Last Updated on August 19, 2024 by Admin
In the rapidly evolving fields of construction, architecture, and engineering, 3D models have become indispensable tools. These digital representations of physical objects and spaces offer a level of detail and accuracy that transforms how professionals in these industries design, plan, and execute projects. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer, a student in the field, or simply someone interested in the latest technological advancements, understanding 3D models is crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
In this post, we’ll explore 3D models, their applications, and how they are revolutionizing various industries. We will also include a few illustrative drawings to help visualize some of the concepts discussed.
Table of Contents
What Are 3D Models?
3D models are mathematical representations of three-dimensional objects created using specialized software. They can represent anything from a simple object like a chair to complex structures like skyscrapers or entire cityscapes. The primary purpose of 3D modeling is to visualize an object or space’s shape, structure, and dimensions in a way that two-dimensional drawings cannot achieve.
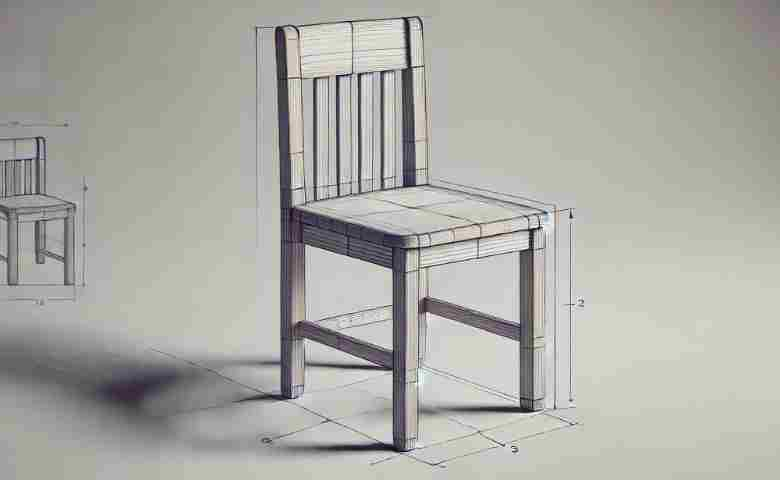

Types of 3D Models
There are several types of 3D models, each with specific applications and advantages. Here are the most common types:
1. Solid Modeling
Solid modeling involves creating a 3D representation of an object with volume. This type of modeling is typically used in engineering and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Solid models are essential for simulations, manufacturing processes, and stress testing.
2. Surface Modeling
Surface modeling focuses on an object’s outer shell or surface. It is widely used in industries like automotive design and animation, where the external appearance of an object is more important than its internal structure.
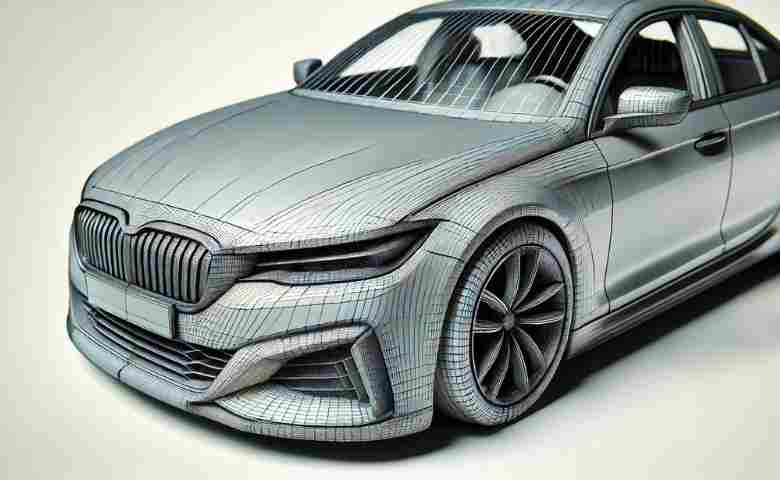

3. Wireframe Modeling
Wireframe modeling is the most basic form of 3D modeling, representing objects using lines and vertices. This method helps visualize the skeletal structure of complex objects and is often used as the first step in creating more detailed models.

