Linux is a versatile operating system. It has many commands that can change the Linux working functionality of the operating system. Every Linux has a different package manager that helps us to install the software in the Linux operating system. The `dnf` command is a package manager command in Red-based Linux distros for example fedora, Cent OS and RHEL. It stands for "Dandified YUM," where YUM is another package manager commonly used in these distributions.
The syntax for the `dnf` command in Linux:
dnf [...COMMANDS] [...PACKAGES]
Commonly used commands in the 'dnf' package manager tool
|
This command helps us to search the package in the repository
|
This command installs the package in your computer system
|
info
| This command returns the information about the package.
|
This command is used to display the list of the packages of certain criteria.
|
This command removes the installed package from the computer system
|
upgrade
| This command is used to upgrade all packages
|
The 'history' command shows the installed and removed history of the packages.
|
This command displays all the available repositories
|
This command shows the dependencies of the package.
|
1. `Search` and `install` the package with dnf command
In this example, we will install tigervnc package in fedora linux. Before installing the package we will search the package.
Command:
dnf search tigervnc
Example:
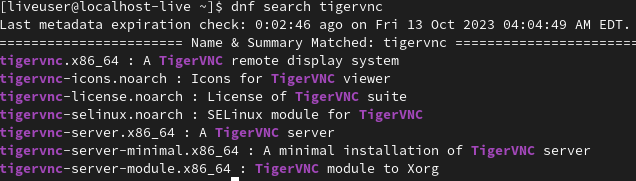
Once you find your package use the dnf search command. you can use the `install` command for installing that package in your linux distro. Here's an example of this command.
Command:
dnf install tigervnc
Example:
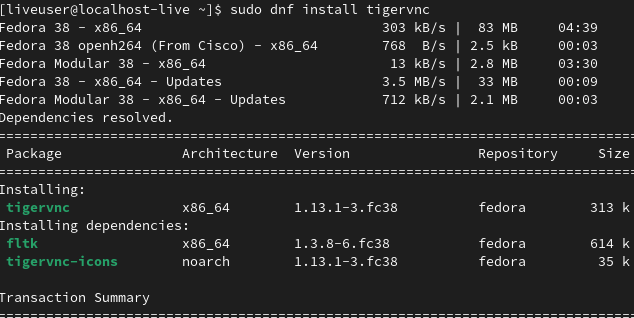
2. See the information of the package using the 'info' command
We can see the information about the package using the `info` command. Here's an example of this command.
Command:
dnf info tigervnc
Example:
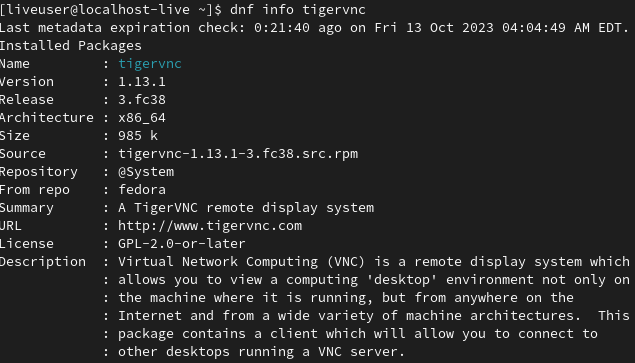
3. List the installed package using the 'list installed' command.
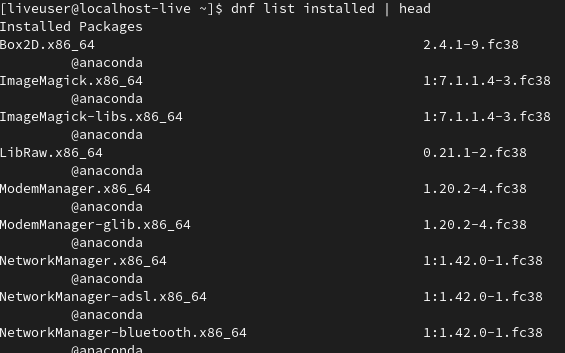
You can see all installed packages using the `dnf` command with the `list` command with the installed parameter. Here, we are using this command with the `head` command. You can use the 'head' command to display only the first few lines of the output
Command:
dnf list installed | head
Example:
4. Remove a package using the 'remove' command.
You can remove the package using the 'remove' command in linux. Here's an example of this command.
