Smart City Mission – Features, Strategy and Challenges
Last Updated :
21 Feb, 2022
Across the world, the pace of migration from rural to urban areas is increasing rapidly. According to United Nations, by 2050, about 68% of the world population will be living in urban areas and India is no exception. While the urban Indian population is currently around 31%(Census, 2011) of the total population, it will be over 50% by 2030 as projected by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs. Considering the enormous importance of urbanization, Smart City Mission(SSM) has been launched by the Government of India in 2015.
Smart City initiative drives economic growth, improves the quality of life, facilitates local development with the help of digital and information technology, follows best practices of urban planning, utilizes public-private partnerships and policy change through smart solutions. A ‘Smart city’ is an urban area that is highly advanced in terms of sustainable land use, transport & communication, market viability, and overall infrastructure. It is a city where technology is the principal source for providing essential services to residents and focuses on sustainable and inclusive development.
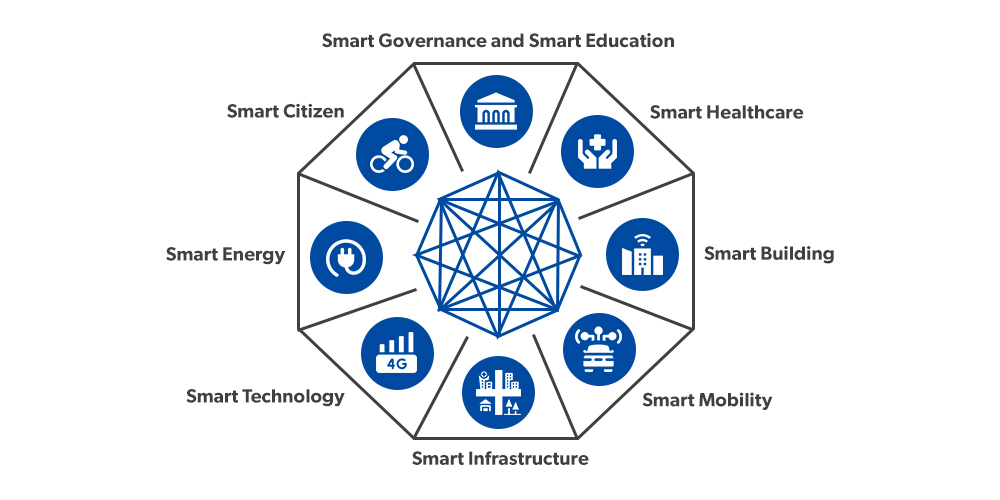
Features of Smart Cities:
- Competitiveness: It refers to the city’s ability to create employment opportunities, attract investments, professionals, and labor, and provide an edge to other cities. The ease of doing business and the quality of life-work it offers determines its competitiveness.
- Sustainability: It includes social sustainability, financial sustainability, and environmental sustainability which lasts for the future.
- Quality of Life: It includes inclusiveness, entertainment, ease of obtaining public services, cost-efficient healthcare, quality education, safety and security, transparency and accountability, opportunities for participation in governance, and a pollution-free environment.
- Housing and Inclusiveness: To expand housing opportunities for all; especially for the poor and marginalized.
- Greenery: Increase the aesthetic value of cities by developing greenery within and outside along with well maintained open spaces like the park
- Pollution Fewer cities: Reduce pollution by promoting public transport or establishing facilities for non-motorized transport (e.g. walking and cycling).
- Identity to the city: Based on the main economic activity of the city such as local cuisine, healthcare, education, arts and craft, heritage, sports, textile, dairy, etc; the city can be identified under the Smart City Mission.
- Smart Solutions: For infrastructure and services development use smart solutions. For example, to make cities less vulnerable to disasters, use fewer resources for development, and provide cheaper services to citizens through smart initiatives.
The Core Infrastructure of a Smart City would include the following:
Adequate water supply assured electricity supply, sanitation facilities including solid waste management, efficient urban mobility, eco-friendly public transport, affordable housing especially for the poor and marginalized, robust digitalization and ITC connectivity, Good governance especially e-Governance, inclusive governance and citizen participation, safety, and security of citizens particularly women, children and elderly, health and education facilities and sustainable environment constitute the core infrastructure of Smart City.
Coverage and Duration of Mission:
The Mission covers 100 cities and is being implemented by the Ministry of Urban Development (MoUD) and all state and union territory (UT) governments. Initially, its duration is of 5 years (FY2015-16 to FY2019-20) but the Ministry has extended the timeline to June 2023 due to the Covid pandemic.
