How To View and Create Hidden Files in Linux
Last Updated :
19 Sep, 2024
In the Linux framework, there are a ton of hidden records that incorporate for the most part the client setup document and the application documents. You can likewise hide your Files and Documents in your framework on the off chance that you are imparting them to another individual or because of any explanation. In any case, recall that hiding the documents doesn’t safeguard your security, as anybody can see hidden records. Hiding Files and Documents simply makes the record imperceptible for the customary client investigating or posting the documents. Likewise, it keeps the index from being jumbled.
Here, we have covered both command-line and graphical user interface (GUI) methods for hiding and unhiding files, along with helpful keyboard shortcuts for easier file management.
Creating Hidden Files in Linux
Creating Hidden Files can be done in two best ways in Linux:
- Method 1: Command Line to Hide Files in Linux
- Method 2: GUI (Graphical User Interface) to Hide Files in Linux
To hide a record in Linux, you have to add a spot (.) toward the start of the filename.
Method 1: Command-line to Hide Files in Linux
Hide the file by moving it under a new filename. The period (.) at the beginning of the new filename indicates that it’s hidden.
$ mv Firefox-Temp-Binary .FF-test
After renaming by adding ‘.’ (dot) with ‘$ls‘ command file cannot be viewed as it is hidden.
Method 2: GUI (Graphical User Interface) to Hide Files in Linux
You can also hide files through the graphical interface by renaming them with a dot at the beginning of the file name.
Step 1: Right-click on the file and select the Rename option.
Step 2: Make the file hidden by placing a .(dot) at the beginning of the filename.
Renaming the file by clicking ‘Rename’ and adding .(dot) at the beginning of the new file name will hide the file. Once renamed, the file will become hidden in your file manager.
Viewing Hidden Files in Linux
Hidden files can be viewed using two different methods: the command line and the GUI.
- Method 1: Command Line to View Hidden Files in Linux
- Method 2: File Manager Toolbar to View Hidden Files in Linux
Method 1: Command line to View Hidden Files in Linux
Execute the below command to view all the hidden files in the terminal itself.
$ ls -a
This command will show every hidden record (whose names start with a . (dot) image) in your ongoing Terminal catalog.
To display hidden records in Linux File manager:
- Open the file manager.
- Click on the “three-bar” or “options” menu at the top right.
- Select “Show Hidden Files” (or press the keyboard shortcut ‘Ctrl + H’).
This will show every hidden record (whose names start with a . (dot) image) in your ongoing Terminal catalog.
Note: “Ctrl + H” is a keyboard shortcut used to show hidden files.
Unhiding files in Linux:
Just as you can hide files, you can also unhide them by renaming them and removing the dot from the beginning of the file name.
We can unhide by 2 different methods:
- Method 1: Command-line to Unhide File in Linux
- Method 2: File Manager toolbar (GUI) to Unhide File in Linux
Method 1: Command-line to Unhide File in Linux
Use the ‘mv’ command to rename the hidden file and remove the dot from the file name:
$ mv .FF-test Firefox-Folder
This command makes the file visible again.
To unhide hidden records in Linux File manager:
- Click the three even bars symbol at the upper right corner of the File Manager. Thusly, a drop-down menu will appear. From that point, check the Show Hidden Files check box. As a result, hidden records can be viewed in the File Explorer. Then renaming the hidden file by removing ‘.’ (dot) at the beginning of the file, the name will unhide the file.
- Click on the Rename option.
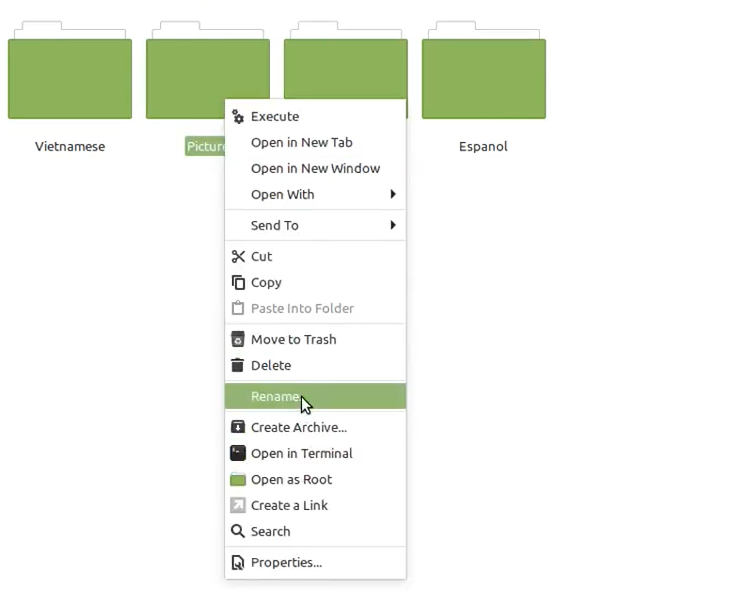
- After renaming the file by removing . (dot) in front of the file will make the file unhidden.
Note: “Ctrl + H” keyboard shortcut is used to show hidden files. After hidden files are shown renaming the file by removing . (dot) in front of it make the file from hidden to normal. That’s how GUI way used to unhide a file.
