tac command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
27 Sep, 2024
tac command in Linux is used to concatenate and print files in reverse. This command will write each FILE to standard output, the last line first. When no file is specified then this command will read the standard input.
Here, we will look deeper into the tac command, exploring its syntax, various options, and practical use cases to help you master this command and boost your productivity in Linux environments.
Syntax
tac [OPTION]... [FILE]...
where,
- [OPTION]: Additional options that modify the behavior of the command (more details below).
- [FILE]: One or more files to process. If no file is specified, tac reads from standard input.
Basic Example
Let’s explore a basic example of how the tac command works.
tac tacexample.txt
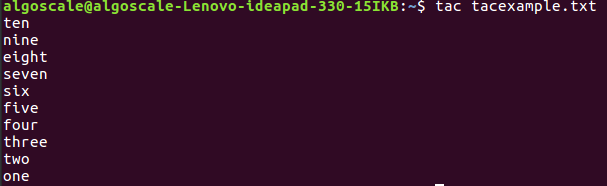
It will print files in reverse.
Key Options for the tac Command
The tac command comes with several options to modify its behavior, providing additional functionality and control over how it processes files.
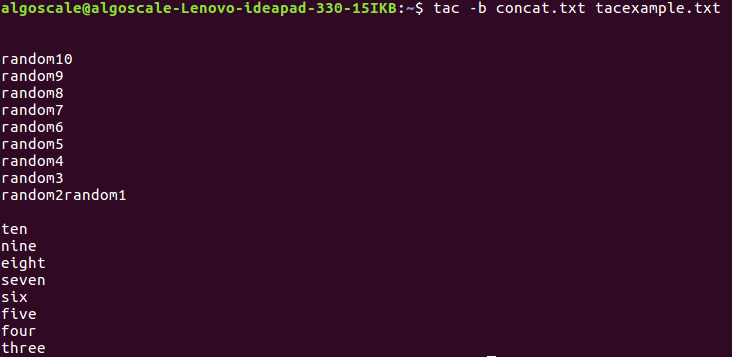
1. tac -b: Attach the Separator Before
The -b option attaches the separator before the line. This option is useful when working with files that have specific delimiter requirements.
Example:
tac -b concat.txt tacexample.txt
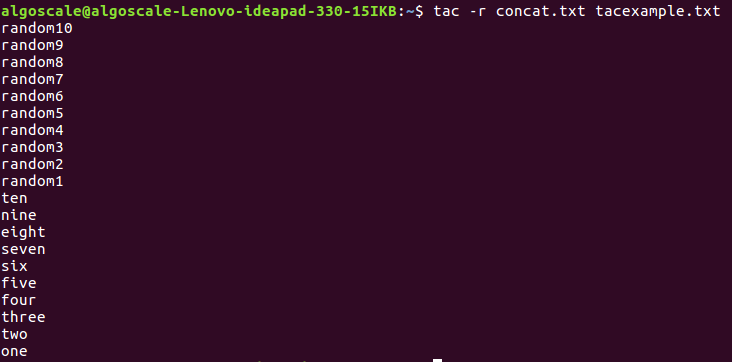
2. tac -r: Interpret the Separator as a Regular Expression
The -r option treats the separator as a regular expression, allowing for more advanced pattern matching.
Example:
tac -r concat.txt tacexample.txt
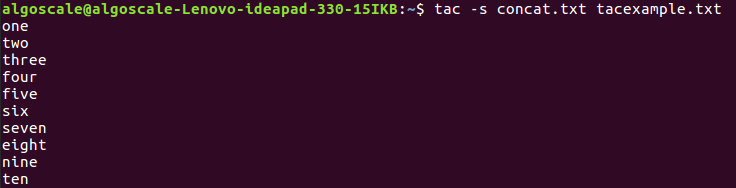
3. tac -s: Use STRING as the Separator Instead of Newline
The -s option allows you to specify a custom string as the separator. This is particularly useful when working with CSV files or other formats that use custom delimiters.
Example:
tac -s concat.txt tacexample.txt
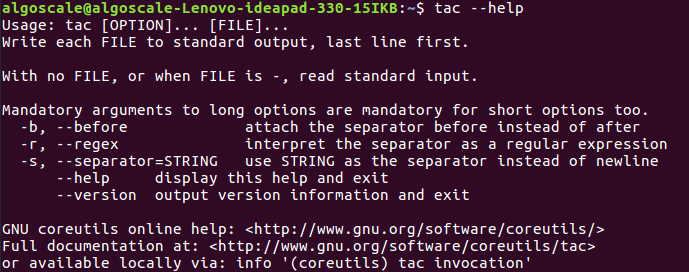
4. tac –help: Display Help Text
This option displays a brief help text, showing all available options and how to use them.
