Ways to Find Out List of All Open Ports in Linux
Last Updated :
13 Dec, 2023
In this guide, we’ll explore how to identify the comprehensive list of open ports in Linux, crucial endpoints for communication within computer networks. Ports, serving as gateways for network communication, are represented by 16-bit numbers ranging from 0 to 65535. These ports play a pivotal role in facilitating communication through Internet transport protocols, including the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
The ports are categorized by the range of port numbers as follows:
- From 0 to 1023: These ports are known as well-known ports. These ports can only be used by system (or root) processes or by programs executed by privileged users.
- From 1024 to 49151: These ports are known as the Registered ports. These ports can be used by ordinary user processes or programs executed by ordinary users.
- From 49152 to 65535: These ports are known as Dynamic Ports.
Before we learn how to find the list of open ports in the Linux system, we must look at how we can get the list of all ports on the system by using the command mentioned below:
cat /etc/services
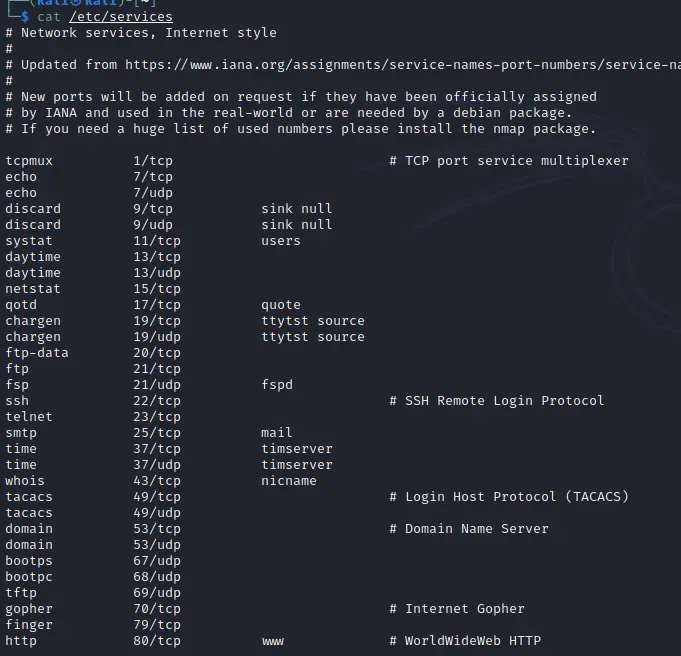
cat /etc/services
Now let’s see how to find out the list of open ports in the Linux systems.
There are three ways by which we can find the list of open ports on the Linux system. Let’s see them one by one.
Using the `netstat` tool to find Open Ports in Linux
Netstat is a tool that gives information about the Linux networking subsystem. We use Netstat to list all open ports on the system. Use the following command to list all open ports on the system.
netstat -lntu
In the above command:
- Option -l: list only listening sockets.
- Option -n: show the port number.
- Option -t: list the TCP ports.
- Option -u: list the UDP ports
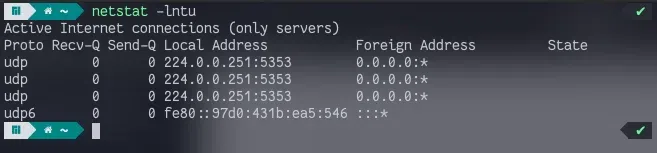
netstat -lntu
Using the `ss` tool to find Open Ports in Linux
ss is another tool to investigate sockets, this is the best alternative to the netstat command? So, we can also use the ss tool to list the open ports on the system. Use the following command to list all the ports on the system.
ss -lntu
The meaning of all options used with the above command is the same as the previous netstat command.
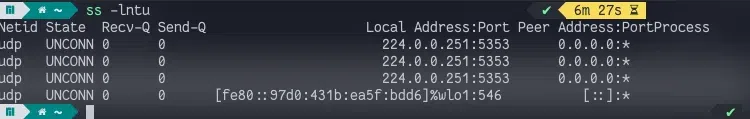
ss -into
Using the `lsof` command to find Open Ports in Linux
lsof is the command that is used to list the files. We can use the lsof command to list the open ports on the system using the following command:
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
In the above command:
- Option -i: selects the listing of files, any of whose Internet address matches the address specified in i.
