How to check the routing table in Linux | route Command
Last Updated :
30 Jan, 2024
The IP/kernel routing table acts as a crucial map, determining how network packets are forwarded between different hosts and networks. By utilizing the route command, Linux administrators and users can establish static routes, enabling precise control over network connectivity and optimizing data transmission. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of the route command in Linux, unravel its functionalities, and delve into detailed examples to gain a profound understanding of its usage.
Installing route Command
Many Linux distributions do not have route commands pre-installed. To install it use the following commands as per your Linux distribution.
In case of Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install net-tools
In case of CentOS/RedHat
sudo dnf install net-tools
In case of Fedora OS
sudo dnf install net-tools
Working with route command
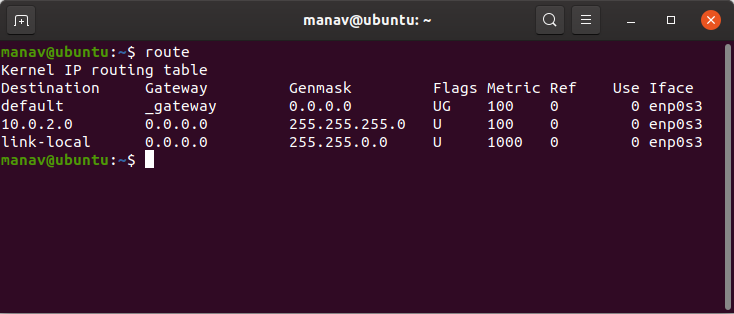
To display the IP/kernel routing table.
route
route
It displays the routing table entries.
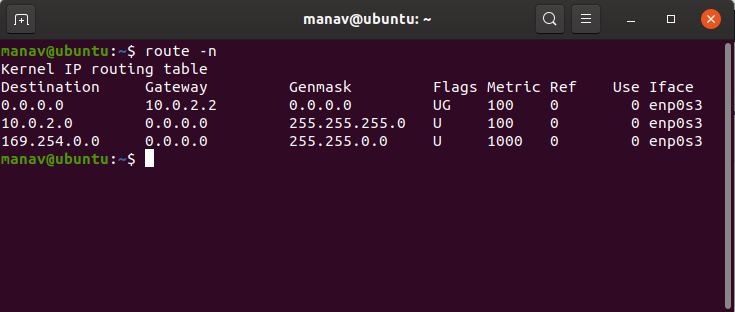
To display routing table in full numeric form.
route -n
route -n
It is even useful when you have to determine why the route to nameserver has even vanished.
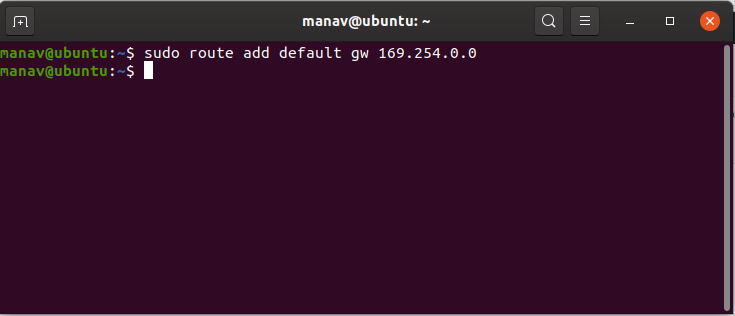
To add a default gateway.
sudo route add default gw 169.254.0.0
add default gateway
This assigns a gateway address to which all the packets that do not belong to the network are forwarded.
Note: In this case the, we wish to choose 169.254.0.0 as the default gateway. You may choose as per your need.
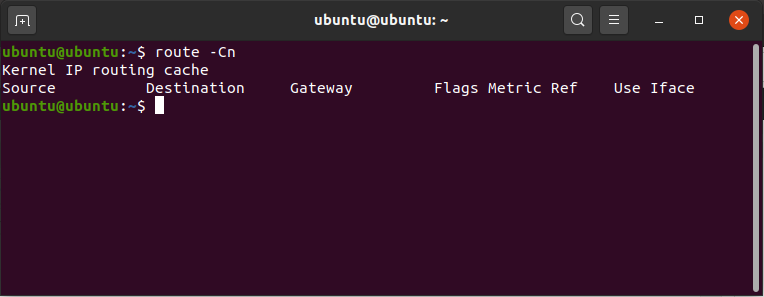
To list kernel’s routing cache information.
route -Cn
route -Cn
To route the packets faster, Kernel maintains this routing cache information. The above command will print the cache information. In this case, the cache information is maintained.
