As businesses face a growing array of cyberthreats, understanding how generative AI can be used in cybersecurity has become vital for organizational resilience. Generative AI is making a remarkable impact across various industries, and cybersecurity is no exception—the technology has numerous applications in the field, from refining threat detection to supercharging employee training. However, using generative AI also brings specific risks for organizations to consider. Establishing best practices and understanding the advantages, and guidelines for secure implementation can help you unlock generative AI’s benefits while safeguarding against vulnerabilities.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- •Using generative AI in cybersecurity offers many advantages, including better security automation, comprehensive analysis, threat detection, and scenario-driven cybersecurity training. (Jump to Section)
- •Generative AI in cybersecurity introduces risks, such as model training vulnerabilities, concerns about data privacy, jailbreaking, exploitation of the technology for cyber attacks. (Jump to Section)
- •Following best practices is key to safe generative AI integration, ensuring that genAI tools are used properly while minimizing risks and maintaining security standards. (Jump to Section)
Featured Partners: Cybersecurity Software
TABLE OF CONTENTS
6 Ways That Generative AI Can Be Used in Cybersecurity
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is reshaping cybersecurity by improving threat detection, elevating employee training, and optimizing security protocols. It empowers organizations to build a more robust defense against cyber threats. There are several ways genAI is used in this area, with numerous tools available to help drive these applications and reinforce security strategies.
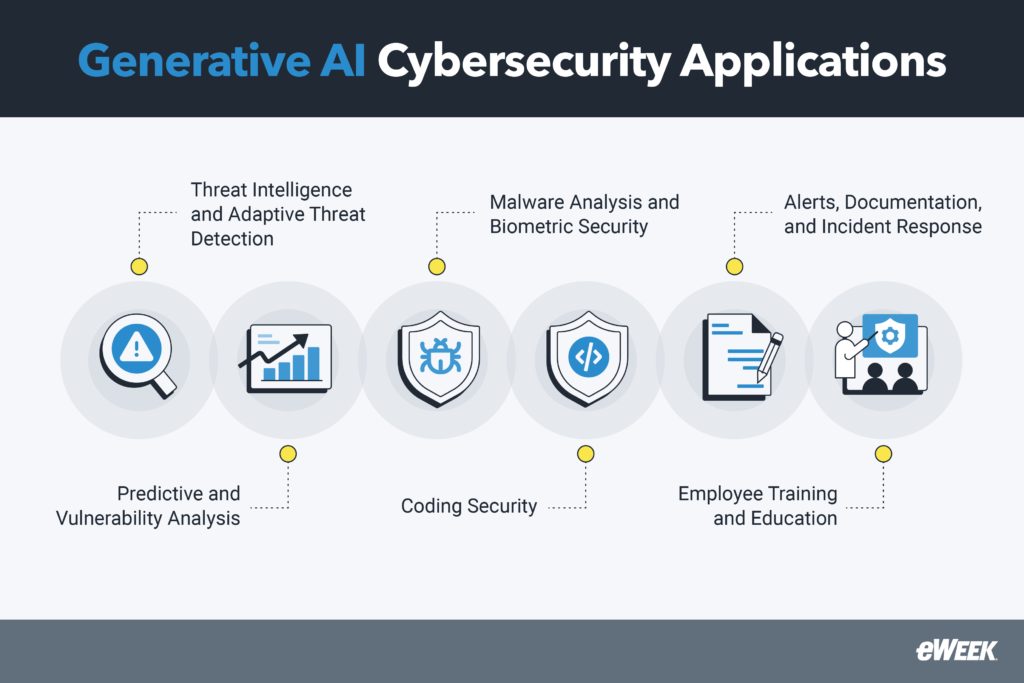
Threat Intelligence and Adaptive Threat Detection
Generative AI enhances threat intelligence by helping cybersecurity teams process large volumes of data more efficiently to prioritize potential threats tailored to your organization’s specific risk profile. It reduces the noise from generic alerts so security professionals can focus on the most urgent threats. By continuously learning from user interactions, generative AI becomes increasingly adept at finding anomalies that could indicate new or evolving threats. This proactive approach allows businesses to stay ahead of cybercriminals by swiftly adapting to their tactics.
