Debian Software Package Management(dpkg) in Linux
Last Updated :
10 Jun, 2024
In Linux, there are a lot of different distributions and each of these distributions has a different package type. For example .rpm or Red hat Package Manager is used as the package in the Linux distribution. A package is the compressed version of the software.
In this article, we will go through the Debian package which is used by Ubuntu. D package or Debian Package is used to install and download the software in Debian based Linux systems. Debian files end with .deb extension.
What is dpkg in Linux?
`dpkg` (Debian Package) is a low-level package management system for Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu. It handles the installation, configuration, upgrade, and removal of software packages. Unlike higher-level tools like `apt`, which resolve dependencies and download packages from repositories, `dpkg` directly manages individual `.deb` files, making it essential for managing local packages and performing detailed package operations.
Basic Syntax
dpkg [options] action
Here,
options – optional tags that modify the behavior of dpkg
action – specifies what dpkg should do
Common Actions of dpkg
The following are the common actions of dpkg:
|
Option
|
Behavior of option
|
|
-i or –install
|
to install a package
|
|
-r or –remove
|
to remove a package
|
|
-p or –pure
|
to remove a package with long its dependencies.
|
|
-s or –status
|
It shows the status of a package.
|
Example
- The following command is used to install a page from .deb files:
sudo dpkg -i package_name.deb
dpkg commands in Linux with Examples
1. Installing a stand-alone package using the Debian package
- To install a package -i flag is used. To download a stand-alone package using the Debian package, this command is used:
sudo dpkg -i name_of_package.deb
Example: To download standalone package for the open-source text editor, atom
sudo dpkg -i atom-amd64.deb

2. Removing a package using the Debian package
- To remove a package -r flag is used
sudo dpkg -r name_of_package
Example: To remove the package for the text editor “atom”
sudo dpkg -r atom

Note: -P flag helps to remove everything including conf files.
dpkg -P [package-name]
dpkg -P googler_3.3.0-1_all.deb
3. Listing the debian packages
dpkg -l
- The above line would give the output similar to the one shown below:
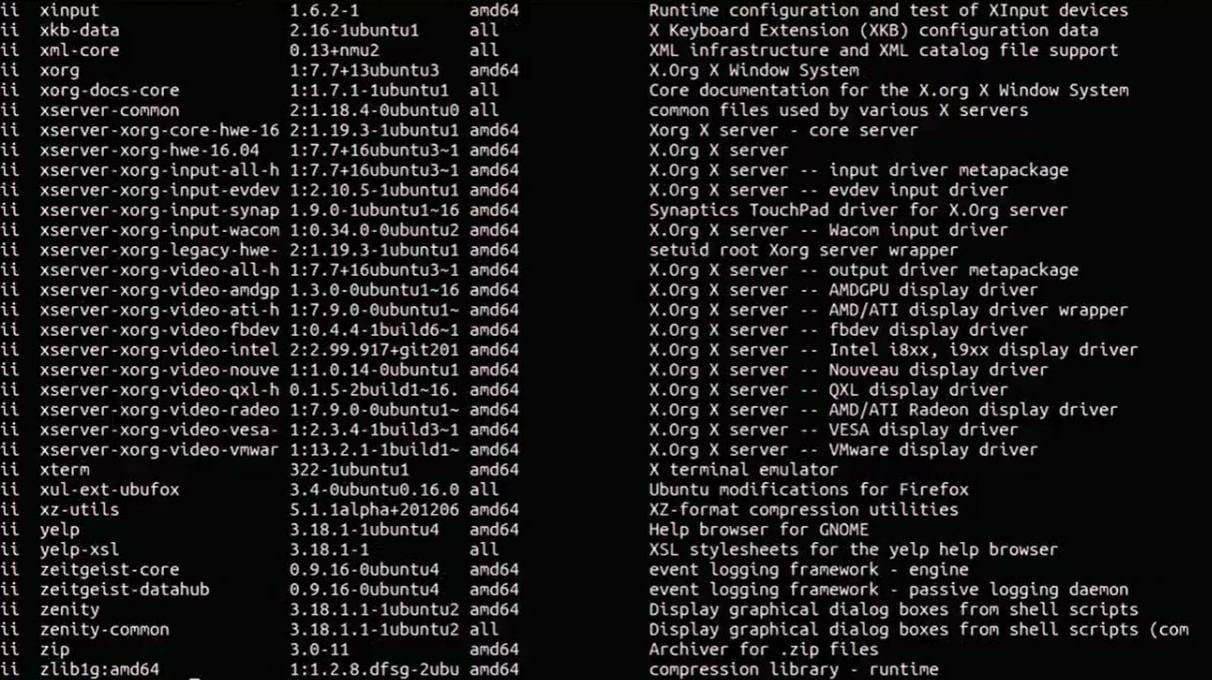
- To find a particular package use the grep command:
dpkg -l | grep name_of_package.
- The output of this command would look similar to the one shown below:

