iftop command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
10 Sep, 2024
The ‘iftop’ command is a powerful network analysis tool used by system administrators to monitor real-time bandwidth usage on network interfaces. It provides a quick and detailed overview of networking activities, helping diagnose network issues by identifying which applications or processes are consuming the most bandwidth. It stands for ‘Interface TOP’ and the top is derived from the top command in Linux. It even acts as a diagnostic to ‘diagnose’ which program is causing the problem to the network.
Installing ‘iftop’ command
Installing ‘iftop’ on Linux varies slightly depending on the distribution you are using. Below are the installation steps for RedHat-based systems and Debian or Ubuntu systems:
1. For RedHat-based Linux (version 8 or below)
yum install epel-release
yum install iftop
2. For RedHat-based Linux (version 9)
sudo dnf install epel-release
sudo dnf install iftop
3. For Debian or Ubuntu Linux
sudo apt install iftop
Key Options available in `iftop` command in Linux
|
Options
|
Description
|
|
iftop
|
Displays basic real-time bandwidth usage of the default network interface.
|
|
-i wlo1
|
Shows real-time bandwidth details of a specific network interface named “wlo1”.
|
|
-n -i wlo1
|
Disables hostname lookup and provides bandwidth statistics for the specified interface “wlo1”.
|
|
-N -i wlo1
|
Disables the conversion of port numbers to services and presents bandwidth stats for the specified interface “wlo1”.
|
|
-b
|
Turns off the display of the bar graph representation for network traffic.
|
|
-t
|
Presents the output in a text interface format without using ncurses.
|
|
-o source
|
Sorts the output based on the source IP address of network flows.
|
|
-o destination
|
Sorts the output based on the destination IP address of network flows.
|
|
-L 2 -i wlo1
|
Specifies that only 2 lines of statistics or bandwidth usage should be printed for the interface “wlo1”.
|
|
-h
|
Displays the help section providing usage information and options for the iftop command.
|
Working with iftop Command
1. To display basic bandwidth usage of the default interface.
iftop
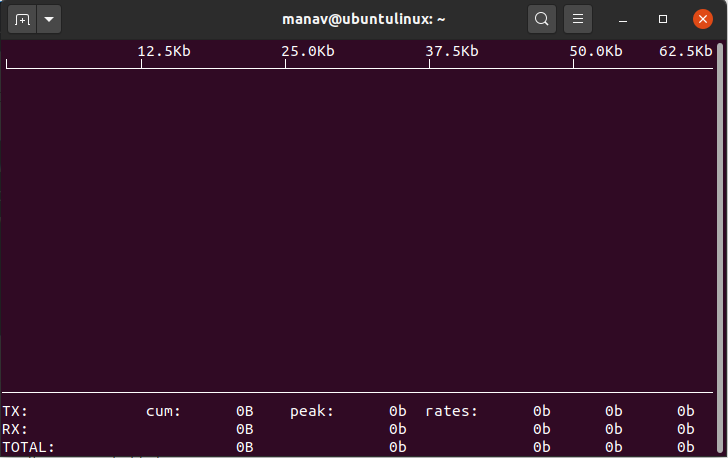
Display Basic bandwidth usage
This command will now display all the bandwidth related stats of the default interface.
2. To display bandwidth details of a specific router
sudo iftop -i wlo1
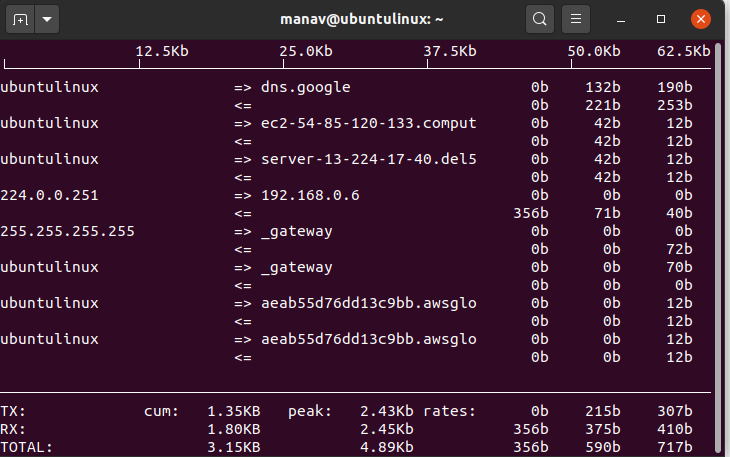
display bandwidth deatil
This command will now display all the bandwidth related stats of the specified network interface which is wlo1.
