What is Rebranding?
Rebranding is defined as a marketing strategy in which a company or organization changes its name, logo, design elements, messaging, or other brand-related aspects to give itself a new identity or refresh its image. Rebranding is an investment of time and resources during which a strategic process focuses on certain elements of a firm's brand identity. It includes an entire upgrade to the brand’s visual appearance, communications, and brand DNA. The objective of the rebranding is to form a different and much-improved brand image that has a close connection with the company’s strategically evolving aims, values, and business positioning.
Geeky Takeaways:
- Companies may rebrand to breathe new life into their brand, especially if they feel their current brand image is outdated or no longer resonates with their target audience.
- When companies merge or are acquired, they may undergo a rebranding process to create a unified brand identity that reflects the new entity.
- Rebranding can help companies expand into new markets or demographics by adopting a brand image that appeals to these new audiences.
Reasons for Rebranding
Organizations rebrand when there are many reasons to do so, and the decision to rebrand usually arises as a result of the business situation, which consists of both internal and external factors. Here are some common reasons for rebranding,
1. Adaptation to Change: Industries always change and will continue to do so, and consumer desires will constantly adjust as well. Branding is an important cycle of business as it equips a company to react to the changing tide to secure a relevant market position in a diverse business environment.
2. Strategic Growth and Diversification: Branding is frequently on the move when either the company decides to offer a richer product or service or expands into new markets. It is practical in the sense that it will create synergy between business objectives and match diverse audiences, as well as achieve greater results.
3. Mergers and Acquisitions: Through the example of mergers or acquisitions, rebranding stages the development of a joint brand identity, which entails both entities' strengths and values.
4. Crisis Management: It could be a strategic choice for companies that are contemplating a reputational challenge, crisis, or situation in which they would be seen as the cause of problems. The companies may aim at distancing themselves from the negative associations, rebuilding trust among the stakeholders, and presenting a new story for the concerned parties.
5. Market Repositioning: Rebranding is a tool to respond to changes occurring in the market once the company optimizes its potential. This could be directed at reaching a specific segment, spotlighting different key values, or building a fresh perception to aid in gaining an edge over competitors.
When should a Company consider Rebranding?
While many factors may lead a company to start its rebranding, the management needs to pay attention to both internal and external variables. This usually demands a careful evaluation of any situation. Here are some key indicators that suggest it might be time for a company to consider rebranding,
1. Change in Business Strategy: When a company sets its sights on a new direction, say a new market, launching a new product line, or highlighting a different customer segment, rebranding will ensure that the brand reflects this strategic decision.
2. Mergers and Acquisitions: The rebranding is likely to be inevitable in a merger or acquisition scenario as it will be required to consolidate the brand image that reflects in effect the unique power and values of the participating entities.
3. Outdated Image: This is particularly relevant if a brand seems outdated, or if it is not communicating anymore with the target market. A rebranding could thus give a company a really modern and modern image.
4. Crisis or Negative Publicity: Following the event of a crisis or bad reports that have caused the falling of the reputation of a company, rebranding can be a useful strategy for the company to vary from the negative connotations and regain consumers’ confidence.
5. Global Expansion: Foreign expansion is when a company spreads its business worldwide; rebranding could be necessary in order to make sure the cultural sense of the brand and its identity is relatable to several audiences.
How to Rebrand?
The rebranding process may be extremely intricate, which stipulates focused planning, thoughtful strategy, and precise implementation. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to approach the rebranding process,
1. Define Your Objectives: Induce the audience to carry out a deep and versatile review of the necessity of the rebrand. Either way, it would be changing the style to reflect the market situations, overcoming the negative perceptions, or entering new markets. Setting a clear aim would be the main guide of the whole process.
2. Conduct a Brand Audit: Weigh up how other brand elements, such as visual identity, message, and customer perception, can either help or hinder your brand’s momentum. Specify what you want to transfer to the future and what you would like it to be better than in the present. Interview stakeholders, employees, and customers to find the intelligence.
3. Establish a Strong Brand Strategy: Either create or strengthen your branding strategy, which involves your mission, beliefs, target market, and differentiating properties. This key element will help your successful rebrand to be seen as supportive of your objectives.
4. Understand Your Audience: Specify your target audience’s mindsets, and think of your product or service as a solution to their needs and problems. Know their expectations, tastes, and conduct towards the company. Then, the branding is tailored to hit the spot so that they feel included and valued.
5. Create a Rebranding Team: Get together a team of enthusiasts where it will be necessary to include representatives of various departments, such as marketing, design, and leadership. Task responsibilities need to be clearly defined in order to ensure smooth and coordinated joint undertakings.
