IT Organizational Charts: 11 Examples for Any Business
Nearly every business now relies on technology, and technologies never run absolutely perfectly. Maintenance is always necessary, which can include repairs, upgrades, and security fixes. These requirements and tasks fall under the category of Information Technology (IT). And so, any organization needs to consider IT initiatives when planning their business strategies.
But when should planning how IT will be implemented begin? IT structure planning should begin when the business begins. It may be a very small set of resources to start. But with how they can affect the operations of the business, it's important to have them planned early on.
This article lists factors that affect IT planning. It also uses IT organizational charts to show examples of how any size or type of business can design their IT teams.
Factors Influencing the Planning of an IT Organizational Structure
Many factors can play a part in how an IT organization is structured:
-
Business and Strategy
- Business Strategy: Aligning IT structure with overall business goals and strategies.
- Industry Type: Industry-specific regulations and standards influence IT structure, e.g., healthcare, finance, or legal.
- Global Presence: Global organizations may require a structure that supports operations across different regions.
- Innovation Goals: Organizations focusing on innovation may have specialized roles and units.
- Change Management: The organization's ability to adapt to change and the need for change management structures.
- Competitive Landscape: The competitive environment and the need for agility and responsiveness.
- Strategic Partnerships: The existence of strategic partnerships and the impact on IT collaboration.
-
Organizational Attributes
- Size and Scale: The size of the organization affects the complexity and layers of the IT structure.
- Culture: The culture of the organization can influence the flexibility and adaptability of the IT structure.
- IT Maturity: The level of IT maturity and technological sophistication within the organization.
- Customer Base: The type and size of the customer base may influence IT service delivery structure.
- Skillset Availability: The availability and distribution of specific skills within the workforce.
- Employee Preferences: Preferences and expectations of the IT workforce.
-
IT Environment
- Number of Projects: The number and complexity of ongoing projects impact the project management and delivery structure.
- Collaboration Requirements: The need for cross-functional collaboration and communication channels.
-
Technology
- Technology Requirements: The nature and complexity of technology used within the organization.
- Digital Transformation Initiatives: Organizations undergoing digital transformation may require a structure that supports new technologies and practices.
- Emerging Technologies: Integration of emerging technologies and the need for specialized roles.
-
Financial
- Budget Constraints: Financial considerations impact the allocation of resources and personnel.
-
Governance and Compliance
- IT Governance: The framework and policies for IT governance impact the decision-making structure.
- Security and Compliance: Stringent security and compliance requirements influence the structure, especially in regulated industries.
- Regulatory Environment: Adherence to industry-specific regulations and compliance requirements.
-
Operations and Delivery
- Outsourcing Strategy: Organizations relying on outsourcing may have a different structure compared to those with in-house capabilities.
- Vendor Relationships: The reliance on external vendors and the need for vendor management structures.
- Data Sensitivity: The sensitivity and criticality of data managed by the IT organization.
- Risk Tolerance: The organization's tolerance for risk and the need for risk management structures.
11 Examples of IT Organizational Charts
The following are various examples of IT organizational charts, from small business to global enterprises, and various industries such has healthcare and financial.
Scroll left-right in each org chart to see the full layout. Org chart styling courtesy of erinesullivan.
Small Business
Click here for an image version.