Command:
sudo dnf remove tigervnc
Example:
5. Upgrade a Package using the 'upgrade' command.
You can upgrade the package using the `upgrade` command in linux. Here's an example of this command.
Command:
sudo dnf upgrade
Example:
You can upgrade the specific package using this command.
sudo dnf upgrade package_name
Here's an example of this command:
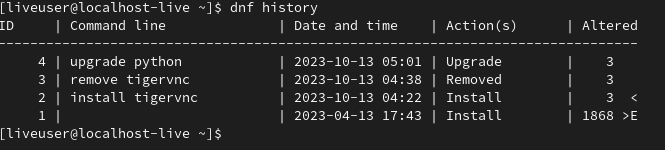
6. View the history installed or remove the package using the 'history' command.
Sometimes It is tedious to write the same command once again. In dnf command solve this problem using the history feature. We can see the history of installing and removing packages using the `dnf` command.
Command:
dnf history
Example:
7. View the available repository using the 'repolist' command.
The dnf repolist command is used to list the available repositories on your system. It's a helpful command to check which repositories are enabled and what packages are accessible through them. Here's an example of this command.
Command:
sudo dnf repolist
Example:
8. View the dependencies using the 'deplist' command
The dnf delist command in Linux is used to display the dependency information for a specific package. This command provides a detailed list of dependencies for a package, including both its runtime and build-time dependencies. Here's an example of this command.
Command:
dnf deplist tigervnc
Example:
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned the `dnf` command. This command is very useful when you are installing and removing the package in Red-hat-based linux distros. Example fedora etc. This command performs many tasks such as installing the package, removing the package, searching the package, updating the software, and much more.
Similar Reads
du Command in LINUX
The du command in Linux is a powerful utility that allows users to analyze and report on disk usage within directories and files. Whether you’re trying to identify space-hogging directories, manage disk space efficiently, or simply gain insights into storage consumption, the du command provides valu
5 min read
'dd' command in Linux
dd is a command-line utility for Unix and Unix-like operating systems whose primary purpose is to convert and copy files. On Unix, device drivers for hardware (such as hard disk drives) and special device files (such as /dev/zero and /dev/random) appear in the file system just like normal files.dd c
5 min read
fuser command in Linux
fuser is a command line utility in Linux. fuser can identify the process using the files or sockets. This command can be also used to kill the process. In this article, we are going to see how to use the fuser command to list the processes and kill the processes associated with files and directories
4 min read
Linux command in DevOps
Linux fundamentals are crucial skills for a DevOps professional. Through this article, we will learn about all the required Linux commands which we will frequently use in a DevOps career. What is linux?Linux is a free and open-source software operating system , which developed by linus torvalds. It
7 min read
ls Command in Linux
ls is a Linux shell command that lists directory contents of files and directories.  It provides valuable information about files, directories, and their attributes. Syntax of `ls` command in Linuxls [option] [file/directory]'ls' will display the contents of the current directory. By default, 'ls'
7 min read
biff command in Linux
biff is a mail notification system for unix that notifies the user at the command line when new mail arrives and tells from whom it is. Syntax: biff [ y | n ] Options: Y : This option is to enable the mail notification. N : This option is to disable the mail notification. Note: When mail notificatio
1 min read
Unzip Command in Linux
As an open-source operating system, Linux presents plenty of powerful and versatile instructions for dealing with files and directories. One such command that performs an important role in coping with compressed files is the "unzip" command. Compressed files are a common way to keep space and share
8 min read
Linux Commands
Linux commands are essential for controlling and managing the system through the terminal. This terminal is similar to the command prompt in Windows. It’s important to note that Linux/Unix commands are case-sensitive. These commands are used for tasks like file handling, process management, user adm
15+ min read
df Command in Linux with examples
There might come a situation while using Linux when you want to know the amount of space consumed by a particular file system on your LINUX system or how much space is available on a particular file system. LINUX being command friendly provides a command line utility for this i.e. 'df' command that
8 min read
df command in Linux with Examples
Ever felt the chilling fear of a "disk full" error message on your Linux machine? Fear not, for the mighty df command stands ready to guide you through the treacherous terrain of disk space management! This article delves deep into the df command, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to navig
5 min read