3. To stop hostname lookup
sudo iftop -n -i wlo
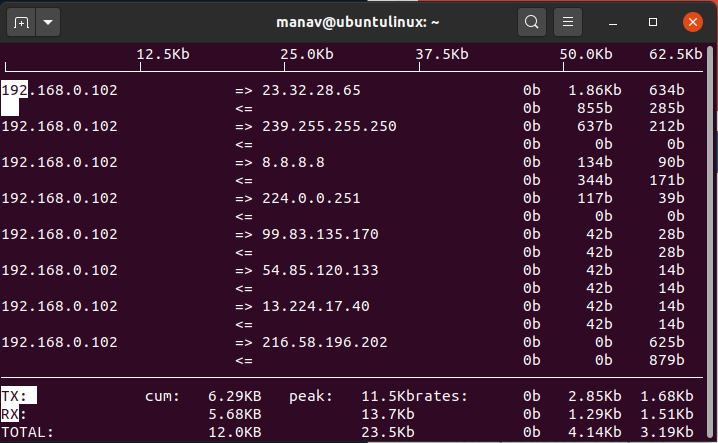
To stop hostname lookup
This command will now stop the lookup of the hostname for the specified network interface which is ‘wlo1’.
4. To stop the conversion of port numbers to services.
sudo iftop -N -i wlo1
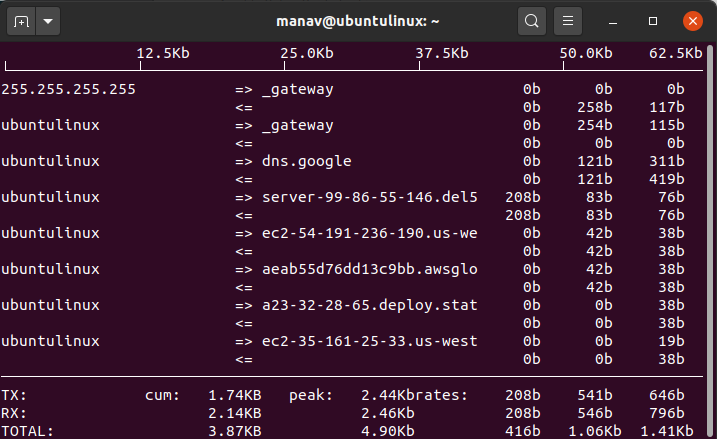
stop the conversion
This command will not convert the port number to services while printing stats for the specified network interface which is ‘wlo1’.
5 To stop the display of bar graph.
sudo iftop -b
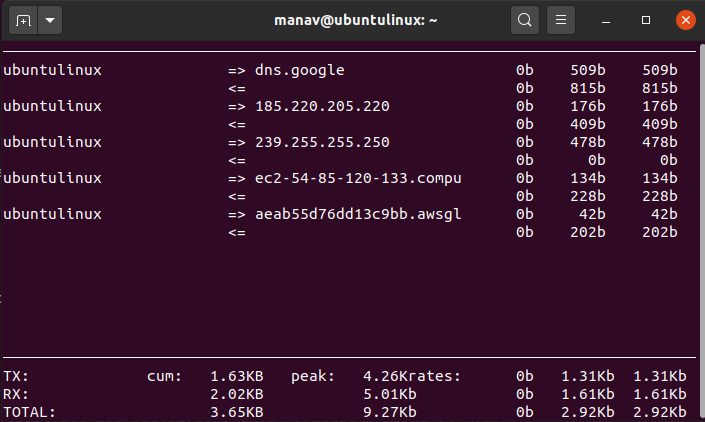
Display a bar graph
This command will remove the bar graph of traffic from the output.