Example:
tac --help
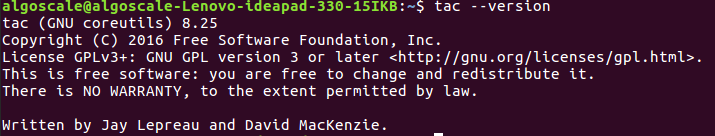
5. tac –version: Display Version Information
To check the current version of the tac command installed on your system, use the –version option.
tac --version
Conclusion
The tac command in Linux is a simple yet highly effective tool for reversing the content of files. Whether you’re analyzing logs, processing CSV files, or working with large datasets, mastering tac can help you work more efficiently. By understanding the available options and combining tac with other Linux utilities, you can unlock its full potential for a wide range of use cases.
tac command in Linux – FAQs
What is the difference between tac and cat in Linux?
The cat command prints file contents in order, while tac prints file contents in reverse order (last line first).
Can I use tac to reverse a file based on a custom delimiter?
Yes, you can use the -s option to specify a custom delimiter, such as a comma, space, or any other character.
How do I reverse multiple files using tac?
You can provide multiple filenames as arguments to tac, and it will reverse the contents of each file in the order they are provided:
tac file1.txt file2.txt
Can tac be used with regular expressions?
Yes, by using the -r option, you can treat the separator as a regular expression.
Similar Reads
How to sort lines in text files in Linux | sort Command
SORT command is used to sort a file, arranging the records in a particular order. By default, the sort command sorts file assuming the contents are ASCII. Using options in the sort command can also be used to sort numerically. SORT command sorts the contents of a text file, line by line.sort is a s
7 min read
Split Command in Linux with Examples
Split command in Linux is used to split large files into smaller files . It splits the files into 1000 lines per file(by default) and even allows users to change the number of lines as per requirement. The names of the files are PREFIXaa, PREFIXab, PREFIXac, and so on. By default the PREFIX of files
6 min read
How to use SSH to connect to a remote server in Linux | ssh Command
Secure Shell, commonly known as SSH, is like a super-secure way to talk to faraway computers, called servers. It's like a secret tunnel on the internet that keeps your conversations safe and private. Imagine you're sending a letter, and instead of sending it openly, you put it in a magic envelope th
8 min read
Strace command in Linux with Examples
'strace' is a powerful tool for monitoring and diagnosing processes in Linux. It is primarily used for debugging programs, troubleshooting issues, intercepting and recording system calls, and tracing running processes. It provides valuable insights into how a program interacts with the system, espec
4 min read
stty command in Linux with Examples
stty command in Linux is used to change and print terminal line settings. This command shows or changes terminal characteristics. Syntaxstty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [SETTING]...stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [-a|--all]stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [-g|--save]where, -F DEVICE or --file=DEVIC
2 min read
sudo Command in Linux with Examples
sudo (Super User DO) command in Linux is generally used as a prefix for some commands that only superusers are allowed to run. If you prefix any command with "sudo", it will run that command with elevated privileges or in other words allow a user with proper permissions to execute a command as anoth
8 min read
sum command in Linux with Examples
The sum command in Linux is used to calculate the checksum and block count of files. This command helps in verifying file integrity by comparing the calculated checksum with an expected value. The sum command can operate on one or more files, and when no file is specified, it reads from standard inp
3 min read
sync command in Linux with Examples
sync command in Linux is used to synchronize cached writes to persistent storage. If one or more files are specified, sync only them, or their containing file systems. Syntax: sync [OPTION] [FILE]... Note: Nothing is being shown in the screenshots just because sync command makes the cache in the bac
1 min read
How to Manage System Services in Linux | systemctl Command
Linux operating systems are known for their robustness and versatility, and managing system services is a crucial aspect of maintaining a well-functioning system. With the advent of systemd, a system and service manager for Linux operating systems, the systemctl command has become an essential tool
8 min read
tac command in Linux with Examples
tac command in Linux is used to concatenate and print files in reverse. This command will write each FILE to standard output, the last line first. When no file is specified then this command will read the standard input. Here, we will look deeper into the tac command, exploring its syntax, various o
3 min read