What are the Roots of Cloud Computing?
Last Updated :
20 May, 2024
Cloud computing is a game changer in tech landscape. Through the internet, we can access the shared pool of resources such as computing, network, storage, computing, and database within a few seconds with minimal management and without service provider interaction. Here we are exploring, how the cloud is growing from mainframe to application service providers (ASPs), and how it works.
Primary Terminologies
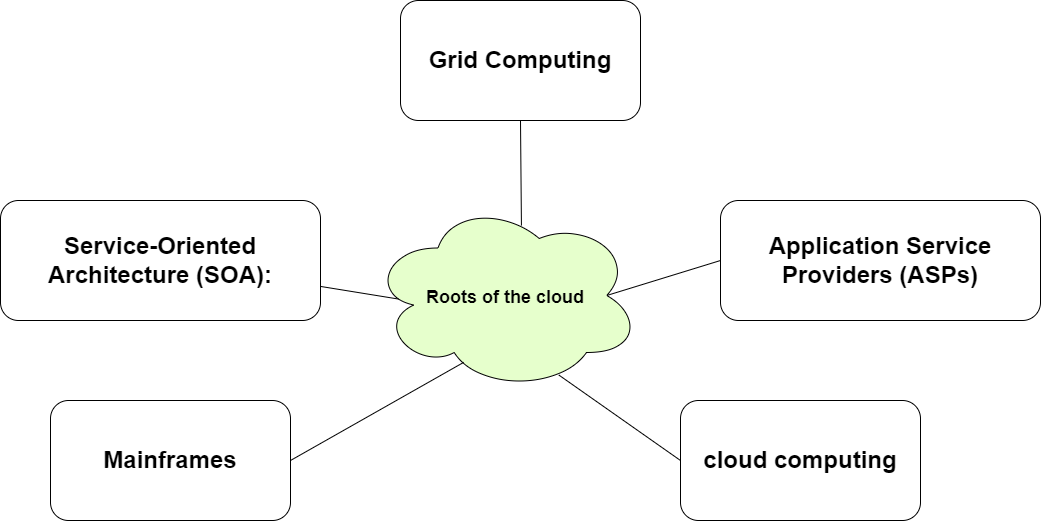
- Mainframe Era: The Mainframe Era was famous in the 1950s–1970s times. and it was a large central computer that was used by many users through terminals.
- Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA): It's a type of design approach where applications are built as smaller, independent pieces called services. and after that, they will be integrated and shared over the network.
- Grid Computing: Grid computing is basically combining many computers together to solve big and complex tasks faster.
- Application Service Providers (ASPs): It's like early versions of cloud services that provide applications or services that you could use through the internet.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is an on-demand self-service model that basically provides a pool of resources such as networks, computing pay-as-you-go, storage, databases, and many more services within a few seconds with minimal management and without human interaction. Another significant advantage is the pay-as-you-go model and time to market.
A Historical Timeline of Cloud Computing
1. Mainframe Era (1950s–1970s)
Imagine a room-size computer! This was the time of mainframes, where big, giant, super-powerful machines were only affordable by big companies. Back then, a computer scientist named John McCarthy had a brilliant idea, what if we could share powerful machines, like how we share electricity from a power plant? This early concept that basically creates the basic building blocks for cloud computing.
Even though mainframes were strong, they were very expensive and difficult to manage and handle, which is why most people did not use them. In short, we say that it was sharing the big machine.
It provides centralized development (monolithic architecture) and complex deployment.
2. Service-Oriented Architecture (1990s)
At The 1990s time Service-Oriented Architecture(SOA) was born as a modular approach to software design. application is built from the smaller, independent chunks Instead of a big complex, large program. and shared over a network and easily connected to it.
This modular approach changes the entire game of the previous technology (mainframes). Here, scalability is high and integration is easy. It provides distributed development and flexible deployment. and also enhance agility through independent and small service.
It mainly focuses on business functionality, and its target users are developers and business analytics. Here, the security concerns are at the service level.