6. To display the text interface without ncurses
sudo iftop -t
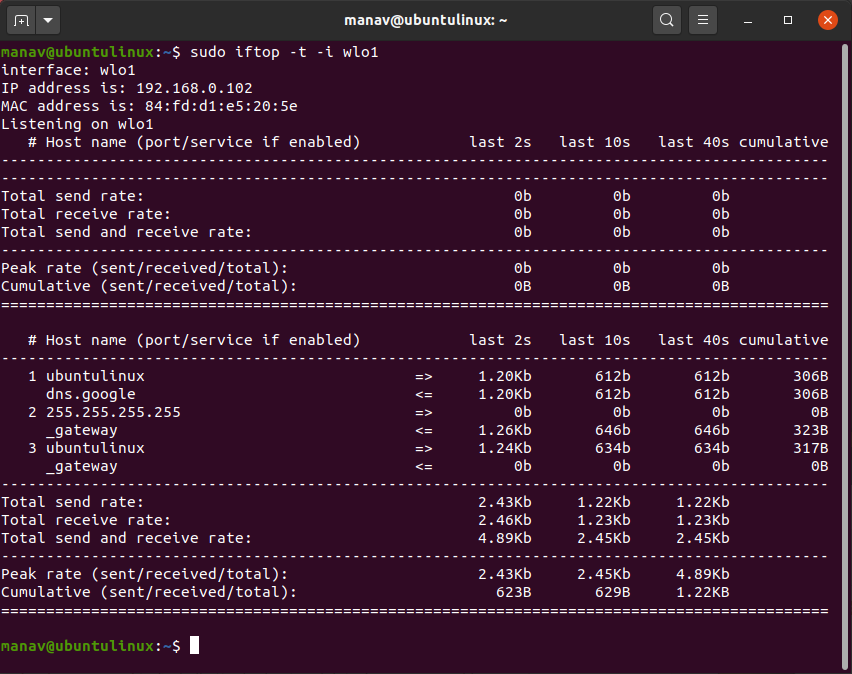
Display without ncurses
This command will display the output in the text interface without ‘ncurses’.
7. To sort output by source address
sudo iftop -o source
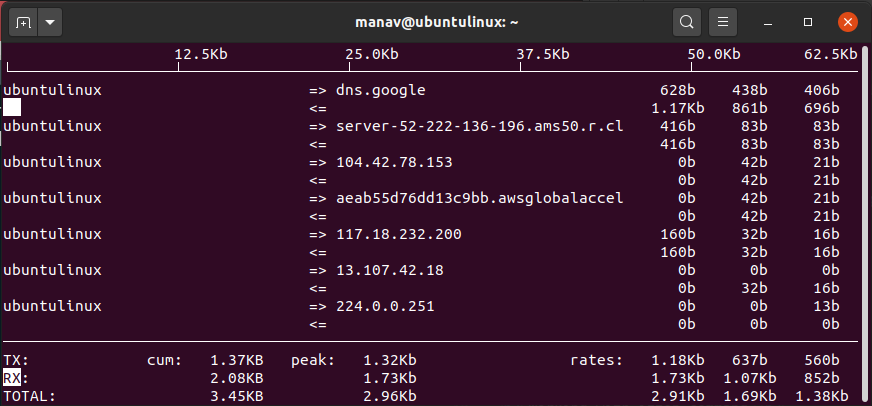
To sort by source
This command will sort the output on the basis of the source address.
8. To sort output by destination address
sudo iftop -o destination
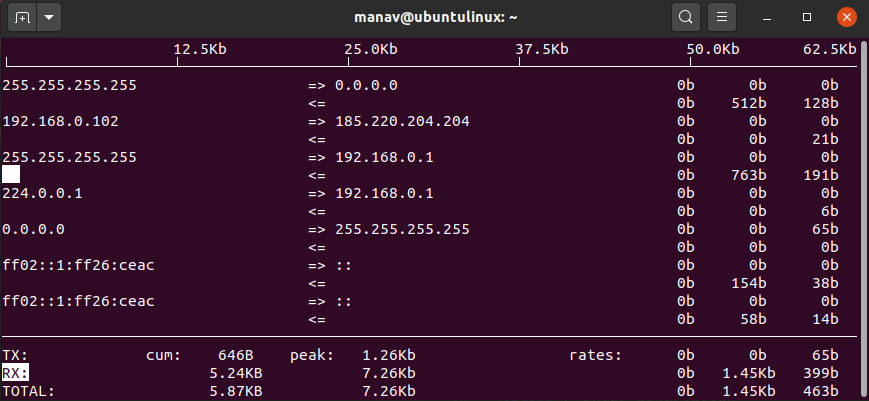
To sort by destination
This command will sort the output on the basis of the destination address.