6. Gather Stakeholder Input: Include the target audience, i.e., customers, employees, and other stakeholders in the rebranding project. Their expressions, whether positive or negative, will serve as a great starting point in developing the new brand portrayal.
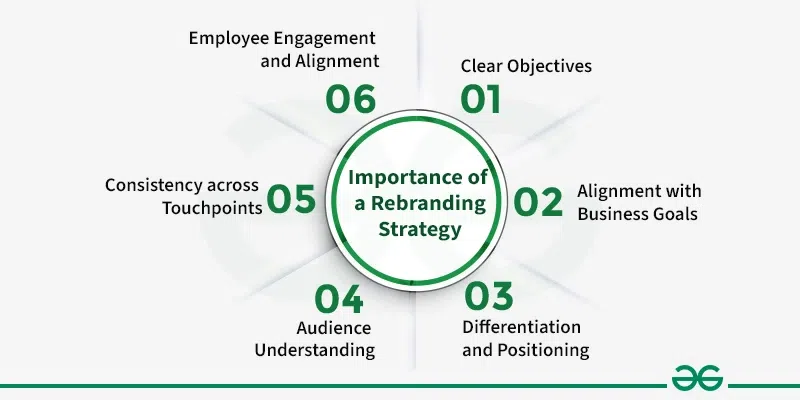
Importance of a Rebranding Strategy
A well-defined rebranding strategy will be the foundation for the entire process, as it will lead and coordinate the whole process while the company will taste the fruits of the rebranding when it matches the company´s goal and becomes the brand identity of the target audience.
1. Clear Objectives: Restrategizing ensures that the details are clear and tangible so as to allow for the choice of objectives for rebranding. Whether it is to clear up any negative perceptions out there, target a whole new customer demographic, or align your marketing efforts with what is currently trending, solid goals help in navigating this process.
2. Alignment with Business Goals: Through rebranding, the brand identity is to be created in such a manner that it will precisely fit into the business goals. The purpose of this is to assess how the rebrand will bring benefits to the company, improve perceptions in the market, and ensure long-lasting organizational success.
3. Differentiation and Positioning: By showing who the brand is and clearly defining the value proposition that makes the company unique and occupies its niche in the market, a rebranding strategy helps the company stand out from the competition. This requires the drafting of visual symbols, screening messages, and branding identity development to emphasize the elevated positioning.
4. Audience Understanding: The strategy encompasses an in-depth study of the clientele, tastes, and tendencies that are sought after. This information is useful in developing a brand that is in tune with the market, which improves the chances of recognition and tolerance.
5. Consistency across Touchpoints: The result of a rebranding approach is being able to harmonize communication and visual components across any type of media, be it a website, social media, marketing materials, or dealing directly with customers. Consistency demonstrates trust and shows the company's identity.
6. Employee Engagement and Alignment: Workers remain a key asset to the organization through the process of rebranding. A strategy with a clearer definition includes communicating and engaging employees at all levels, aligning the changes with the new brand values, and watching them happen in real time. This interrelatedness of internal organization is critical for any brand’s consistent and unified external brand image.
Successful Rebranding Examples
The implementation of an ideal branding strategy is what determines how the new identity of a company will be communicated and felt by the target audience in a way that will be up to their satisfaction. Here are examples of companies that have undergone successful rebranding,
1. Apple: Apple started as a computer company in 1976 and then evolved through different logos/brand identities for it brand. In 1997, when Steve Jobs was the leader of the company, it took the Apple brand a radical turn and began its notable history. The classical rainbow apple was substituted by a one-tone apple with a bite-taken removed. The traditional logo, which had the original logo hand-drawn and scanned, was simplified and made to look modern in this version. The logo was the company’s representation of simplicity and innovation.
2. Nike: Being “Blue Ribbon Sports” first, Nike settled for its present title with a curving signature logo in 1971. In 1995 the company started introducing the modern simple swoosh that has become a simple timeless symbol known to everyone, it conveys the message of movement and speed. This made Nike get a high profile, and it ended up being one of the most recognizable and successful sportswear brands.
3. Starbucks: Starbucks started as a small ‘vendors’ coffee bean shop in 1971 with a brown seafaring-themed logo. In 2011, Starbucks introduced a new logo, and together with the siren, there was no longer an address. May help refresh the current image and make it clearer, and more versatile which corresponds to the business development as the brand is going further with the coffee into other beverages and products.