For example, Google Threat Intelligence incorporates its generative AI model Gemini to handle the heavy lifting in data analysis. Gemini sifts through extensive datasets, including information from Mandiant’s threat research and VirusTotal’s global community. It surfaces the most relevant threats to an organization by continuously learning and tailoring its insights. Additionally, Gemini generates AI-powered summaries of possible risks, distilling complex reports into clear, digestible information. As a result, security teams can quickly understand and respond to emerging threats.
Predictive and Vulnerability Analysis
GenAI can make accurate predictions on future cyber threats and pinpoint the most pressing vulnerabilities within enterprise systems. By analyzing past attack patterns and scanning vulnerabilities, it helps organizations strengthen their security before threats materialize. This dual function of predictive and vulnerability analysis helps teams to concentrate on high-risk areas and enables them to be more forward-thinking, addressing vulnerabilities early and reducing exposure to future exploits.
Tenable.io uses generative AI to analyze historical vulnerability data and predict future threats. It aids enterprises in prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their possible impact and the likelihood of exploitation, promoting better risk management and resource allocation.
Malware Analysis and Biometric Security
Researchers can use generative AI to create synthetic data for studying malware behavior and bolstering biometric security systems, providing a safe and effective way to enhance cybersecurity measures. GenAI can produce realistic malware samples, allowing security teams to safely study threat behaviors and observe how they interact with different systems.
Similarly, in biometric security, genAI can create synthetic biometric data-–real fingerprints and facial recognition patterns, for example—to enable businesses to rigorously assess their authentication systems against spoofing attempts. Enterprises can partner with firms like Syntheticus, which specializes in synthetic data generation, to create artificial datasets for malware testing and biometric security. Syntheticus can generate realistic data that mirrors the statistical properties of real-world information while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Development Assistance and Coding Security
Generative AI serves as a reliable assistant for developers, guiding them in writing secure code with real-time feedback and promoting adherence to best practices. Coding assistants with artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities can learn from previous examples to give clear recommendations or flag potential security risks before code is deployed. With genAI, developers can avoid common pitfalls and coding errors throughout the software development process.
GitHub Copilot is an AI-powered coding assistant that can help augment coding security with its Copilot Autofix feature. This feature specifically addresses security vulnerabilities by quickly finding and suggesting fixes for issues detected in the code. It uses generative AI to analyze code for vulnerabilities, explain their implications, and offer solutions.
Alerts, Documentation, and Incident Response
By streamlining alert management and documentation, genAI significantly boosts efficiency within cybersecurity teams. The technology can translate complex alerts and detailed documentation into clear summaries, helping analysts to clearly grasp urgent situations. This clarity reduces response times and enables teams to prioritize security issues more accurately. After processing alerts and documentation, generative AI provides actionable recommendations so organizations can conduct helpful countermeasures for risk mitigation.
ServiceNow Security Operations automates incident report generation and alerts using generative AI. It translates complicated issues into concise, understandable summaries for security teams. This includes structured incident summaries that contain key sections, such as nature of the incident, detailed context, observations from related records, and actions taken. By simplifying technical details, it aids analysts in understanding the incident without going through extensive logs or records.
Employee Training and Education
Training employees on cybersecurity best practices and enterprise technologies is another primary use of generative AI. By crafting interactive training modules, it can educate team members on recognizing threats and the value of following security protocols. This helps minimize human error—a major factor in many cyberattacks—ultimately fortifying an organization’s defenses.
CybSafe is a human risk management platform that employs genAI to make cybersecurity training better for employees by delivering personalized and interactive learning experiences. It evaluates user behavior to customize training modules that address specific risks, ensuring relevant content for each employee. Through real-time simulated phishing attacks, CybSafe tests users’ recognition skills and gives immediate feedback to reinforce learning.