9. To specify number of lines to be printed
sudo iftop -L 2 -i wlo1
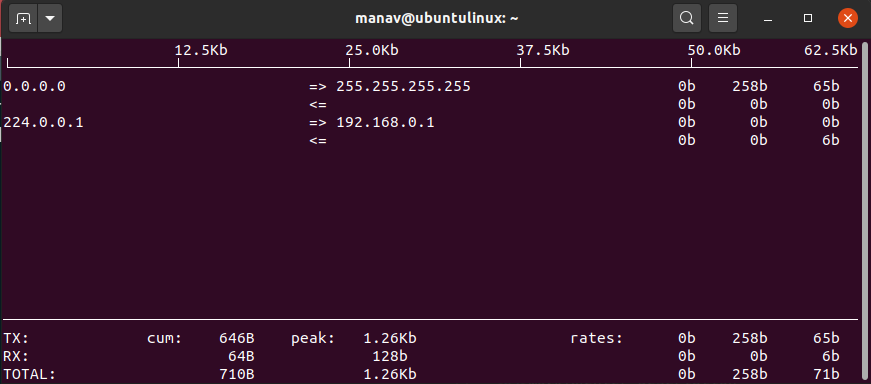
To display specific number
This command will print 2 output lines of statistics or bandwidth usage and not more than 2 lines will be printed.
10. To display help
sudo iftop -h
help
This command will display the help section of the iftop command.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed ‘iftop’ command which is a valuable network analysis tool for administrators, providing real-time bandwidth usage stats and aiding in network troubleshooting. With customizable options, it offers efficient monitoring and sorting capabilities. By installing ‘iftop’ on Linux distributions, administrators can gain insights into network traffic and optimize network performance effectively.
‘iftop’ command in Linux – FAQs
What is the ‘iftop’ command used for in Linux?
The ‘iftop’ command is used for monitoring real-time bandwidth usage on network interfaces in Linux. It provides a quick overview of networking activities and helps identify which processes or applications are consuming bandwidth.
How do I install the ‘iftop’ command on RedHat-based Linux systems?
For RedHat-based Linux (version 8 or below), use:
yum install epel-release
yum install iftop
For RedHat-based Linux (version 9), use:
sudo dnf install epel-release
sudo dnf install iftop
How can I install ‘iftop’ on Debian or Ubuntu Linux?
You can install ‘iftop’ on Debian or Ubuntu by running:
sudo apt install iftop
How do I display basic bandwidth usage of the default network interface using ‘iftop’?
Simply run the command:
iftop
Similar Reads
How to Display Command History in Linux | history Command
The command-line interface in Linux provides powerful tools for users, and mastering command history is essential for efficient navigation and retrieval of previously executed commands. The history command is a valuable utility that allows users to view and search through their command history. In t
4 min read
host command in Linux with examples
host command in Linux system is used for DNS (Domain Name System) lookup operations. In simple words, this command is used to find the IP address of a particular domain name or if you want to find out the domain name of a particular IP address the host command becomes handy. You can also find more s
2 min read
hostid command in Linux with examples
hostid is a command in Linux that is used to display the Host's ID in hexadecimal format. It provides a quick and straightforward way to retrieve the host ID, allowing administrators to associate it with software licenses or perform system-specific operations. Syntax of `hostid` command in Linuxhost
1 min read
hostname command in Linux with examples
hostname command in Linux is used to obtain the DNS (Domain Name System) name and set the system's hostname or NIS (Network Information System) domain name. A hostname is a name given to a computer and attached to the network. Its main purpose is to uniquely identify over a network. Â Syntax of the `
6 min read
hostnamectl command in Linux with Examples
hostnamectl command provides a proper API used to control Linux system hostname and change its related settings. The command also helps to change the hostname without actually locating and editing the /etc/hostname file on a given system. Syntax: hostnamectl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND .... Where COMMAND c
2 min read
htop command in Linux with examples
htop command in Linux system is a command line utility that allows the user to interactively monitor the system’s vital resources or server’s processes in real-time. htop is a newer program compared to top command, and it offers many improvements over top command. htop supports mouse operation, uses
4 min read
hwclock command in Linux with examples
hwclock also called Real Time Clock (RTC), is a utility for accessing the hardware clock. The hardware clock is independent of the OS(operating system) you use and works even when the machine is shut down. The hardware clock is also called a BIOS clock. A user can also change the date and time of th
3 min read
iconv command in Linux with Examples
The iconv command is used to convert some text in one encoding into another encoding. If no input file is provided then it reads from standard input. Similarly, if no output file is given then it writes to standard output. If no from-encoding or to-encoding is provided then it uses current local's c
3 min read
id command in Linux with examples
The 'id' command in Linux is a powerful tool used to display user and group names along with their numeric IDs (User ID - UID or Group ID - GID) of the current user or any specified user on the system. This command is particularly useful for system administrators and users who need to verify user id
3 min read
if command in linux with examples
if command in Linux is used for conditional execution in shell scripts.The if command is essential for writing scripts that perform different actions based on different conditions. if COMMANDS list is executed, if its status is true, then the then COMMANDS list is executed. Otherwise, each elif COMM
4 min read