Examples of Rebranding Failures
Relabeling is a dicey venture that is often not in the winning position, and some relabeling initiatives completely fail. Here are some examples of rebranding failures,
1. Gap Rebranding Attempt: In 2010, Gap published a new logo that substituted the old blue box emblem with a sleek, lowercase "gap" set against a color-amazing kind of background.
2. Tropicana Rebranding Attempt: In 2009, the iconic orange and the straw were substituted with a minimalist and sleeker image on Tropicana's packaging. Consumers did not have a clue how to deal with the new packaging system, and sales plummeted by a big margin. Tropicana had to revert to its original design within the first couple of months, which once again hints at the fact that branding elements should be identifiable.
3. New Coke (Coca-Cola) Rebranding Attempt: It was the time in 1985 when Coca-Cola rolled out its tastier variation in order to gain more market share against Pepsi. The renovation involved a shift from the taste the beverage used to have and from its packaging. The reaction of consumers was negative and harsh. People turned out to protest and wrote petitions to the company to restore the old formula. After having to respawn its iconic product, The Coca-Cola Company brought back the original formula again under the name Coca-Cola Classic and thus showed the importance of their historical brand as well as the consumers' connection with the old taste and (false) nostalgia.
Rebranding vs. Relaunching vs. Redesign
Basis
| Rebranding
| Relaunching
| Redesign
|
|---|
Scope of Change
| Involves a comprehensive overhaul of the brand identity, including its name, logo, messaging, and visual elements. | Focuses on reintroducing a product, service, or brand to the market with significant changes or improvements, which may include updates to the product/service itself, as well as its marketing strategy. | Primarily concerns updating the visual appearance, functionality, or user experience of a product, website, or other brand elements, without necessarily changing the brand's core identity or offerings. |
Purpose
| Aims to create a new perception in the minds of consumers, often driven by shifts in the market, changes in company vision/values, or the need to target a different audience. | Aims to generate excitement and interest around a refreshed or improved product, service, or brand, often in response to declining sales, outdated offerings, or new market opportunities. | Aims to enhance the appeal, usability, and effectiveness of a product or brand without fundamentally altering its core identity, driven by changing design trends, technological advancements, or customer feedback. |
Extent of Change
| Involves a complete transformation of the brand identity, often resulting in a new name, logo, and overall brand image. | May involve significant changes to the product/service itself, as well as updates to its marketing strategy and positioning, but does not necessarily require a complete rebranding. | Focuses primarily on updating the visual appearance, functionality, or user experience of existing brand elements, without fundamentally changing the core identity or offerings. |
Rebranding -FAQs
What is rebranding?
Rebranding refers to the image and positioning of the brand, and the process involves changing the visual identity, messaging, and overall image to make it better resonate with the current goals, target market, or positioning.
What is the reason why these companies are in the process of rebranding?
Organizations may resort to rebranding for a myriad of reasons, among which are changes in market dynamics, changes in the target audience, mergers of companies, or the updating of their image.
When is a company going to decide if it should or not be rebranded?
It's true that it isn't set in stone when rebranding takes place. This will be based on the business's peculiarities and desirable outcome. Companies that keep changing the logo every few years remain topical and stay in trend, whereas some firms restart the rebranding less often.
How long is the rebranding process, and how much will it cost?
The period of time a brand repositioning takes also depends on the scale and the level of changes. It might be several months to a year or even more if we are starting the process from the planning stage of the brand to the actual implementation of it.
What is the approximate price for a branding makeover?
The cost of rebranding can be highly variable, and the pricing model will depend upon factors including the size of the company, the scope of the changes, and whether outside agencies are involved or not. Expenses will include design, rebranding, updating the website, and any other related costs.
Similar Reads
Rebranding : Meaning, Reason, Importance, and Examples
What is Rebranding?Rebranding is defined as a marketing strategy in which a company or organization changes its name, logo, design elements, messaging, or other brand-related aspects to give itself a new identity or refresh its image. Rebranding is an investment of time and resources during which a
12 min read
Career Pathing | Meaning, Importance, Kinds and Examples
Permanent change has taken place in the labour market, favouring employees. In the current competitive job market, more than merely providing a satisfactory work environment is required to attract and retain talented employees. Businesses must enable employees to assume responsibility for their work
8 min read
Remarketing: Meaning, Importance, Working and Types
What is Remarketing?Remarketing, often known as retargeting, is one of the most popular and widely used digital marketing strategies. Regardless of whether they completed a certain activity or not, it entails showing advertisements to visitors who have already visited a website or a particular page.
