.size, repeat))
oa_mse = np.zeros((n_samples_range.size, repeat))
lw_shrinkage = np.zeros((n_samples_range.size, repeat))
oa_shrinkage = np.zeros((n_samples_range.size, repeat))
for i, n_samples in enumerate(n_samples_range):
for j in range(repeat):
X = np.dot(np.random.normal(size=(n_samples, n_features)), coloring_matrix.T)
lw = LedoitWolf(store_precision=False, assume_centered=True)
lw.fit(X)
lw_mse[i, j] = lw.error_norm(real_cov, scaling=False)
lw_shrinkage[i, j] = lw.shrinkage_
oa = OAS(store_precision=False, assume_centered=True)
oa.fit(X)
oa_mse[i, j] = oa.error_norm(real_cov, scaling=False)
oa_shrinkage[i, j] = oa.shrinkage_
# plot MSE
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.errorbar(
n_samples_range,
lw_mse.mean(1),
yerr=lw_mse.std(1),
label="Ledoit-Wolf",
color="navy",
lw=2,
)
plt.errorbar(
n_samples_range,
oa_mse.mean(1),
yerr=oa_mse.std(1),
label="OAS",
color="darkorange",
lw=2,
)
plt.ylabel("Squared error")
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.title("Comparison of covariance estimators")
plt.xlim(5, 31)
# plot shrinkage coefficient
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.errorbar(
n_samples_range,
lw_shrinkage.mean(1),
yerr=lw_shrinkage.std(1),
label="Ledoit-Wolf",
color="navy",
lw=2,
)
plt.errorbar(
n_samples_range,
oa_shrinkage.mean(1),
yerr=oa_shrinkage.std(1),
label="OAS",
color="darkorange",
lw=2,
)
plt.xlabel("n_samples")
plt.ylabel("Shrinkage")
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.ylim(plt.ylim()[0], 1.0 + (plt.ylim()[1] - plt.ylim()[0]) / 10.0)
plt.xlim(5, 31)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.400 seconds)
Related examples

Shrinkage covariance estimation: LedoitWolf vs OAS and max-likelihood

Normal, Ledoit-Wolf and OAS Linear Discriminant Analysis for classification