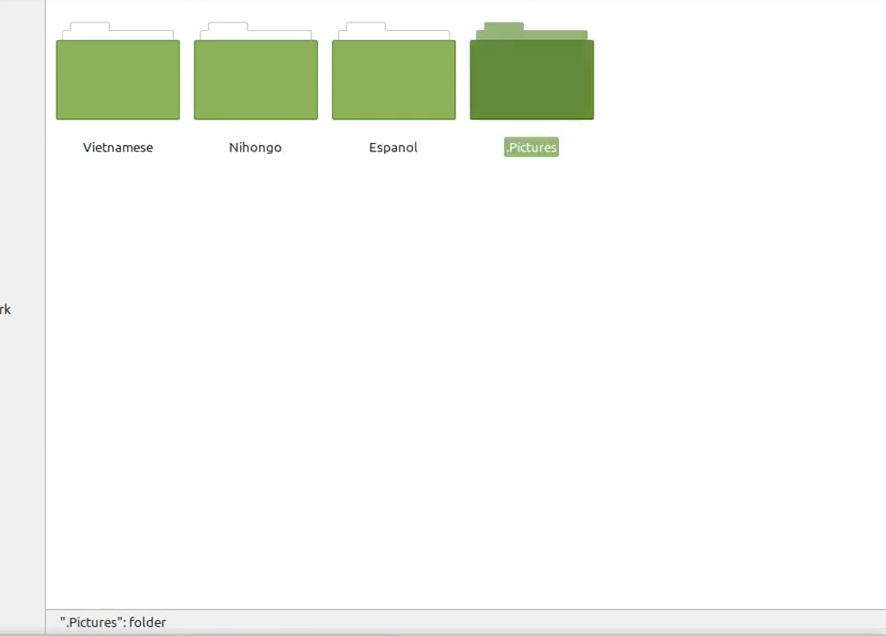
After renaming the file removing .(dot) in front of the file will make the file unhidden.

Hiding Files via Keyboard shortcut (GUI)
To hide unhidden files in Linux “Ctrl + H” keyboard shortcut is used.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed the process of hiding files in Linux which offers a practical way to manage your system’s organization. However, it’s crucial to remember that hidden files in Linux are not entirely secure. You can effectively hide and unhide files using both command line and GUI methods. Additionally, the “Ctrl + H” keyboard shortcut provides a convenient way to toggle the visibility of hidden files in Linux. These techniques help Linux users streamline their file management, ensuring that specific files remain out of view when necessary.
How To View and Create Hidden Files in Linux – FAQs
How do I hide a file in Linux?
To hide a file, simply rename it and add a dot (.) at the beginning of the file name using the command line or file manager.
Can hidden files be accessed in Linux?
Yes, hidden files can be accessed by viewing them with ls ‘-a’ in the command line or using the “Show Hidden Files” option in the file manager.
How can I unhide a file in Linux?
You can unhide a file by renaming it and removing the dot (.) from the beginning of the file name.
What keyboard shortcut shows hidden files in Linux?
In most Linux desktop environments, pressing “Ctrl + H” will show or hide hidden files in the file manager.
Is hiding files in Linux a security measure?
No, hiding files in Linux is not a security measure. It simply makes the file less visible to casual users.
Similar Reads
How To View and Create Hidden Files in Linux
In the Linux framework, there are a ton of hidden records that incorporate for the most part the client setup document and the application documents. You can likewise hide your Files and Documents in your framework on the off chance that you are imparting them to another individual or because of any
6 min read
How to Create a VIM File in Linux CMD
In Linux, there are many ways to open and create files, but Vim stands out as a powerful and versatile text editor. It comes pre-installed on most Linux systems and allows you to create, edit, and manage files directly from the terminal. In this article, we will explain you, how to create a new file
3 min read
How to Create File in Linux
Today, we're going to learn about something really important – how to create files in Linux. It's like creating a fresh piece of digital paper to write or store things. We'll explore different ways to do this using simple commands. Whether you're just starting out or have been using Linux for a bit,
7 min read
How to View the Content of File in Linux | cat Command
The cat command in Linux is more than just a simple tool, it's a versatile companion for various file-related operations, allowing users to view, concatenate, create, copy, merge, and manipulate file contents. Let's see the details of some frequently used cat commands, understanding each example alo
7 min read
How to Find a File in Linux | Find Command
Linux, renowned for its robust command-line interface, provides a suite of powerful tools for efficient file and directory management. Among these, the "find" command stands out as an indispensable asset, offering unparalleled versatility in searching for files based on diverse criteria. This articl
9 min read
How to Hide files using Command-line Interface?
If you're looking to hide files using the command line, it's a quick and efficient way to protect sensitive data on your system. Whether on Windows, macOS, or Linux, you can use the command line to hide files or folders with just a few simple commands. This guide will help you understand how to hide
3 min read
How to Compress Files in Linux | Tar Command
File compression is a fundamental task in managing and transferring data efficiently on a Linux system. The Tar command, short for Tape Archive, is a powerful tool that allows users to create compressed and archived files. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various options and examples
11 min read
How to Show Hidden Files and Folders in Windows 10
Hidden Files and Folders are generally system-protected features in Windows OS. This feature is generally used to hide files or folders to avoid any accidental usage. However, you can undo this setting to view hidden files and folders in Windows 10 by using a few simple steps. Here are different app
5 min read
How to Create a Password Protected ZIP File in Linux?
Linux provides Zip command to work with a file like compressing the file and decompressing with a password. It's not come with built-in you need to install from an external source. The Zip command has two different utility(zip and unzip). zip is used for compressing the file and unzip is used for de
2 min read
How to Create a File in the Linux Using the Terminal?
In this article, we will learn to create a file in the Linux/Unix system using the terminal. In the Linux/Unix system, there are the following ways available to creating files. Using the touch commandUsing the cat commandUsing redirection operatorUsing the echo commandUsing the heredocUsing the dd c
4 min read