- Option -P: inhibits the conversion of port numbers to port names for network files.
- Option -n: inhibits the conversion of network numbers to host names for network files.
.webp)
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
Frequently Asked Questions
1) How do I find the open ports on a specific IP address?
We can use the methods that are mentioned above with `-a` option to display all the connections and listening ports associated with a specific IP address.
Syntax:
netstat -ant | grep <IP address>
Here, enter your desired IP address in place of <IP address>.
2) How do I close an Open port in Linux?
First, we can find the process using `lsof` command and the terminate it with `kill` command.
Syntax:
sudo lsof -i :<port number>
Here, enter your desired port number in place of <port number>.
sudo kill <process ID>
Here, enter the process ID you get from above step in place of <process ID>.
3) How do I block incoming traffic to a specific port in Linux?
We can use firewall to block incoming traffic to a specific port by using `ufw` command.
Syntax:
sudo ufw deny <port_number>/tcp
Here, enter your desired port number in place of <port number>.
Conclusion
This article provides insights into open ports in Linux, categorizing them as well-known, registered, and dynamic. We discuss how to list all ports on your system with the $cat /etc/services command. We explore three methods to find open ports: using netstat to list listening sockets, the ss tool as an alternative, and lsof to identify open ports and associated processes. We answer common questions about finding open ports on specific IP addresses, closing open ports, and blocking incoming traffic using ufw. With this knowledge, you can effectively manage and secure your Linux system’s network communication by controlling open ports.
Similar Reads
Ways to Find Out List of All Open Ports in Linux
In this guide, we'll explore how to identify the comprehensive list of open ports in Linux, crucial endpoints for communication within computer networks. Ports, serving as gateways for network communication, are represented by 16-bit numbers ranging from 0 to 65535. These ports play a pivotal role i
4 min read
How to List Open Files in Linux | lsof Command
In the world of Linux, understanding and managing open files is crucial for system administrators and users alike. The Linux operating system provides a powerful utility called lsof (List Open Files) that allows users to gain insights into the files currently open on their system. In this article, w
7 min read
How to Open Ports in Linux Server Firewall
Management of the server firewall and therefore control of the ports that are open is a very significant and fundamental procedure that any system administrator needs to master in order to control the network accessibility by closing sensitive ports. Firewalls are boundaries, that regulate traffic o
5 min read
List out all the Shells Using Linux Commands
There are various methods to list all the shells which are installed in our Linux system. A Shell is a software program that acts as an interface between the user and the operating system(OS). It can also be thought of as a command interpreter that is used to execute another program. Method 1: Using
1 min read
How to List Network Interfaces in Linux?
In Linux, a Network Interface serves as the communication link between a computer and a network. It is a crucial component that enables the transmission and reception of data between the system and external networks, such as the Internet or local area networks. Each network interface is associated w
5 min read
How to List Installed Packages on Linux
Managing installed packages is a core aspect of maintaining a clean and efficient Linux system. Whether you're troubleshooting software conflicts, planning system updates, or freeing up disk space, knowing how to list installed packages is essential or finding installed software in Linux. In this ar
9 min read
How to List Current Logged-In Users in Linux | who Command
Linux provides several command-line tools to manage and monitor user activity. One common administrative task is identifying and listing the currently logged-in users on a Linux system. In this article, we will delve into multiple ways to achieve this, exploring commands such as who, user, w, last,
6 min read
PortSpider - Advance Network Port scanner on Kali Linux
PortSpider is a free and open-source tool available on GitHub. PortSpider is an Open Source Intelligence and network scanning Tool based on (OSINT). This tool can scan huge network ranges to find open and closed ports and all the vulnerable services running on the server or on the system, not only s
2 min read
Changing Nginx Port in Linux
Nginx, written by Igor Sysoev and released on October 4th, 2003, is a fast, open-source multi-functional web server. It also acts as a reverse proxy and loads balancer, apart from being a web server, allowing it to handle large numbers of concurrent HTTP connections and is mostly preferred to Apache
2 min read
How to Find Hidden Processes in Linux
Hidden or unlisted running processes in Linux can indicate issues like misconfigured applications or potential security threats, including malware or rootkits. Identifying and addressing these hidden processes is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient system. This guide provides simple and a
5 min read