4. List the dpkg commands available
- -help option lists all the available dpkg commands
dpkg –help
- Output of this command would look similar to the one shown below:
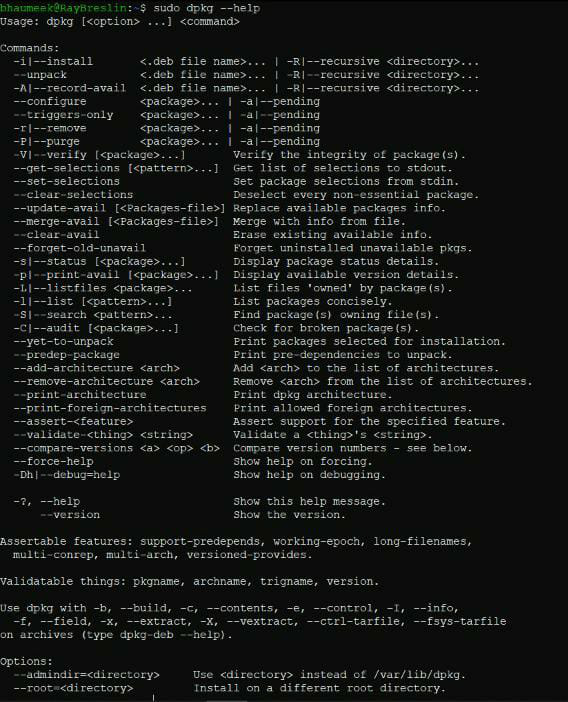
- The following are the a few more options of dpkg:
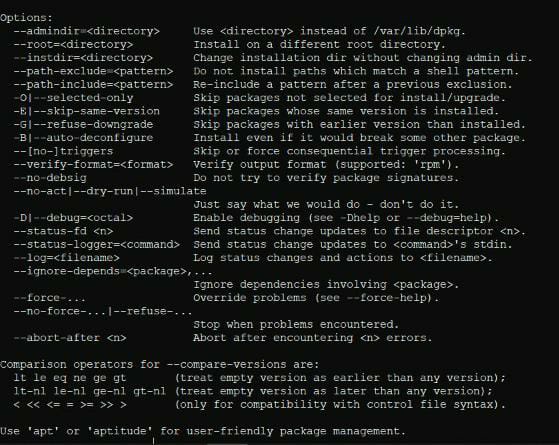
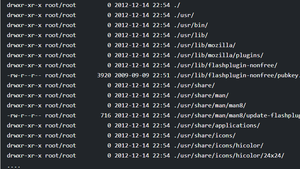
5. View the content of a particular package
- To view the content of the particular package -c flag is used
dpkg -c [name of the package]
dpkg -c flashplugin-nonfree_3.2_i386.deb
- Output of this command would look similar to the one shown below:
6. Print architecture of dpkg installs
- –print-architecture command prints the architecture of dpkg installs
dpkg --print-architecture
- Output could be amd64, i386, etc.
- For example, the output produced by the above code is as shown:

7. Unpack a package
- –unpack flag helps us unpack the package.
dpkg --unpack [package-name]
dpkg --unpack flashplugin-nonfree_3.2_i386.deb
- The output would look as shown below:

- The package can be later configured using –configure flag.
dpkg --configure [package-name]
dpkg --configure flashplugin-nonfree