To reject routing to a particular host or network.
sudo route add -host 192.168.1.51 reject
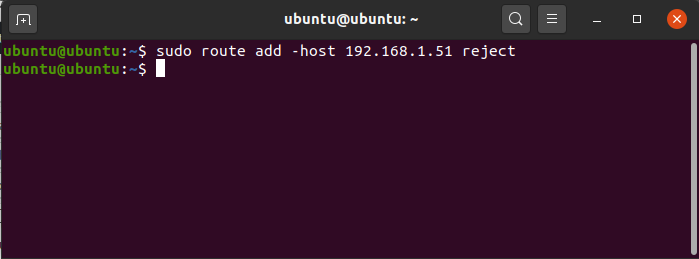
reject routing
Now if you ping to the above-mentioned IP it will display “Network is unreachable”.
To get details of the kernel/IP routing table using ip command.
ip route
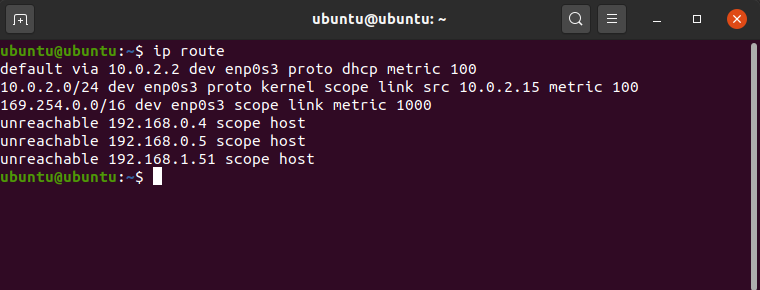
Details of IP routing table
This will give the details of the kernel/IP routing table and in this case, we have used IP command.
To delete the default gateway.
route del default
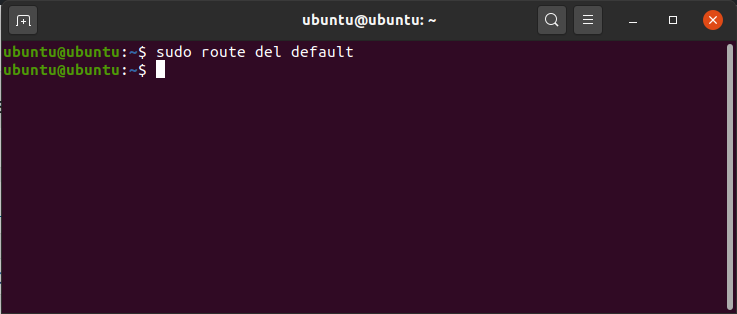
delete gateway
Caution:
This may lead to some malfunctioning of the internet. Keep a note of your default gateway before proceeding with the command. This will remove the default gateway.
To get the details of the local table with destination addresses assigned to the local host.
ip route show table local
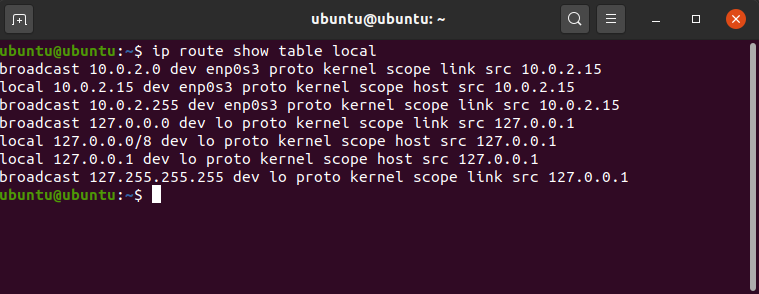
ip route show table local
This will print the details of the local table.
To get output related to IPv4.
ip -4 route
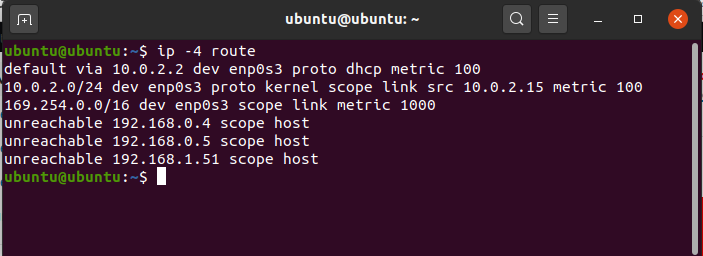
output related to IPv4
This will only display the entries with ipv4.
To get output related to IPv6.
ip -6 route
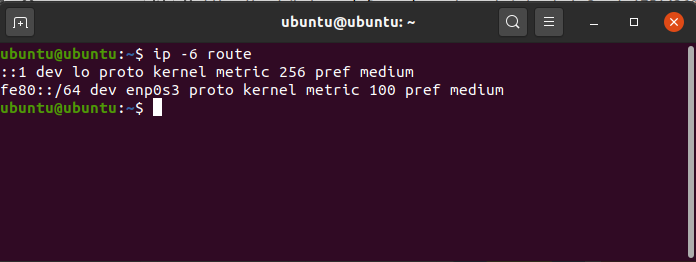
output related to IPv6
This will only display the entries with ipv6.