-
Owner / CEOUltimately responsible for IT decisions aligning with business goals.
-
IT ManagerA single IT manager overseeing the entire IT function.
-
IT Support SpecialistProvides day-to-day technical support to end-users.
-
Network and Systems AdministratorManages the company's computer networks and IT infrastructure.
-
Developer / ProgrammerDesigns, develops, and maintains software applications.
-
Security and Compliance OfficerManages basic security measures and ensures IT compliance.
-
Business Analyst / Project ManagerAnalyzes business processes and oversees small IT projects.
-
IT TrainerProvides training on IT tools and systems to end-users.
-
-
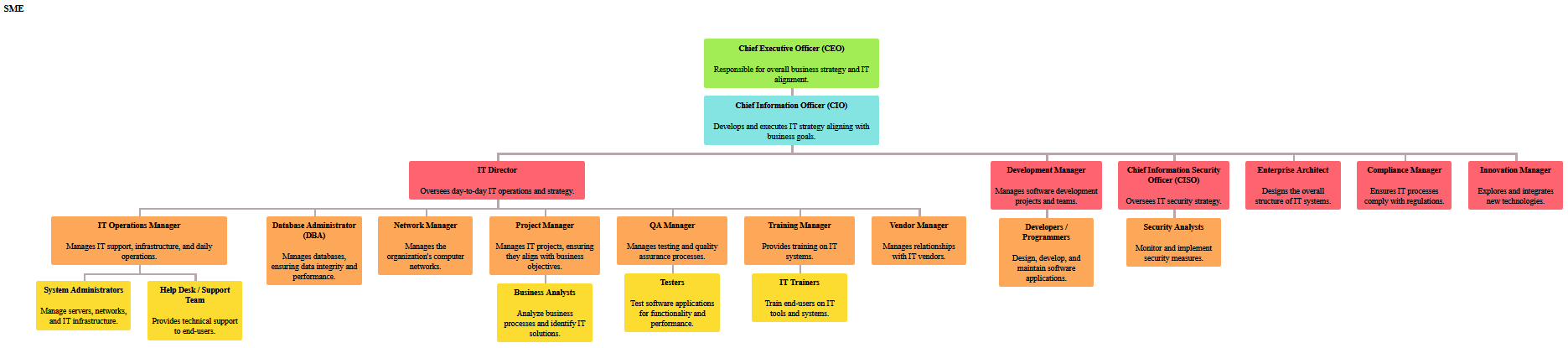
SME
Click here for an image version.
-
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Responsible for overall business strategy and IT alignment.
-
Chief Information Officer (CIO)Develops and executes IT strategy aligning with business goals.
-
IT DirectorOversees day-to-day IT operations and strategy.
-
IT Operations ManagerManages IT support, infrastructure, and daily operations.
-
System AdministratorsManage servers, networks, and IT infrastructure.
-
Help Desk / Support TeamProvides technical support to end-users.
-
-
Database Administrator (DBA)Manages databases, ensuring data integrity and performance.
-
Network ManagerManages the organization's computer networks.
-
Project ManagerManages IT projects, ensuring they align with business objectives.
-
Business AnalystsAnalyze business processes and identify IT solutions.
-
-
QA ManagerManages testing and quality assurance processes.
-
TestersTest software applications for functionality and performance.
-
-
Training ManagerProvides training on IT systems.
-
IT TrainersTrain end-users on IT tools and systems.
-
-
Vendor ManagerManages relationships with IT vendors.
-
-
Development ManagerManages software development projects and teams.
-
Developers / ProgrammersDesign, develop, and maintain software applications.
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees IT security strategy.
-
Security AnalystsMonitor and implement security measures.
-
-
Enterprise ArchitectDesigns the overall structure of IT systems.
-
Compliance ManagerEnsures IT processes comply with regulations.
-
Innovation ManagerExplores and integrates new technologies.
-
-
Large Company
Click here for an image version.