Generative AI’s Benefits and Risks to Cybersecurity
Generative AI is becoming a major component in cybersecurity, automating complex tasks and helping organizations stay ahead of the emerging threats. But as the technology continues to grow, so do the issues it presents. Understanding both the advantages and risks of using generative AI in cybersecurity is of utmost importance as more organizations start to integrate this technology into their security strategies.
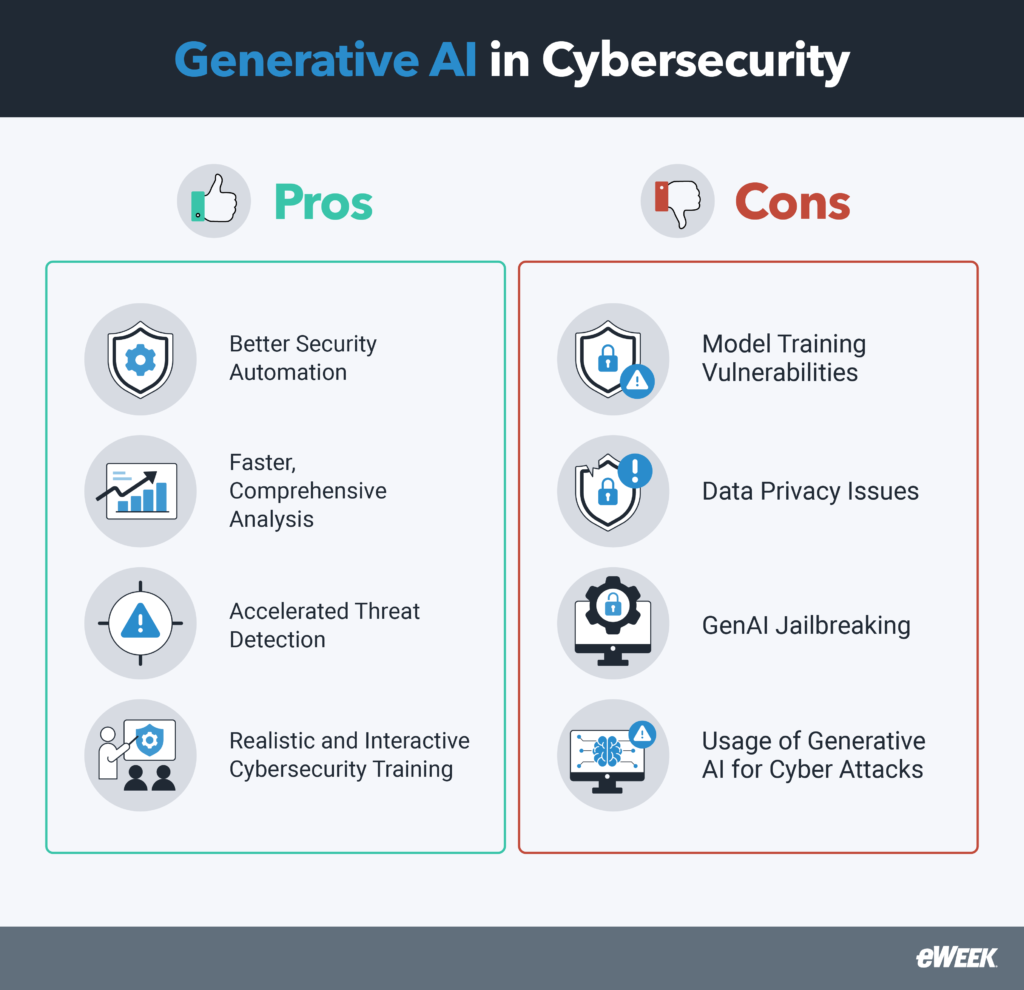
GenAI’s Top Cybersecurity Benefits
GenAI introduces a range of advantages that can dramatically augment cybersecurity strategies. The most common include the following:
- Enhanced Security Automation: GenAI streamlines the deployment of cybersecurity protocols, minimizing the need for manual oversight. This automated approach allows for rapid adjustments to defenses in real-time, substantially improving response times compared to traditional methods that often rely on human intervention.