How to Check the routing Table in Linux – FAQs
How do I check the routing table in Linux using the route command?
To view the routing table in Linux, you can use the `route` command. Simply open a terminal and type `route` or `route -n` to display the routing table. This command provides information about the network routes configured on your system.
Can I filter the output of the route command to display specific information?
Yes, the `route` command allows you to filter the output. For example, you can use `route -n` to display numerical IP addresses instead of hostnames. Additionally, you can use grep or awk commands to further filter and format the output as needed.
How can I add a new route to the routing table in Linux?
To add a new route, you can use the `route add` command followed by the destination network and gateway. For example, `sudo route add -net 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.0.1` adds a route to the 192.168.1.0 network via the gateway 192.168.0.1.
What is the difference between the route and ip route commands in Linux?
Both `route` and `ip route` commands can be used to display and manipulate the routing table. However, `ip route` is considered more modern and flexible. It provides additional features and is recommended for users working with newer Linux systems.
How do I make a route persistent across reboots in Linux?
To make a route persistent, you need to add the route configuration to the appropriate network configuration file. The file location may vary depending on the Linux distribution. For example, on systems using systemd, you can add the route to a .network file, while on older systems, you might modify the /etc/network/interfaces file or use custom scripts in /etc/network/if-up.d/.
Conclusion
In this article we have discussed about `route` command in Linux which is used for managing the IP/kernel routing table. It allows displaying, adding, deleting, and modifying routing table entries. The command is useful for tasks such as setting up static routes, adding a default gateway, rejecting routing to specific hosts/networks, and accessing detailed routing information. Caution should be exercised while making changes to avoid disruptions to network connectivity.
Similar Reads
readlink command in Linux with Examples
The 'readlink' command in Linux is a valuable tool used to print resolved symbolic links or canonical file names. In simpler terms, when dealing with symbolic links and you need to know the actual path they represent, the 'readlink' command reveals the path of the symbolic link. This command is part
3 min read
Reboot Linux System Command with Examples
Rebooting a Linux system is a fundamental administrative task necessary for applying updates, troubleshooting, or system maintenance. Various commands are available to reboot a Linux system, each with specific options and use cases. This guide explores essential reboot commands such as `reboot`, `sh
11 min read
How to Rename File in Linux | rename Command
Changing the names of files in Linux is something we often do, and the "rename" command is like a helpful friend for this job. This guide is like a journey to becoming really good at renaming files on Linux, showing you how handy and useful the "rename" command can be. Whether you're just starting o
8 min read
reset command in Linux with Examples
reset command in the Linux system is used to initialize the terminal. This is useful once a program dies leaving a terminal in an abnormal state. Note that you may have to type reset to get the terminal up and work, as carriage-return may no longer work in the abnormal state. Also, the terminal will
3 min read
restore command in Linux with Examples
restore command in Linux system is used for restoring files from a backup created using dump. The restore command performs the exact inverse function of dump. A full backup of a file system is being restored and subsequent incremental backups layered is being kept on top of it. Single files and dire
5 min read
return command in Linux with examples
return command is used to exit from a shell function. It takes a parameter [N], if N is mentioned then it returns [N] and if N is not mentioned then it returns the status of the last command executed within the function or script. N can only be a numeric value. The return command is especially usefu
2 min read
rev command in Linux with Examples
rev command in Linux is used to reverse the lines characterwise. This utility reverses the order of the characters in each line by copying the specified files to the standard output. If no files are specified, then the standard input will be read. Here, we will explore the syntax, examples, and opti
3 min read
rm command in Linux with examples
rm stands for remove here. rm command is used to remove objects such as files, directories, symbolic links and so on from the file system like UNIX. To be more precise, rm removes references to objects from the filesystem, where those objects might have had multiple references (for example, a file w
5 min read
rmdir Command in Linux With Examples
In Linux, managing directories efficiently is a crucial skill for both system administrators and everyday users. The 'rmdir' command is a specialized tool designed specifically for removing empty directories, helping to maintain a clean file system and avoid accidental data loss. This guide delves i
6 min read
rmmod command in Linux with Examples
The rmmod command in Linux is used to remove or unload a module from the kernel. Modules are pieces of code that can be dynamically loaded into the Linux kernel to extend its functionality, such as drivers for hardware devices. When a module is no longer needed, it can be removed using rmmod. Althou
3 min read