3. Grid Computing (1990s-2000s)
At the same time, when SOA comes, another new concept called grid computing emerges. Imagine that groups of computers are working together to solve a big problem. Grid computing works similarly by connecting more machines to solve a big task or problem that is too difficult to solve using a single machine. here the idea of sharing resources are the creation of basic building blocks of cloud service like resource pooling, at the same time resources are pool to serve multiple users.
In short, we say that it was sharing power like a team.
This service is accessible through grid middleware. It uses a distributed architecture. and here security concerns access control of grid resources.
4. Application Service Providers (ASPs) (Late 1990s)
Imagine a time before you could download apps or programs. At the end of 1990s, companies called Application Service Providers (ASPs) introduce a new way to use software. Instead of buying and installing it manually, you can pay subscription of it online and access it through a web-based interface. This was an early stage of the cloud-based software-as-a-service we use today, like renting a bike instead of buying it!
This early concept that basically create basic building blocks for Software as a Service (SaaS), where you access programs or service like email service or other writing tools directly though the internet, with no downloads needed.
in short we say that it was Renting Software Online.
5. Why Cloud Computing is famous too much: Saving Money and Making IT Easier
Below two things make cloud computing super attractive in the late 1900s and early 2000s:
- On-premise IT: When you start any on-premise datacenter so that time you required some space or room, needs power source and power-backups, needs some cooling equipment and different administrators such as database administrator, network administrator, server administrator, security administrator and many more, and some times hardware failure which is too much expensive and some times unpredictable spike in usage that time we require more hardware which is also increase the total cost of investment (TCO).
- The Internet Grew Up: As the internet became faster and more reliable, it opened the door for technology to doing something innovative and amazing and think out of the box.
Due to this economic pressure cloud computing become hot because it provide fully flexible and cheaper solution through pay as you go model (PAYG) and companies will pay only what they uses like network bandwidth, compute power, and service charges can be reducing through paying advance or upfront costs.
Understanding Cloud Computing with Examples
Imagine a company that has it's own infrastructure but they can't afford to add more resources, the required skill base of staff, and additional infrastructure maintenance costs like cooling equipment, electricity, etc. Sometimes, when load increases or there is an unpredictable spike in usage, we are adding horizontally or vertically scaling of the servers.
Now, cloud computing removes this burden of purchasing external hardware and software for a particular time period. Instead, we use on-demand services from the cloud platform, and within a few seconds, it will work efficiently. Here, you have complete control over the virtual resource and only pay for what you use.
The best things about pricing and billing services in the cloud are:
- Pay as you go model (per hour, minute, and second base charges that totally depend on service and platform).
- It provides discounts based on long-term service commitment.
- If your workload is not critical at that time, you can use the spot instance service, which basically allocates computing power when it is in a free state when someone is using it. At that time, it will stop, and after that same routine, it will follow.
Cloud Computing - FAQs
What are the main difference between three service model?
There are main three types of cloud computing services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Physical infrastructure that can be globally accessible over the internet. those service or resources in the form of virtualized resources. it's also known as hardware as a service.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a managed platform where you can run, testing ,developing ,deploying, building and managing applications within a single location or platform unit and you doesn't need to manage underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Use software and application over the internet and pay as you use like subscription based, this server is hosted centrally and it's also known as on-demand software.
Security concern about cloud computing ?
Security is the one of the main important aspect and requirement of the cloud computing, but one thing that you should know about security and compliance is the shared responsibility between consumer and service provider. basically the application's data and identity and access management(IAM) is the responsibility of the cloud consumer.
What are key benefits of cloud computing?
- Scalability & Agility: When your application getting more traffic that time cloud service provider adding and removing capacity based on load.
- Cost-Effective: Pay only for what you use, and pay less when you use more like commitment of service for 1 to 3 years, as the cloud company grows that time cost will decreases .
- High Reliability: Cloud providers provide robust disaster recovery solutions for any kind of failure.
What are the main difference between three deployment model?
- Public Cloud: It supports multiple customers known as multi-tenancy and it is highly scalable but security is dependent on service provider.
- Private Cloud: High upfront cost for Dedicated resources for your organization, it's provide highest level of security and performance.
- Hybrid Cloud: it's Combination of public and private clouds, provide mix benefits flexibility, scalability, performance, security, and control.