At least six distinct botnet malware operations are hunting for TP-Link Archer AX21 (AX1800) routers vulnerable to a command injection security issue reported and addressed last year.
Tracked as CVE-2023-1389, the flaw is a high-severity unauthenticated command injection problem in the locale API reachable through the TP-Link Archer AX21 web management interface.
Several researchers discovered it in January 2023 and reported to the vendor through the Zero-Day Initiative (ZDI). TP-Link addressed the problem with the release of firmware security updates in March 2023. Proof-of-concept exploit code emerged shortly after the security advisories became public.
Following that, cybersecurity teams warned about multiple botnets, including three Mirai variants (1, 2, 3) and a botnet named "Condi," that targeted unpatched devices.
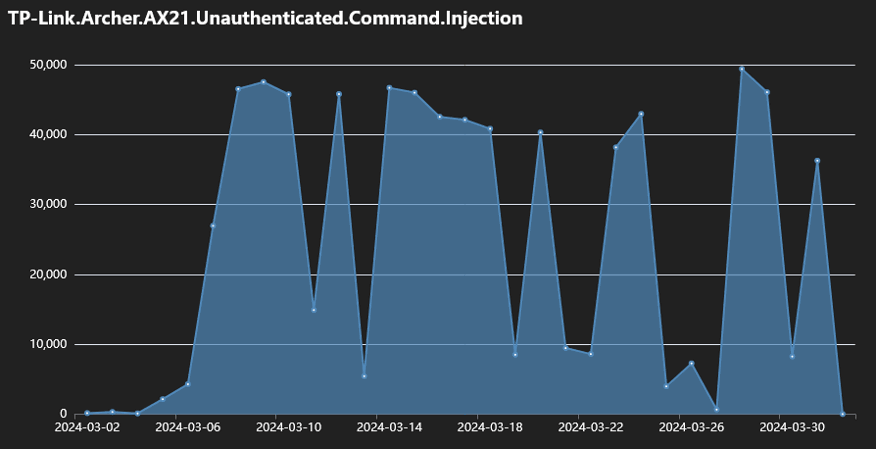
Yesterday, Fortinet issued another warning saying that it observed a surge in the malicious activity exploiting the vulnerability, noting that it originated from six botnet operations.
Fortinet's telemetry data shows that starting in March 2024, daily infection attempts leveraging CVE-2023-1389 often went beyond 40,000 and up to 50,000.
(Fortinet)
Each of these botnets utilizes different methods and scripts to exploit the vulnerability, establish control over the compromised devices, and command them to take part in malicious activities such as distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
- AGoent: Downloads and executes scripts that fetch and run ELF files from a remote server, then erases the files to hide traces.
- Gafgyt variant: Specializes in DDoS attacks by downloading scripts to execute Linux binaries and maintaining persistent connections to C&C servers.
- Moobot: Known for initiating DDoS attacks, it fetches and executes a script to download ELF files, executes them based on architecture, and then removes traces.
- Miori: Utilizes HTTP and TFTP to download ELF files, executes them, and uses hardcoded credentials for brute force attacks.

(Fortinet)
- Mirai variant: Downloads a script that subsequently fetches ELF files, which are compressed using UPX. Monitors and terminates packet analysis tools to avoid detection.
- Condi: Uses a downloader script to enhance infection rates, prevents device reboots to maintain persistence, and scans for and terminates specific processes to avoid detection.

(Fortinet)
Fortinet's report indicates that despite the vendor's release of a security update last year, a significant number of users continue to use outdated firmware.
TP-Link Archer AX21 (AX1800) router users are advised to follow the vendor's firmware upgrading instructions, available here. They should also change the default admin passwords to something unique and long, and disable web access to the admin panel if not needed.








Comments
jkr4m3r - 8 months ago
I had this router, and it had quit updating automatically or even when manually logging in and checking with the update button a couple of years ago. I had to go to the site, download the firmware, and manually install it. When logged in to the router it always showed the wrong hardware version also, I had to look at the label on the bottom of the unit to avoid bricking it with the wrong firmware file.
Moral of the story?
TP-Link can go F themselves.
b1k3rdude - 8 months ago
Welp, their kit is cheap and does what it says on the tin, but the issue is they as many users have found out after the fact, are utterly rubbish at updates beyond a year past date of manufacture.
Its why mine got relegated to wi-fi access point duty and the firewall was replaced with a custom passively cooled embedded PC running PfSense.
electrolite - 8 months ago
Time and time again, the main vector in most of these router hacks are through the access of the web interface through the WAN port. Just blocking this on the WAN side (which should be the default) would prevent so many botnets from recruiting their armies.