- Accelerated Comprehensive Analysis: Generative AI systems can swiftly analyze vast amounts of data from diverse sources, such as logs and network traffic. This capability brings near-instant insights into potential threats, contrasting sharply with traditional analysis methods that can take hours to yield results.
- Proactive Threat Detection: By spotting subtle indicators of compromise that conventional cybersecurity tools might overlook, generative AI helps organizations boost their ability to detect threats before they escalate. This enables earlier intervention against sophisticated attacks, decreasing overall risk.
- Immersive Scenario-Driven Cybersecurity Training: Realistic training simulations that reflect current cyber threats and vulnerabilities are facilitated by generative AI. This modern approach to employee training surpasses traditional methods by offering dynamic, scenario-based learning experiences that better prepare staff to distinguish and respond to real-world cyber incidents.
Gen AI’s Top Cybersecurity Risks
While generative AI presents numerous advantages, it also poses risks to cybersecurity that organizations must carefully consider. Some of the most onerous include the following:
- Vulnerabilities in Model Training: The training process for generative AI models often involves large datasets that may contain sensitive information—if not properly managed, confidential data could be exposed or reproduced in the model’s outputs. GenAI models may also unintentionally learn and perpetuate biases present in the training data, resulting in discriminatory outputs. If a model is biased, it may disproportionately flag certain demographics based on flawed training data.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Generative AI systems can unintentionally store and recall sensitive data, making it challenging to ensure privacy. Once sensitive information is inputted into a model, it may linger within the system without a clear mechanism for deletion. This is a significant risk as confidential business information can be accessed or misused by unauthorized parties.
- Jailbreaking: Malicious actors can manipulate generative AI models to bypass restrictions and access sensitive information or generative harmful content. This could lead to creating misleading or dangerous outputs, undermining trust in AI systems and causing harm if used inappropriately.
- Exploitation of Generative AI for Cyber Attacks: Cybercriminals use generative AI to modernize their attack strategies by creating convincing phishing emails and using deepfake technologies that trick victims into trusting fraudulent communications. GenAI also expedites the rapid development of adaptable malware, making it increasingly difficult for traditional defenses to keep pace.
Cybersecurity Tips and Best Practices for Using Generative AI
Generative AI holds great promise in boosting productivity and innovation, as well as inherent risks that open new doors for cyber threats. By adopting targeted cybersecurity practices, you can use generative AI more confidently and mitigate risks associated with it.

Closely Read Security Policies From Generative AI Vendors
Before using any genAI tool, review the generative AI vendor’s security policies to understand how it handles your data and complies with industry regulations to find out the possible risks of using the tool. Look for transparency in how it protects sensitive information and any limitations on data retention or sharing.
Don’t Input Sensitive Data When Using Generative Models
Generative AI models are only as secure as the data they process. Avoid entering sensitive data—whether it’s confidential business information, financial records, or intellectual property—into genAI tools. Many generative systems may store and reuse data to improve capabilities, which can expose private information. Limiting the type of data you input helps reduce the risk of data breaches.
Keep Your Generative AI Models Updated
Regular updates are paramount for maintaining the security of your generative AI models. Make sure that you use the latest version of your generative AI tools, which often includes patches for vulnerabilities and performance upgrades. This helps to close any gaps that cybercriminals may exploit. Work with genAI companies that frequently update their models and communicate any security changes in a timely manner.
Use Data Governance and Security Tools
Employ robust data governance and security tools to ensure safety when using genAI. Data encryption, access controls, and regular auditing ensures that sensitive data stays protected. Additionally, data loss prevention (DLP) and identity access management (IAM) solutions can help prevent unauthorized access or leakage of information.