-
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Overall responsibility for the company's strategy, including IT alignment.
-
Chief Information Officer (CIO)Develops and executes IT strategy in alignment with business goals.
-
IT Operations DirectorOversees all aspects of IT operations.
-
Infrastructure DirectorManages IT infrastructure and data centers.
-
Team Leaders / Supervisors (Various Teams)Lead and manage specific teams of customer service representatives. Provide guidance, support, and performance management.
-
Customer Service Representatives (Various Teams)Frontline staff handling customer inquiries, issues, and support. Categorized into different teams based on specialization or product lines.
-
-
Technical Support Managers and Specialists (if needed)Managers oversee technical support teams. Specialists handle complex technical issues.
-
Escalation Managers and SpecialistsManage and handle complex or escalated customer issues. Collaborate with other departments for resolution.
-
-
Network DirectorManages the organization's complex computer networks.
-
Support Services DirectorManages IT support services for end-users.
-
Service Desk ManagerManages the IT service desk.
-
-
Database DirectorManages the company's databases and data integrity.
-
Database Administrators (DBAs)Specialized roles managing specific databases.
-
-
Network DirectorManages the overall network architecture.
-
Network ManagersOversee regional or functional network teams.
-
-
QA DirectorManages testing and quality assurance processes.
-
QA ManagersOversee specific QA teams.
-
-
Training and Support Services DirectorManages IT training and support services.
-
Training ManagersOversee training programs.
-
-
-
Development DirectorManages software development projects and teams.
-
Application Development ManagersOversee specific application development teams.
-
Lead Developers / ArchitectsProvide technical leadership for development projects.
-
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees IT security strategy and implementation.
-
Security Directors / ManagersManage specific aspects of IT security (e.g., network security, data security).
-
-
Project Management Office (PMO) DirectorEnsures effective project management and governance.
-
Project ManagersOversee large-scale IT projects.
-
Business AnalystsAnalyze business processes and requirements.
-
-
-
Enterprise Architecture DirectorDesigns and oversees the overall IT architecture.
-
Solution ArchitectsDesign solutions for specific projects.
-
-
Governance and Compliance DirectorEnsures IT processes comply with regulations.
-
Compliance ManagersOversee compliance in specific areas.
-
-
Vendor Management DirectorManages relationships with IT vendors.
-
Vendor ManagersOversee specific vendor relationships.
-
-
Innovation DirectorExplores and integrates new technologies.
-
Innovation ManagersFocus on specific innovation areas.
-
-
-
Chief Technology Officer (CTO)Focuses on technology strategy and innovation.
-
Online B2C Business
Click here for an image version.

-
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Overall responsibility for the business strategy, including the online presence.
-
Chief Digital Officer (CDO) or Chief E-commerce OfficerDrives the digital strategy, focusing on online customer experience and e-commerce growth.
-
IT Operations DirectorLeads the online customer service department. Sets strategic goals, policies, and procedures specific to the online platform.
-
E-commerce Operations ManagerManages day-to-day operations of the e-commerce platform.
-
Web and Infrastructure TeamManages web servers, networks, and online infrastructure.
-
Database DirectorManages databases supporting online operations.
-
E-commerce Database Administrators (DBAs)Specialized roles managing databases for the e-commerce platform.
-
-
-
Development DirectorManages software development for the online platform and applications.
-
E-commerce Development ManagerFocuses on the development of the e-commerce platform.
-
Frontend and Backend DevelopersDesign and implement online interfaces and backend systems.
-
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees online security measures.
-
Online Security AnalystsMonitor and implement security measures for the online platform.
-
-
Governance and Compliance ManagerEnsures online operations comply with regulations.
-
Compliance AnalystsFocus on compliance in online operations.
-
-
Vendor Management ManagerManages relationships with IT vendors supporting online operations.
-
E-commerce Vendor ManagersOversee relationships with vendors specific to the e-commerce platform.
-
-
-
SaaS B2B Business
Click here for an image version.

-
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Overall responsibility for the business strategy, including SaaS product offerings.
-
Chief Technology Officer (CTO)Drives the technology strategy, overseeing product development and innovation.
-
Product Development DirectorManages the overall product development lifecycle.
-
Product ManagersOversee individual SaaS products, from conception to delivery.
-
Development TeamsDevelopers working on different aspects of SaaS product development.
-
-
-
Infrastructure DirectorManages the technology infrastructure supporting SaaS products.
-
Cloud ArchitectsDesign and manage the cloud infrastructure.
-
Database DirectorManages databases supporting SaaS applications.
-
Database Administrators (DBAs)Specialized roles managing databases for SaaS applications.
-
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees security measures for SaaS products.
-
Security AnalystsMonitor and implement security measures for SaaS applications.
-
-
QA DirectorManages testing and quality assurance processes for SaaS products.
-
QA ManagersOversee QA teams focused on different aspects of SaaS testing.
-
-
Governance and Compliance ManagerEnsures SaaS operations comply with regulations.
-
Compliance AnalystsFocus on compliance in SaaS operations.
-
-
Vendor Management ManagerManages relationships with third-party vendors supporting SaaS infrastructure.
-
SaaS Vendor ManagersOversee relationships with vendors providing SaaS-related services.
-
-
Innovation ManagerExplores and integrates new technologies for enhancing SaaS products.
-
-
Local Brick and Mortar Business
Click here for an image version.