14 min read
Planning: Meaning, Features, Importance and Limitations
What is Planning?Planning is a blueprint of the course of action to be followed in the future. It is also a mental exercise that requires imagination, foresight, and sound judgment. It is thinking before doing. It is a preparatory step and refers to detailed programs regarding the future course of a
9 min read
Organising : Meaning, Importance and Process
What is Organising in Management?Organising refers to a process consisting of a series of steps to identify and group various activities, collect or assemble various resources and establish authority relationships with responsibility amongst job positions. It can be mentioned as collecting and utili
5 min read
Staffing : Meaning, Definition, Features and Importance
What is Staffing?Staffing is that part of management concerned with obtaining, utilizing, and maintaining capable people to fill all positions in the organization from top level to bottom level. It involves the scientific and systematic procurement, allocation, utilization, conservation, and develop
3 min read
Product Labelling : Types, Importance & Examples
What is Product Labelling?Product labelling is defined as the practice of putting information on a product's packaging or the product itself to provide details about it. It is like the product's storyteller, sharing essential facts with consumers. This information typically includes the product's na
12 min read
Packaging: Meaning, Levels, Importance and Functions
What is Packaging?The act of designing and producing the container and wrapper of a product is known as packaging. It plays a very important role in today's world as packaging can be a reason for the success or failure of many products. Appropriate containers and wrappers provide protection and conv
4 min read
Importance of Training and Development to Organisation and Employees
What is Training and Development? Training is a process by which the skills, talents, and capabilities of the employees of an organization are increased. Training helps employees to grasp new skills and utilize the knowledge provided. It is not only required by the new employees, but it is also nece
4 min read
Mental Models : Meaning, Benefits, Limitations and Examples
What are Mental Models?Mental Models serve as cognitive aids that assist individuals in comprehending the world, making decisions, and tackling problems by simplifying intricate concepts into practical frameworks. Acting as unique lenses, these models provide diverse viewpoints and uncover essential
12 min read
Features and Importance of Motivation
What is Motivation?The process of stimulating and inspiring people at work to contribute to the best of their capability for the achievement of organisational objectives is known as Motivation. Motivation is the inner psychological force that activates and compels a person to behave in a particular
4 min read
Importance of Design Thinking in UX
Design thinking is a way of providing a human-centric approach to problem-solving that has revolutionized the way we approach User Experience (UX) design. By bringing Design Thinking into their design workflow, UX professionals can create intuitive, user-friendly, and innovative solutions that are s
5 min read
Difference between Teaching and Training
Teaching and Training are essential for individual development and organizational success, but they serve different purposes and require distinct approaches. Teaching focuses on imparting knowledge and fostering understanding; whereas, Training is more aligned with practical skills acquisition and j
5 min read
POSDCORB : Meaning, Full form and Elements
What is POSDCORB?POSDCORB is a seminal concept in the field of management, attributed to Luther Gulick, a prominent American public administration theorist and consultant. Originating in the early 20th century, Gulick introduced this acronym as a systematic framework to delineate the essential funct
8 min read
Price Lining : Meaning, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages and Examples
Price lining is a way businesses organize similar products or services into different price categories. This tactic makes it easier for consumers to choose by presenting options in specific price ranges. While commonly used in retail, price lining is adaptable across industries. Its purpose is to ad
10 min read
Manufacturing (Mfg) : Full Form, Types, Process and Examples
What is Manufacturing?Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials, components, or parts into finished goods that are ready for use or sale. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from product design and material sourcing to production, assembly, quality control, and distribution.
11 min read
Soil Conservation- Methods and Importance
Soil Conservation: Soil conservation refers to the process in which the fertility of the soil is maintained at the optimal level of soil characteristics like texture, pH, and so on. It involves the prevention of soil erosion, salinization, and acidification. Due to overexploitation and misuse, human
8 min read
Demarketing : Meaning, Types, Strategies and Examples
What is Demarketing?Demarketing is a strategic marketing method in which the goal is to purposefully lower demand for a given sector, product, or service. Demarketing tries to control demand to solve different issues including resource scarcity, environmental sustainability, overconsumption, or regu
11 min read
Customer Service : Meaning, Working, Benefits and Challenges
Customer service is the bedrock of a positive customer experience, encompassing a wide array of interactions aimed at creating value for customers. At its core, it involves understanding and responding to the unique needs and expectations of customers across various stages of their journey with a bu
11 min read
Demutualization: Meaning, Process, Types & Examples
Have you ever used a credit union or been a policyholder with a mutual insurance company? These organizations function differently than traditional businesses. Unlike companies with shareholders you might invest in on the stock market, member-owned companies are owned by the very people who use thei
7 min read