Pillars of Smart City:
Institutional Infrastructure, Physical Infrastructure, Social Infrastructure, and Economic Infrastructure constitute the basic pillars on which a smart city rests and it works towards ensuring the best for its people, regardless of social status, political affiliation, age, income, gender, etc. These are
- Institutional Infrastructure: It refers to the activities that relate to the governance and management of urban areas. The information & communication technology (ICT) has provided a new dimension to this system making it efficient, accountable, transparent, and citizen-centric. It includes participatory governance, e-governance, and inclusive governance.
- Physical Infrastructure: It refers to cost-efficient and intelligent physical infrastructure which has urban mobility systems, the energy system, the water supply system, sewerage system, sanitation facilities, solid waste management system, drainage system, etc., and all are well integrated through the use of technology.
- Economic Infrastructure: For a city to attract economic opportunities, investments and to create the appropriate employment, it has to first identify its core areas and competence, comparative advantages and strength, and analyze its potential for generating appropriate economic activities.
- Social Infrastructure: It is related to the development of human and social capital. Along with education and healthcare; it includes creative arts, sports, children’s parks, gardens, and open spaces. The city must have facilities that bring disadvantageous sections i.e. SCs, STs, minorities, disabled people, and women into the mainstream of development.
The Strategy of Smart Cities Mission:
The strategic components of area-based development in the Smart Cities Mission are as follows: City improvement (retrofitting), city renewal (redevelopment), and city extension (greenfield development) plus a Pan-city initiative in which smart methods are applied to cover a large part of the city.
- Retrofitting: It introduces planning in an existing built-up area to achieve Smart City objectives, along with other objectives, to make the existing area more efficient, effective, and livable. In this, an area consisting of more than 500 acres is to be identified by the city body in consultation with citizens.
- Redevelopment: It affects a replacement of the existing built-up environment and enables the co-creation of new structures with enhanced infrastructure using mixed land use, increased density, and new technology.
- Greenfield Development: It introduces most of the Smart Solutions in a vacant area with innovative planning, plan to finance, and plan implementation tools (e.g. land pooling/ land reconstitution) for affordable and sustainable housing especially for the poor.
- Pan-City Development: It envisages the application of selected Smart City Solutions to the existing city-wide infrastructure. Application of Smart Solutions will involve the use of technology, information, and data to make infrastructure, governance, and services better.
Implementation and Financing of Smart City:
The implementation of the SCM is to be done by a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). It will plan, appraise, approve, finance, implement, manage, organize, monitor, and evaluate the Smart City projects. It is headed by a full-time CEO and has nominees of Central Government, State Government, and ULB. The Mission is financed by Central Government to the extent of Rs. 48,000 crores over five years as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) and an equal amount have to be contributed by the State and ULB; therefore, nearly Rupees one lakh crore of Government/ULB funds be available for Smart Cities development across India.
Challenges Faced by Smart City Mission:
- Design-related challenges: The smart city concept is based on the belief that technology can solve any problem without fundamentally changing lifestyles which may be an oversimplification of reality. Seeing the diversity of a country like India, the heterogeneity of its cities cannot be accommodated in a linear vision that is backed by technology. Also, the combined funding from the union and state governments, as well as the urban local bodies, for all cities is less than Rs 1 lakh crore which is disproportionately a small sum to develop 100+ Smart Cities. Smart city projects have sidelined state ministries and agencies by establishing direct contact and transfer of funds to urban bodies by the Centre. Also, the municipal commissioners, who are trained to administer the city, are struggling to make the transition in their roles from city administrator to city planner.
- Implementation-related challenges: Implementation of any mission related to urban infrastructure is the biggest challenge; as seen in Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM) nearly 54 percent of such projects are yet to be completed even after 15 years. Selection of Investment model and continuity of model is a big issue; as many private investors back off such large scale mission. Also, most ULBs have limited technical capacity, manpower, and financial crunches. And for timely completion of the project, all clearances should use online processes and be cleared in a time-bound manner.
