Vector Operations in Pytorch
Last Updated :
23 Jan, 2023
In this article, we are going to discuss vector operations in PyTorch. Vectors are a one-dimensional tensor, which is used to manipulate the data. Vector operations are of different types such as mathematical operation, dot product, and linspace.
PyTorch is an optimized tensor library majorly used for Deep Learning applications using GPUs and CPUs. It is one of the widely used Machine learning libraries, others being TensorFlow and Keras.
We can create a vector by using the torch.tensor() function
Syntax:
torch.tensor([value1,value2,.value n])
where values are the input values that take input as a list
Example:
Python3
import torch
A = torch.tensor([7058, 7059, 7060, 7061, 7062])
print(A)
|
Output:
tensor([7058, 7059, 7060, 7061, 7062])
Now let us discuss each vector operation supported under tensor.
Arithmetic operations
The procedure is extremely simple, just create two vectors and perform operations on them like you are performing them on two regular variables.
Example:
Python3
import torch
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
B = torch.tensor([100, 120, 140, 160, 180])
print("Addition of two vectors:", A+B)
print("subtraction of two vectors:", A-B)
print("multiplication of two vectors:", A*B)
print("multiplication of two vectors:", A*B)
print("division of two vectors:", A/B)
print("floor division of two vectors:", A//B)
print("modulus operation of two vectors:", A % B)
print("power operation of two vectors:", A**B)
|
Output:
Addition of two vectors: tensor([158, 179, 200, 221, 242])
subtraction of two vectors: tensor([ -42, -61, -80, -99, -118])
multiplication of two vectors: tensor([ 5800, 7080, 8400, 9760, 11160])
multiplication of two vectors: tensor([ 5800, 7080, 8400, 9760, 11160])
division of two vectors: tensor([0.5800, 0.4917, 0.4286, 0.3812, 0.3444])
floor division of two vectors: tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
modulus operation of two vectors: tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
power operation of two vectors: tensor([ 0, -4166911448072485343, 0,8747520307384418433, 0])
Unary operations
It is similar to arithmetic operations except that the other vector part is replaced by a constant.
Example:
Python3
import torch
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
print(A/2)
print(A*2)
print(A-2)
|
Output:
tensor([29.0000, 29.5000, 30.0000, 30.5000, 31.0000])
tensor([116, 118, 120, 122, 124])
tensor([56, 57, 58, 59, 60])
Dot product
dot() is used to get the dot product. The vectors in consideration just need to be passed to it.
Syntax:
torch.dot(vector1,vector2)
Example:
Python3
import torch
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
B = torch.tensor([8, 9, 6, 1, 2])
print(torch.dot(A, B))
|
Output:
tensor(1540)
Linspace function
linspace is used to arrange data linearly in the given space. It is available in the torch package and using linspace() function with values for start and end are enough.
Syntax:
torch.linspace(start,end)
where start is the starting value and end is the ending value.
Example
Python3
import torch
print(torch.linspace(2, 10))
|
Output:
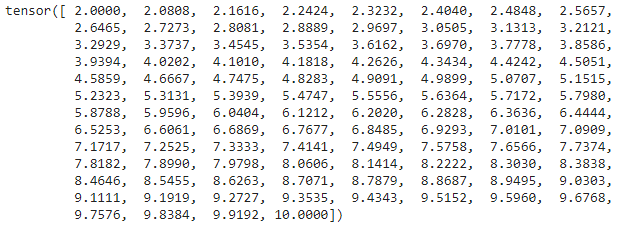
Plotting a function on the two-dimensional coordinate system
The linspace function is used to plot a function on two-dimensional coordinate systems. For the x-axis, we create a land space from 0 to 10 in an interval of 2.5, and Y will be the function of each x value.