-
Business Owner / ManagerThe owner or manager responsible for overall business operations.
-
IT ManagerManages all IT-related functions for the local business.
-
IT Support SpecialistProvides technical support for day-to-day IT issues.
-
System AdministratorManages local servers, networks, and IT infrastructure.
-
Point-of-Sale (POS) AdministratorManages and supports the POS systems.
-
Developer / ProgrammerManages and maintains any local business-specific applications.
-
Database Administrator (DBA)Manages databases related to local business operations.
-
Network AdministratorManages local network infrastructure.
-
Security OfficerImplements basic security measures for the local business.
-
Training ManagerProvides training on IT tools and systems to local staff.
-
IT TrainersTrain end-users on local IT systems.
-
-
Vendor ManagerManages relationships with local IT vendors.
-
Innovation CoordinatorExplores and suggests technology improvements for local operations.
-
-
Global Enterprise
Click here for an image version.

-
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Overall responsibility for the global business strategy.
-
Chief Information Officer (CIO)Drives the global IT strategy, aligning with business goals.
-
Global IT Operations DirectorOversees global IT operations, ensuring standardization and efficiency.
-
Regional IT Directors / ManagersManage IT operations in specific regions.
-
Regional IT Operations TeamsLocal teams managing day-to-day IT operations in different regions.
-
-
-
Global Development DirectorManages global software development projects.
-
Development ManagersOversee development teams in specific regions.
-
Regional Development TeamsDevelopment teams working on projects in different regions.
-
-
-
Global Infrastructure DirectorManages global IT infrastructure and architecture.
-
Infrastructure ManagersOversee infrastructure teams in specific regions.
-
Regional Infrastructure TeamsManage regional IT infrastructure and architecture.
-
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees global IT security strategy.
-
Global Security ManagersManage security measures globally.
-
Regional Security TeamsImplement security measures in specific regions.
-
-
-
Global Project Management Office (PMO) DirectorEnsures standardized project management globally.
-
Global Project ManagersOversee global IT projects.
-
Regional Project ManagersManage projects in specific regions.
-
-
-
Global QA DirectorManages global testing and quality assurance processes.
-
QA ManagersOversee QA teams globally.
-
Regional QA TeamsImplement testing processes in specific regions.
-
-
-
Global IT Support and Training DirectorManages global IT support services and training programs.
-
IT Support ManagersOversee IT support teams globally.
-
Regional IT Support TeamsProvide local support in specific regions.
-
-
-
Global Vendor Management DirectorManages relationships with global IT vendors.
-
Vendor ManagersOversee vendor relationships in specific regions.
-
Regional Vendor ManagersManage local vendor relationships
-
-
-
Global Innovation DirectorExplores and integrates new technologies globally.
-
Innovation ManagersFocus on innovation in specific regions.
-
-
-
Healthcare Organization/Hospital
Click here for an image version.

-
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Overall responsibility for the healthcare organization/hospital.
-
Chief Information Officer (CIO)Drives the IT strategy aligning with healthcare goals.
-
Health IT Operations DirectorOversees IT operations specific to healthcare.
-
Clinical Systems ManagerClinical Systems Manager
-
Health IT Support TeamsProvides technical support for healthcare systems.
-
-
-
Health IT Development DirectorManages development of healthcare applications and integrations.
-
Health IT DevelopersDevelop and maintain healthcare-specific software applications.
-
Integration SpecialistsFocus on integrating various health IT systems.
-
-
Health IT Infrastructure DirectorManages infrastructure and security for healthcare systems.
-
Health IT Security OfficerFocuses on security measures for healthcare information.
-
Health IT Infrastructure TeamManages healthcare-specific network and server infrastructure.
-
-
Health IT QA DirectorManages testing and quality assurance processes in healthcare IT.
-
Compliance Manager (Healthcare)Ensures healthcare IT compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
-
Health IT Compliance AnalystsFocus on compliance in healthcare IT operations.
-
-
-
Health IT Support and Training DirectorManages IT support services and training for healthcare staff.
-
Health IT TrainersProvide training on healthcare IT systems to staff.
-
Clinical Informatics SpecialistsBridge the gap between IT and healthcare, optimizing technology use.
-
-
Health IT Governance DirectorOversees governance and innovation in healthcare IT.
-
Health IT Innovation ManagerExplores and integrates new technologies for healthcare.
-
Clinical Informatics ManagersManage informatics initiatives that improve patient care.
-
-
Health IT Vendor Management DirectorManages relationships with vendors providing healthcare IT solutions.
-
Health IT Vendor ManagersOversee relationships with specific healthcare IT vendors.
-
Clinical Systems AnalystsAnalyze and optimize healthcare information systems.
-
-
-
-
Finanical Institution
Click here for an image version.

