Mental health issues have come into a clearer focus amid the pandemic. Depression became endemic, but it still too often goes undetected. Even when it does, healthcare providers struggle to meet demand. Two women engineers — both of whom experienced depression and had trouble finding therapy — thought the answer might be helping medical pros detect depression.
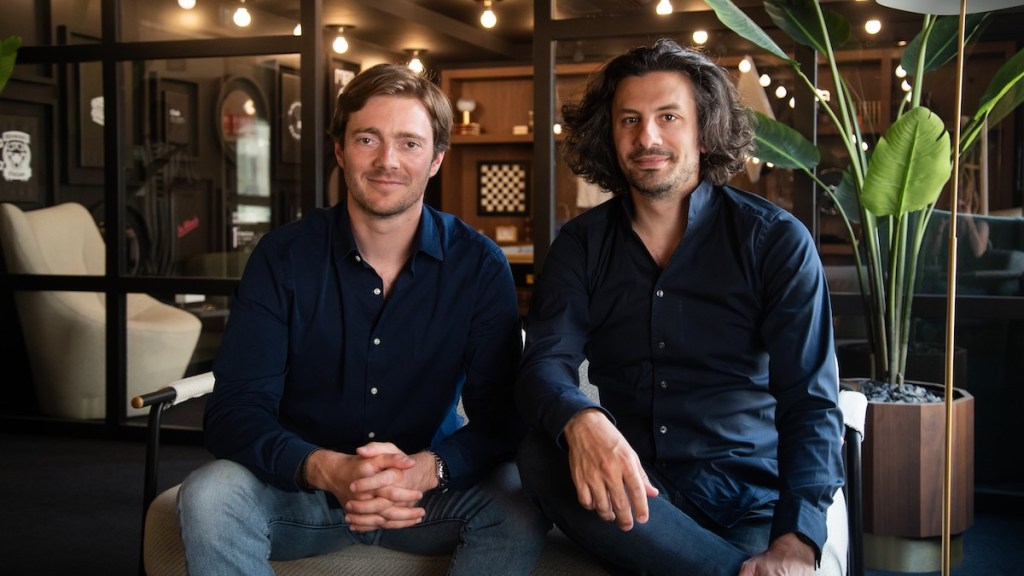
Kintsugi is a startup that wants to put technology to work on the problem. Co-founder and CEO Grace Chang saw this as an access issue: Both founders experienced bouts of depression and found it difficult to get clinicians to help, leading them to think about it from their perspective as engineers.
They figured that if it was possible to identify the people who need therapy the most, it would be easier to achieve the goal of directing those people to suitable treatment. So Chang and co-founder Rima Seiilova-Olson built an API to detect signs of depression through voice.
“We saw this as an infrastructure problem where you have so many people trying to jam through that front door, but not a lot of visibility as to who is severely depressed and who is in this low to moderate phase. And if we can provide this information to those practitioners, we can really deeply affect the specific problem,” she said.
Why voice?
People who are feeling blue tend to have a flat voice, something that clinicians have observed for decades. This is true regardless of language or culture and appears to be a universal human reaction to depression, according to Seiilova-Olson.
“Psychomotor retardation is the process of slowing down of thought and muscle movements. And it’s universal no matter where you’re born or what language you speak,” she said.
Psychiatrists who observe severely depressed patients notice this symptom, Seiilova-Olson noted. Kintsugi is attempting to use technology to build a machine learning model with many more samples than any individual clinician could see in a lifetime. The solution measures the likelihood of depression on two scales, the PHQ-9 (0-27 with a higher numbers indicating higher severity) and GAD-7 (0-21, same). After a patient grants permission, the clinician can get immediate feedback based on the score. The score, which becomes part of the patient notes, is protected under doctor-patient privilege, according to the company.
“Our neural network model has been trained on tens of thousands of depressed voices. So it can be like a set of psychiatrists, but it’s much more sensitive. It can pick it up even when the depression is at mild or moderate levels,” she said.
Even before the pandemic, depression was rampant. The World Health Organization reports that 5% of adults worldwide suffer from clinical depression. That adds up to 280 million people. It is the leading cause of disability in the world, and it doesn’t have to be that way.