Establish Clear Usage Policies
Define acceptable use for generative AI tools within your organization in your AI policy. Specify which AI applications are permitted and outline consequences for violations. This clarity will set expectations and fosters a culture of responsibility.
Train Employees on Appropriate Use
One of the most common risks in using generative AI is human error. Training employees on the proper use of genAI tools is necessary in preventing accidental misuse that could compromise security. This training should cover what data is safe to input, how to identify phishing attempts or malicious outputs, and general cybersecurity awareness. Proper education is key to maximizing the benefits of generative AI while minimizing risks.
3 Generative AI and Cybersecurity Courses to Learn More
As cybercriminals begin using generative AI to launch more sophisticated attacks, security professionals and organizations must stay informed about these advanced threats. Appropriate training courses can help you develop the necessary skills to successfully address these challenges.
Generative AI – Risk and Cyber Security Masterclass 2024
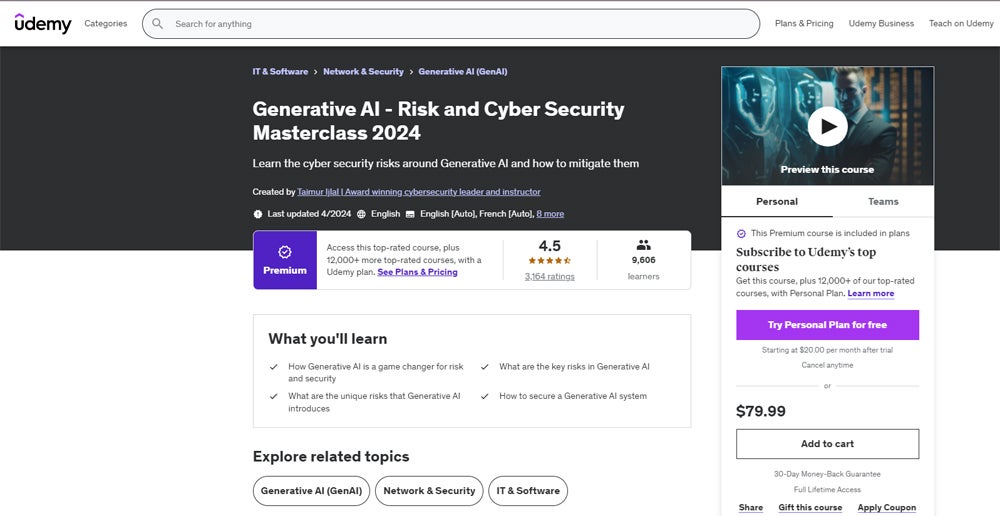
The Generative AI – Risk and Cyber Security Masterclass 2024 on Udemy is a focused course that spans two and a half hours of on-demand video content aimed at cybersecurity professionals and AI practitioners who want to know the risks related to generative AI technologies. The course covers topics such as genAI’s security risks including data privacy concerns, prompt injections, and data poisoning. It also gives strategies for securing generative AI systems. You can access this course for $79.99 or through a monthly Udemy subscription starting at $20. Prerequisites include a basic knowledge of IT and cybersecurity, but no prior expertise in AI is necessary.