Similar Reads
Smart City Mission - Features, Strategy and Challenges
Across the world, the pace of migration from rural to urban areas is increasing rapidly. According to United Nations, by 2050, about 68% of the world population will be living in urban areas and India is no exception. While the urban Indian population is currently around 31%(Census, 2011) of the tot
7 min read
Artificial Intelligence in NASA and DARPA in 2000s
Artificial Intelligence was developed very rapidly and was being deployed successfully at NASA. In the year 1999, Remote Agent took Deep Space 1 on a galactic ride. In May 1999, an AI program called Remote Agent autonomously ran the spacecraft Deep Space 1 for two days. The remote agent system was s
5 min read
Goal-based AI Agents
Goal-based AI agents represent a sophisticated approach in artificial intelligence (AI), where agents are programmed to achieve specific objectives. These agents are designed to plan, execute, and adjust their actions dynamically to meet predefined goals. This approach is particularly useful in comp
6 min read
Classification of Smart objects
Smart Objects: Smart Object is an object that enhances interplay with not solely humans however also with different smart objects. Also recognized as smart connected products or smart connected things (SCoT), they are products, assets, and different matters embedded with processors, sensors, softwar
6 min read
Project Idea | Drone Delivery
Project Title: Drone Delivery – Make a step ahead for Future Introduction: At present we all were in the Generation where each and every door delivery is given by a Man. So to make a step ahead for Future towards the Technology, I would like to introduce my Project “Drone Delivery – Make a Step ahea
3 min read
7 Amazing Applications of AI in Space Exploration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various industries, and space exploration is no exception. AI's ability to process vast amounts of data, make autonomous decisions, and operate in harsh environments makes it an invaluable tool for space missions. In this article we will explore Top 7
4 min read
Attentive Inc Secures $7 Million in Series A Funding for AI-driven SaaS Solutions
Attentive Inc., a SaaS startup specializing in AI-based sales automation, successfully raised $7 million in a Series A funding round. The funding was led by Vertex Ventures Southeast Asia and India, and had contributions from existing investors Peak XV Partners and InfoEdge Ventures, reflecting the
4 min read
Top 15 AI Tools for Supply Chain and Logistics in 2024 [Free + Paid]
In 2024, the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools in the stream of supply chain and logistics is poised to bring about a significant transformation in the industry. These AI tools are designed to streamline various tasks, including but not limited to, handling customs paperwork, thereby influen
9 min read
What is a Smart City? - Definition, Highlights, Functions, Examples
Our Prime Minister Narendra Modi sent off a mission of computerized India in which he centered to form the urban communities into shrewd urban communities. His vision is to concocted 100 shrewd urban communities all over India to help the improvement of the nation and open an entryway for worldwide
6 min read
Intent Based Networking (IBN)
Intent-based networking (IBN) is a systematic approach to bind infrastructure management and business intent. It is a network management approach in which artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a major role by automating all the organizational tasks which can be applied across t
3 min read
How Does NASA Use Machine Learning?
NASA has been trying to solve all these questions on a daily basis. Do you ever look at the night sky and wonder what is beyond the stars? Do you ever wonder if there is life somewhere else in the universe? Do you want to travel to some faraway galaxy and find out the secrets of the universe?!! NASA
9 min read
What is Smart Technology?
Smart technology includes devices, systems, and places that use advanced technologies to interact intelligently with people and other devices. These technologies use sensors, connections, and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate tasks, make things more convenient, and work more efficiently. They
6 min read
10 Best Cloud Computing Project Ideas
Cloud Computing is responding well to the changing needs of the current times. Those needs are either be of businesses or educational institutions like colleges, schools which have to be fulfilled with cost-effective and scalable solutions. And to learn how one can implement such solutions well, it
11 min read
Project Idea | Smart Waste Management System
INTRODUCTION: Brief presentation of the project (MUST SEE before reading further) The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept in which surrounding objects are connected through wired and wireless networks without user intervention. In the field of IoT, the objects communicate and exchange information
9 min read
Top 10 Intelligent Automation Companies
Intelligent automation (IA), or cognitive automation, combines AI, BPM, and RPA to improve decision-making across organizations. From simplifying tasks to amplifying efficiency, IA is reshaping industries. Let's explore the top 10 companies at the forefront of this transformative movement. What is I
6 min read
Informatica Work Experience
Welcome to my blog! I'm thrilled to share my journey working at Informatica, specifically focusing on Master Data Management (MDM). At Informatica, I am a part of the Master Data Management (MDM) team, diving deep into the architecture and processes that make this platform a leader in the industry.
4 min read
The Future of DevOps – Top Trends and Future Predictions
DevOps has quietly but powerfully emerged as a game-changer in the tech world. It started off as just an initiative to bridge the gap between development and operations, and now it's grown into a movement reshaping how we think about developing and delivering software. Remember when the internet was
11 min read
Project Idea | SmartStreet
Project Title: SmartStreet - An Adaptive & Self-Learning Smart Street Lighting Automation Introduction: Adaptive Smart Street Lightning is a module to automate existing street lights infrastructure using deployment of cost-efficient ESP8266 WiFi chipsets. The module optimizes group's net intensi
3 min read
7 Best AI Tools for IT Professionals (2024)
With time and technology, the one thing that has been through major upliftment and development is the IT sector. As the IT industry keeps on growing with time, managing the work of the IT sector becomes one great task that needs to be done with accuracy and professionalism. Starting from keeping the
9 min read
What is the Best Azure IoT Service for You?
Internet of Things is a raging technology. The term 'internet of things ' describes a network of connected devices that sends data to and receives instructions from a centralized computer system by using the internet as a communication channel. A very simple illustration for IoT could be smart light
6 min read