8. Check if the package is installed or not
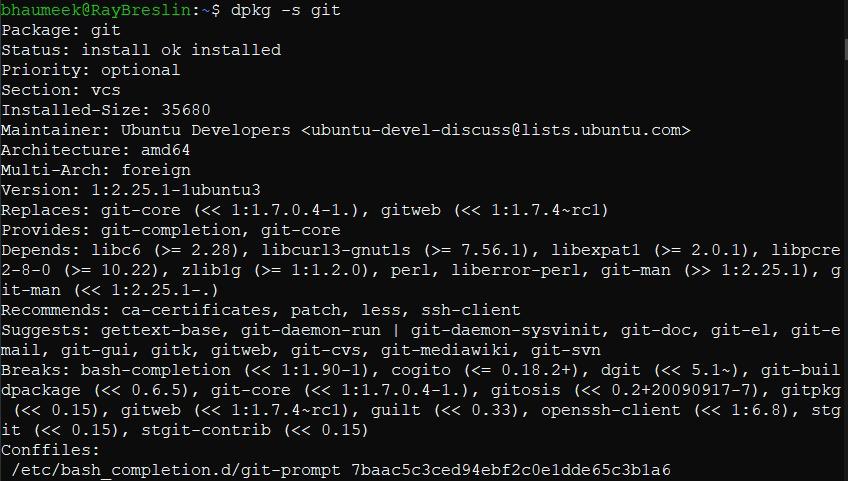
- To check if a particular package is installed or not -s flag is used.
dpkg -s [package-name]
dpkg -s git
- The output would look as shown below:
9. Reconfigure the installed package
- To reconfigure the already installed package dpkg-reconfigure command is used
dpkg-reconfigure [package-name]
Locate the installed package
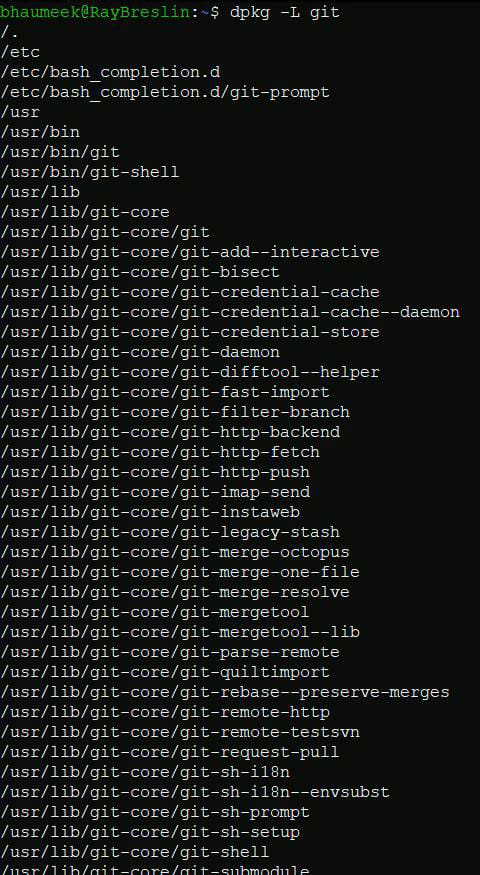
- The location of the installed package can be found using -L flag.
dpkg -L [package-name]
dpkg -L git
- The output would look as shown below:
10. Check for any issue with the installed package
- –audit flag would be used to check for the issues with the package.
dpkg --audit
11. Erase information
- –clear-avail Erases available information about the current packages
dpkg –-clear-avail
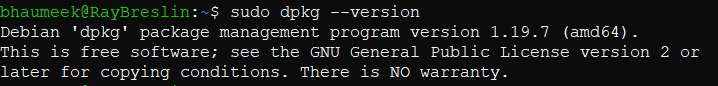
12. Display dpkg version
- dpkg –version is used to display dpkg version information.
sudo dpkg --version
Linux dpkg – FAQs
Is dpkg the same as apt?
No, dpkg is a low-level package manager, while apt is a higher-level tool that handles dependencies and repositories.
How do I run a dpkg file?
Use sudo dpkg -i package_name.deb to install a .deb package.
How to check if dpkg is installed in Linux?
Run dpkg --version to check if dpkg is installed.
How do I see what’s installed on Linux?
Use dpkg --list to list all installed packages.
How to check if a Python package is installed in Linux?
Run pip show package_name to check if a Python package is installed..