Generative AI for Security Professionals
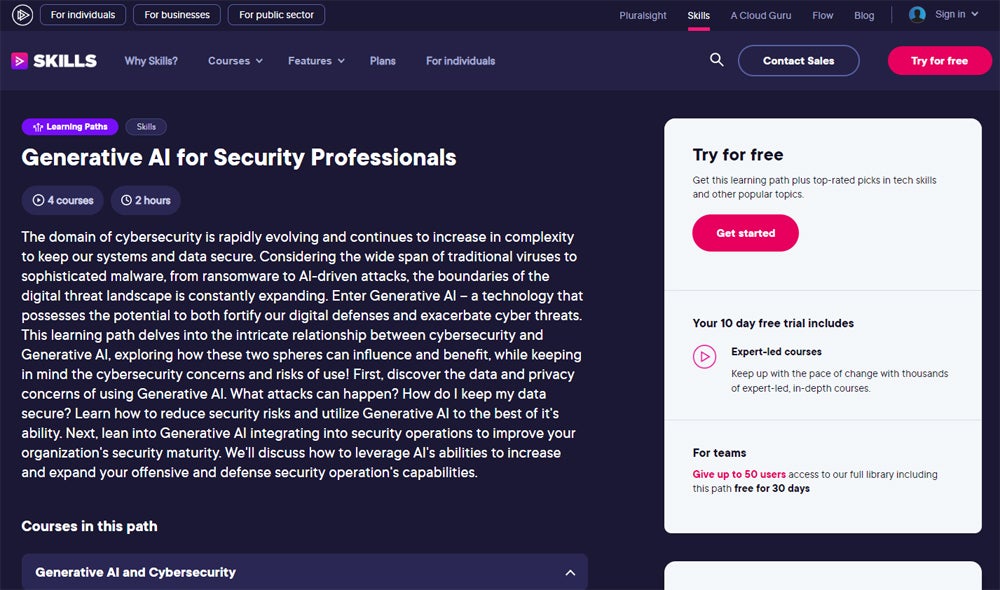
Pluralsight’s Generative AI and Cybersecurity consists of two hours of content designed for individuals looking to understand the interplay between genAI and cybersecurity. The course discusses such key topics as data and privacy concerns, potential cyber threats from generative AI, and techniques for mitigating security risks while effectively using AI technologies in security operations. Participants will learn how to increase their organization’s security maturity by integrating generative AI into offensive and defensive strategies. You need a Pluralsight subscription plan to access the course, with options available from $19 per month. No previous experience in generative AI or cybersecurity is necessary.
Generative AI: Boost Your Cybersecurity Career
IBM’s Generative AI: Boost Your Cybersecurity Career course on Coursera teaches learners how to use the latest generative AI tools to address difficult cybersecurity challenges. It explores fundamental topics, like generative AI real-life applications in cybersecurity and the technology’s impact on threat intelligence, phishing, and malware. The course also has hands-on exercises, such as report and playbook creation, so participants can apply their knowledge. A part of the Generative AI for Cybersecurity Professionals specialization, it can be completed in approximately nine hours. To enroll in this course you’ll need a $59 per month subscription to Coursera Plus.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
AI is unlikely to replace cybersecurity entirely; instead, it will continue to serve as a powerful tool that enhances human capabilities in the field. While AI can automate various security tasks like threat detection and data analysis at unprecedented speeds, it lacks the intuition, ethical judgment, and adaptability of humans. Rather than replacing human cybersecurity professionals, AI will allow them to redirect their efforts on more demanding challenges while automating mundane tasks.
AI has valuable contributions to cybersecurity, but it also has notable limitations. For example, AI systems can hallucinate and produce false positives and negatives, leading to wasted resources or overlooked threats. In addition, AI’s complexity makes it difficult to understand and its implementation can be too expensive for many organizations. Finally, if AI systems themselves are compromised, they can become tools for attackers, further jeopardizing security.
Bottom Line: Generative AI and Cybersecurity
Generative AI holds the power to be both a solution and a challenge in cybersecurity, but its greatest potential lies in thoughtful application. When used responsibly, it can take enterprise security to new heights and solidify defenses from emerging risks. Keep in mind that it’s equally important to remain vigilant about the dangers associated with generative AI’s impact on cybersecurity. Be mindful of how you interact with generative AI systems, including content or AI art generators. By embracing generative AI’s capabilities and staying mindful of its risks and limitations, organizations can make the most of this advanced technology while being protected from its vulnerabilities.
Discover the top names behind AI’s biggest breakthroughs by reading our article on top AI companies today.