Example 1: sin function
Python3
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
y = torch.sin(x)
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
plt.show()
|
Output:
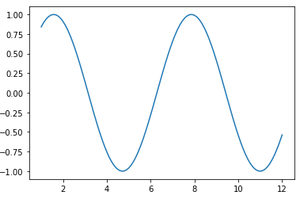
Example 2: cos function
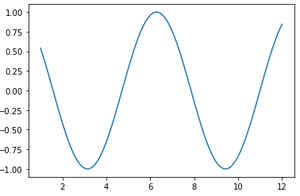
Python3
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
y = torch.cos(x)
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
plt.show()
|
Output:
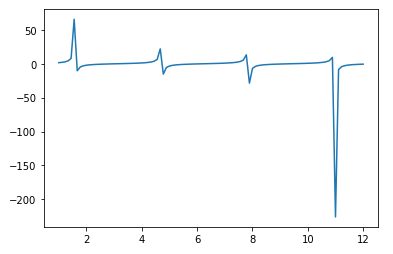
Example 3: tan() function
Python3
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
y = torch.tan(x)
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
plt.show()
|
Output:
Similar Reads
Vector Operations in Pytorch
In this article, we are going to discuss vector operations in PyTorch. Vectors are a one-dimensional tensor, which is used to manipulate the data. Vector operations are of different types such as mathematical operation, dot product, and linspace. PyTorch is an optimized tensor library majorly used f
4 min read
Tensor Operations in PyTorch
In this article, we will discuss tensor operations in PyTorch. PyTorch is a scientific package used to perform operations on the given data like tensor in python. A Tensor is a collection of data like a numpy array. We can create a tensor using the tensor function: Syntax: torch.tensor([[[element1,e
5 min read
Pytorch - Index-based Operation
PyTorch is a python library developed by Facebook to run and train deep learning and machine learning algorithms. Tensor is the fundamental data structure of the machine or deep learning algorithms and to deal with them, we perform several operations, for which PyTorch library offers many functional
7 min read
How to Perform in-place Operations in PyTorch?
In this article, we will see different in-place operations performed on tensors in PyTorch. Inplace operations are used to directly alter the values of a tensor. The data collected from the user will not be copied. The fundamental benefit of adopting these procedures is that they reduce memory stora
3 min read
How to set up and Run CUDA Operations in Pytorch ?
CUDA(or Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a proprietary parallel computing platform and programming model from NVIDIA. Using the CUDA SDK, developers can utilize their NVIDIA GPUs(Graphics Processing Units), thus enabling them to bring in the power of GPU-based parallel processing instead of t
4 min read
Python - PyTorch is_tensor() method
PyTorch torch.is_tensor() method returns True if the passed object is a PyTorch tensor. Syntax: torch.is_tensor(object) Arguments object: This is input tensor to be tested. Return: It returns either True or False. Let's see this concept with the help of few examples: Example 1: # Importing the PyTor
1 min read
Creating a Tensor in Pytorch
All the deep learning is computations on tensors, which are generalizations of a matrix that can be indexed in more than 2 dimensions. Tensors can be created from Python lists with the torch.tensor() function. The tensor() Method: To create tensors with Pytorch we can simply use the tensor() method:
6 min read
Tensor Bitwise operations
Tensor bitwise operations in Python involve performing logical operations at the bit level on tensors, which are multi-dimensional arrays widely used in machine learning and deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. These operations enable the manipulation of binary data efficiently, ess
5 min read
Python PyTorch – torch.polar() Function
In this article, we will discuss the torch.polar() method in Pytorch using Python. torch.polar() method torch.polar() method is used to construct a complex number using absolute value and angle. The data types of these absolute values and angles must be either float or double. If the absolute value
2 min read
Python - PyTorch is_storage() method
PyTorch torch.is_storage() method returns True if obj is a PyTorch storage object. Syntax: torch.is_storage(object) Arguments object: This is input tensor to be tested. Return: It returns either True or False. Let's see this concept with the help of few examples: Example 1: # Importing the PyTorch l
1 min read