Related CAD Courses:
- Building Estimation Course and Quantity Surveying With Cad
- Catia V5 Zero to Hero! Catia V5 Beginners Course in CAD
- Fusion 360, Solidworks & CATIA – CAD Mastery Workshop
- Microstation – Learn 2D and 3D CAD design
Applications of 3D Models
3D models are used across various industries, each leveraging the technology to meet specific needs. Here are some key applications:
1. Architecture and Construction
3D models are used in architecture and construction to create detailed representations of buildings and infrastructure. These models help in visualizing the final product, conducting simulations, and identifying potential issues before construction begins. Building Information Modeling (BIM), a subset of 3D modeling is particularly crucial in this sector because it integrates various aspects of the building process.
2. Engineering
Engineers use 3D models to design and test parts and assemblies. This process includes stress analysis, motion simulations, and manufacturing design optimization. The ability to test a model virtually saves time and reduces costs by minimizing the need for physical prototypes.
3. Entertainment and Media
The entertainment industry uses 3D models extensively in video games, movies, and virtual reality experiences. Characters, environments, and special effects are all created using sophisticated 3D modeling techniques, making the unreal appear natural.
4. Healthcare
In healthcare, 3D models are used for a variety of purposes, including the visualization of human anatomy, planning surgeries, and creating custom prosthetics. These models help medical professionals better understand complex cases and improve patient outcomes.
5. Manufacturing
Manufacturers use 3D models to design products and plan production processes. These models are critical in identifying design flaws, optimizing parts for production, and ensuring that final products meet stringent quality standards.
Top-Rated Revit Online Courses:
- Virtual Building Design for Engineers Using Autodesk Revit
- Autodesk Certified Professional: Revit for Architectural Design Exam Prep
- Autodesk Certified Professional: Revit for Structural Design Exam Prep
- BIM Application for Engineers
- 3D Architectural Design and Modeling with Revit
The Process of Creating 3D Models
Creating a 3D model typically involves several steps, depending on the object’s complexity. Here’s an overview of the process:
1. Conceptualization
The first step is to conceptualize the object or structure. This involves creating sketches or 2D drawings that outline the model’s basic shape, size, and features.
2. Modeling
The conceptualized design is then turned into a digital model using 3D modeling software. This step requires precision and attention to detail, as the model must accurately represent the real-world object.
3. Texturing
Texturing adds color, patterns, and surface details to the 3D model. This step is crucial in industries like entertainment and architecture, where the model’s appearance is crucial.
4. Lighting and Rendering
Once the model is textured, lighting is applied to simulate the object’s appearance in different environments. Rendering is the final step, where the model is processed into a high-quality image or animation.
5. Testing and Refinement
Before a 3D model is finalized, it undergoes testing to ensure it meets all specifications. This may involve stress tests, motion simulations, or visual inspections. Any issues identified are corrected, and the model is refined as needed.
Related 3D Modelling courses:
- Master SOLIDWORKS 3D CAD using real-world examples
- HANDS ON Step By Step 3D CAD Modeling SOLIDWORKS Pro Course
- 3D CAD Application
- SOLIDWORKS CAD Fundamentals
Benefits of 3D Modeling
3D modeling offers several key benefits that are transforming how industries operate:
- Improved Visualization: 3D models provide a realistic representation of objects, making it easier to visualize the final product.
- Enhanced Precision: The detailed nature of 3D models allows for greater accuracy in design and construction.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: By identifying potential issues early in the design process, 3D models help reduce the need for costly changes during construction or production.
- Better Communication: 3D models serve as a universal language, helping teams from different disciplines communicate more effectively.
Conclusion
3D models have revolutionized industries by providing a powerful visualization, design, and testing tool. From architecture and engineering to entertainment and healthcare, the applications of 3D modeling are vast and continue to expand as technology advances. By understanding the types, applications, and benefits of 3D models, professionals and students alike can harness this technology to enhance their work and achieve tremendous success in their respective fields.
Related Posts:
- The Evolution Of Smart Tech In Modern Homes
- What is Civil 3D Software and why it is Important to Learn?
- Unlocking the Power of 3D Analysis
- Essential Skills for a BIM Professional
- Mastering Business and Financial Modeling for Construction Projects: A Comprehensive Guide


