Difference between merge() and concat() in Pandas
Last Updated :
25 Nov, 2024
When working with data in pandas, combining multiple DataFrames is a common task. Two primary methods for this are merge() and concat(). While both functions help combine DataFrames, they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways.
Merge function is used to merge two dataframes based on the common columns or indexes and use concat() when you want to stack DataFrames either vertically or horizontally without needing a key. Below is a sample example that illustrates the use of merge and concat.
Python
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [1, 2, 3],'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie']})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [2, 3, 4],'Age': [25, 30, 35]})
# Merge dataframes on 'ID'
merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='ID', how='inner')
print("Merged DataFrame (using merge):")
print(merged_df)
# Concatenating the two dataframes along columns (axis=1)
concat_df = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1)
print("\nConcatenated DataFrame (using concat):")
print(concat_df)
Output:
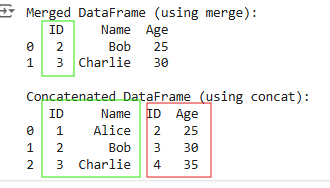 merge() and concat() in pandas
merge() and concat() in pandasIn merge, we can see that based on ID we have merged two dataframes. When we are using concat operation, we are not using any condition and just placing the tables side by side.
When to use merge and concat?
These two functions totally serve different purpose. Merge should be used when we need the rows that satisfy the criteria's. In simple terms, Merge basically filters the data. Concat on the other hand is used when we need to add more data. Using concat we can add rows or columns as per our requirements.
Characteristics | merge | concat |
|---|
Use | Used to join dataframes based on common columns. | Used to combine dataframes along any axis. |
|---|
Common keys | Merge makes use of common columns to join the dataframes | Concat does not make use of common columns |
|---|
Joins | Merge supports four types of joins: inner, outer, left and right. | Concat supports only two types of joins: outer and inner. |
|---|
Axis | Does not make use of any axis parameter | Makes use of axis parameter. Axis=0 denotes rows and Axis=1 denotes columns. |
|---|
on parameter | Makes use of on parameter. In this the common column names are passed. | Does not make use of on parameter. |
|---|
1. Using merge function on common columns
Merge function is used to merge two or more dataframes based on common columns which basically acts like conditions. It can be compared to the joins in SQL. Here we can perform 4 types of joins or merge operations. They are as follows:
- Inner: This basically returns the rows that have matching values in both the dataframes.
- Outer: This basically returns all the rows. For those rows whose particular value does not exists, it returns NaN value.
- Left: It returns all the rows from the left table or the first table and the matching rows from the second table.
- Right: It is similar to the left join. It returns all the rows from the second table and matching rows from the first table.
By default merge function joins on the basis of inner join.
Syntax:
pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner', on=None, left_on=None, right_on=None, left_index=False, right_index=False, suffixes=('_x', '_y'))
- df1 is the first table.
- df2 is the second table.
- how basically defines the type of join. It can be inner, outer, left or right.
- on denotes the common columns.
- left_on and right_on is used if the common columns have different column names.
- left_index and right_index is used when index can be used as common column to merge the tables.
- suffixes is used for other overlapping common column names.
Below is an example that makes use of merge operation.
Python
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'Roll Number': [101, 102, 103],'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],'Marks': [85, 92, 78]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'Roll Number': [101, 102, 103],'Subject': ['Math', 'Science', 'English']})
# Merging the two DataFrames on 'Roll Number'
merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Roll Number', how='inner')
print(merged_df)
Output:
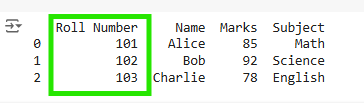 Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandas
Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandas2. Using concat function to combine along any axis
Concat is used to combine two or more dataframes along column or row manner. In simple terms we can say that we can stack either horizontally or vertically. Unlike merge function, concat does not need any common column and is mainly used when we need to add more data to our dataframes.
Syntax
pd.concat(objs, axis=0, join='outer', ignore_index=False, keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False, sort=False, copy=True)
- objs represents the list of dataframes.
- axis denotes row wise concatenation or column wise concatenation. 0 denotes row and 1 denotes column
- join can be either inner or outer
- keys is used to keep track of the dataframes in hierarchical format.
- levels is used to specify custom indexes.
- Name is used to define name for the hierarchical indexes.
- verify_integrity ensures that the indexes are unique.
- sort is used to sort the columns.
- copy is used to keep the copy of data.
Below is an example that makes use of concat operation.
Python
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'Roll Number': [101, 102, 103],'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],'Marks': [85, 92, 78]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'Roll Number': [104, 105, 106],'Name': ['David', 'Eve', 'Frank'],'Marks': [88, 95, 82]})
# Concatenating the two DataFrames
concatenated_df = pd.concat([df1, df2], ignore_index=True)
print(concatenated_df)
Output:
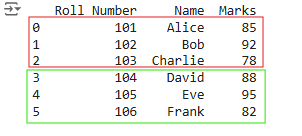 Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandas
Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandasAs we can see that the two tables have been stacked on over another. Although there are common columns, but it in concat it does not make use of common columns.
Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandas - Examples
Here in this we have implemented the use of Merge and concat in the dataframes.
Example 1: In this example we have two dataframes. One dataframe comprises of fruit names along with other details and the second dataframe comprises of fruit name, origin etc. We will use merge function and inner join to combine two dataframes.
Python
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Fruit': ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry'],
'Color': ['Red', 'Yellow', 'Red'],
'Origin': ['USA', 'Ecuador', 'Turkey']
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Fruit': ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Mango'],
'Price': [1.2, 0.5, 1.5],
'Store': ['Walmart', 'Costco', 'Trader Joe\'s']
})
print('-----merge-----')
# Merge based on 'Fruit' column (inner join by default)
merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Fruit', how='inner')
print(merged_df)
Output:
 Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandas
Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandasExample 2: Here we are calculating the net sales in North and South region. For this we will use concat and join them row wise.
Python
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Region': ['North', 'North'],
'Product': ['Apples', 'Bananas'],
'Sales': [120, 80]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Region': ['South', 'South'],
'Product': ['Apples', 'Oranges'],
'Sales': [100, 150]
})
# Concatenating rows
result = pd.concat([df1, df2], ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
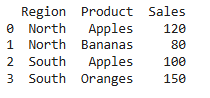 Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandas
Difference(s) between merge() and concat() in pandasFAQs on differences between merge() and concat() in pandas
Explain the two functions merge and concat?
Merge is used when we want to filter rows based on common column values. Concat is used when we need to combine dataframes either horizontally or vertically.
Explain what does axis=0 and axis=1 mean in concat?
Axis=0 means adding rows or joining two dataframes vertically. Axis=1 means adding columns or joining two dataframes horizontally.
Can we perform left and right join in concat?
No in concat we can perform two types of joins: inner and outer. By default outer join is passed as value in concat.
Similar Reads
Difference between merge() and concat() in Pandas
When working with data in pandas, combining multiple DataFrames is a common task. Two primary methods for this are merge() and concat(). While both functions help combine DataFrames, they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways. Merge function is used to merge two dataframes based on t
6 min read
The Difference Between cat() and paste() in R
In R Programming Language efficient data manipulation and string, concatenation are essential for various tasks ranging from data preprocessing to generating informative reports. Two commonly used functions for string manipulation in R are cat() and paste(). While both functions serve similar purpos
2 min read
What is the difference between join and merge in Pandas?
In Pandas, both join() and merge() are used to combine two DataFrames, but they differ in how they align the data. The primary distinction is that join() merges DataFrames based on their indices, while merge() merges based on specified columns. Additionally, join() defaults to a left join, whereas m
4 min read
Git - Difference Between Merging and Rebasing
When working with Git, two common strategies for integrating changes from different branches are merging and rebasing. Both techniques serve the purpose of combining code from multiple branches, but they do so in different ways. This article will help you understand the differences between merging a
3 min read
Difference between Pandas VS NumPy
Python is one of the most popular languages for Machine Learning, Data Analysis, and Deep learning tasks. It is powerful because of its libraries that provide the user full command over the data. Today, we will look into the most popular libraries i.e. NumPy and Pandas in Python, and then we will co
3 min read
Difference between Pandas and PostgreSQL
Pandas: Python supports an in-built library Pandas, to perform data analysis and manipulation is a fast and efficient way. Pandas library handles data available in uni-dimensional arrays, called series, and multi-dimensional arrays called data frames. It provides a large variety of functions and uti
4 min read
Difference Between Pandas Head, Tail And Sample
Prerequisites: Basic Understanding Of Pandas In this article, we are going to see the difference between Pandas Head, Tail And Sample using Python Pandas is an open-source library that is made mainly for working with relational or labeled data both easily and intuitively. It provides various data st
3 min read
Difference between array_merge() and array_combine() functions in PHP
array_merge() Function: The array_merge() function is used to merge two or more arrays into a single array. This function is used to merge the elements or values of two or more arrays together into a single array. The merging occurs in such a manner that the values of one array are appended at the e
3 min read
Difference between map, applymap and apply methods in Pandas
Pandas library is extensively used for data manipulation and analysis. map(), applymap(), and apply() methods are methods of Pandas library in Python. The type of Output totally depends on the type of function used as an argument with the given method. What is Pandas apply() method The apply() metho
3 min read
Pandas - Find the Difference between two Dataframes
In this article, we will discuss how to compare two DataFrames in pandas. First, let's create two DataFrames. Creating two dataframes C/C++ Code import pandas as pd # first dataframe df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'Age': ['20', '14', '56', '28', '10'], 'Weight': [59, 29, 73, 56, 48]}) display(df1) # second da
2 min read