The WHO reports that all forms of depression — whether mild, moderate or severe — are treatable if detected. But too often those with depression suffer in silence and don’t seek help for their condition. A 2017 article published in the SSM Population Health Journal cites a 1999 study that found two-thirds of depression cases in the U.S. go undiagnosed.
This is even more tragic when you consider that 700,000 people take their own lives each year as a result of depression, according to the WHO. Among the problems with getting people into treatment is a lack of trained professionals to help diagnose it, and the fact that medical professionals tend to tackle this problem only when patients report symptoms, which can be unreliable.
Finding a data source
Before Chang and Seiilova-Olson could build a model to detect depression signals through voice, they needed data. The first step involved interviewing around 200 psychologists, psychiatrists and clinicians. They learned through their research that journaling was a good way for people to sort out their feelings.
So the first thing they did was build a voice journaling app ($19.99), also called Kintsugi. With that, they were able to access thousands of voice samples that they used to train the model on what a depressed voice sounds like.
If you’re worried about privacy here, the terms of service indicated that the data could be used for research purposes. In terms of security, entries are encrypted in transit and at rest, but they are also shareable publicly if people are inclined to do that. Further, Chang said they deliberately made the choice upfront not to use natural language processing, which keeps the content of the journals out of the equation. Their goal was simply to understand how people were speaking, rather than what they were saying, which was really not relevant to the issue they were trying to solve.
Chang said this solved three problems. For starters, they didn’t have to worry about protecting the privacy of their individual users because the content was not the target of their research. It also simplified the underlying technology and enabled them to focus on building a scoring system based on the pattern in the voice. Finally, using pattern recognition allowed them to be language-agnostic — it didn’t matter what people were saying or what language they were speaking.
Building the solution
The founders thought long and hard about how to incorporate this solution into a clinical setting, and they decided to build an API that connects into the clinical notes section of the patient’s electronic health record.
Patients are sometimes asked to assess their own mental health state as part of the patient intake process, but they often don’t accurately assess their condition. That’s where the Kintsugi solution comes into play.
“We have an API, which is just a software layer that is integrated into clinical call centers and telehealth applications … and it is for nurses and care managers when they do their outbound calls to patients to understand in that short window of time if that patient is struggling with a behavioral health issue, and if the patient is struggling to provide information to that patient with what different types of care are available to him or her,” Chang explained.
The company points out that while it is working with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for what is called De Novo approval, the solution is identified as a Clinical Decision Support tool under the 21st Century Cures Act. Such support tools do not require explicit FDA approval, the founders told me.
Kintsugi also conducted a clinical study and is in the process of publishing a paper in a peer-reviewed journal with the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS), but it didn’t want to share details until the official announcement.
The two founders met at a hackathon in 2019 and were excited just to encounter another woman at such an event, which tend to be attended mostly by men. They bonded over a mutual love of coding and their similar immigrant experiences: Chang grew up in Taiwan, while Seiilova-Olson grew up in Kazakhstan.
As they got to know each other, they realized that each had struggled to find mental health care when they needed it and began exploring the idea of building a solution to help. They raised an initial $8 million seed round to build the product last year and another $20 million Series A earlier this year.
Fundraising as two immigrant women founders presented its own unique challenges, Chang said. “The barrier for women is that you can’t paint a story of all these things that you’re going to do. You already must have these things done for people to invest in you, and so I think that is quite a challenge, probably not just for women, but for minorities more broadly I would imagine,” she said.
They are not alone in this space. Ellipsis Health, Sonde Health, Vocalis Health and Winterlight Labs are working on similar voice-based solutions for identifying mental health conditions. Some of these companies have identified problems providing consistent results across different dialects and demographics, but Kintsugi’s founders believe their approach overcomes these issues.
Kintsugi already has contracts with a couple of large healthcare companies and is working to build on that.
Prioritizing tech in 2021 will be the path to pandemic recovery for mental health






























Comment