-
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Overall responsibility for the financial institution.
-
Chief Information Officer (CIO)Drives the IT strategy aligning with financial goals.
-
IT Operations DirectorOversees day-to-day IT operations for the financial institution.
-
Infrastructure ManagerManages the IT infrastructure, including servers and networks.
-
Support Services ManagerManages technical support services for end-users.
-
-
Applications Development DirectorManages development of financial applications and software.
-
Applications Development ManagersApplications Development Managers
-
Financial Systems AnalystsAnalyze and optimize financial software and systems.
-
-
-
Database Administration DirectorManages databases supporting financial systems.
-
Database Administrators (DBAs)Specialized roles managing databases for financial applications.
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees IT security strategy, particularly for financial data.
-
Security ManagersManage security measures specific to financial systems.
-
-
Compliance OfficerEnsures IT compliance with financial regulations.
-
QA DirectorManages testing and quality assurance processes for financial applications.
-
QA ManagersOversee QA teams focusing on financial software.
-
Testing AnalystsConduct testing for financial systems and applications.
-
-
-
Governance and Risk Management DirectorOversees IT governance and risk management in the financial context.
-
Risk ManagersManage IT-related risks specific to financial operations.
-
Compliance Analysts (Financial)Focus on compliance related to financial regulations.
-
-
Training and Support Services DirectorManages IT training and support services.
-
IT TrainersProvide training on financial systems and applications.
-
Financial Systems Support SpecialistsProvide specialized support for financial applications.
-
-
Vendor Management DirectorManages relationships with IT vendors providing financial solutions.
-
Financial Systems Vendor ManagersOversee relationships with vendors of financial applications.
-
Financial Systems Analysts (Vendor Relations)Analyze and optimize relationships with financial systems vendors.
-
-
-
-
Law Firm
Click here for an image version.

-
Managing Partner or Chief Executive Officer (CEO)Overall responsibility for the law firm.
-
Chief Information Officer (CIO)Drives the IT strategy aligning with legal practice goals.
-
IT Operations DirectorOversees day-to-day IT operations for the law firm.
-
Infrastructure ManagerManages the IT infrastructure, including servers and networks.
-
Support Services ManagerManages technical support services for end-users.
-
-
Legal Systems ManagerManages legal case management systems and related software.
-
Legal Systems AnalystsAnalyze, configure, and optimize legal case management systems.
-
-
Legal Applications Development DirectorManages development of legal applications and software.
-
Applications Development Managers (Legal)Oversee development teams for legal applications.
-
Legal Applications DevelopersDevelop and maintain software tailored for legal processes.
-
-
-
Database Administration DirectorManages databases supporting legal applications.
-
Legal Database Administrators (DBAs)Specialized roles managing databases for legal systems.
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees IT security strategy, with a focus on legal data protection.
-
Legal Security ManagersManage security measures specific to legal operations.
-
-
Legal Compliance OfficerEnsures IT compliance with legal and regulatory standards.
-
QA DirectorManages testing and quality assurance processes for legal applications.
-
Legal QA ManagersOversee QA teams focusing on legal software.
-
Legal Testing AnalystsConduct testing for legal systems and applications.
-
-
-
Governance and Risk Management DirectorOversees IT governance and risk management, tailored for legal practice.
-
Legal Risk ManagersManage IT-related risks specific to legal operations.
-
Legal Compliance AnalystsFocus on compliance related to legal and regulatory standards.
-
-
Training and Support Services DirectorManages IT training and support services for the law firm.
-
Legal IT TrainersProvide training on legal systems and applications.
-
Legal Support SpecialistsProvide specialized IT support for legal applications.
-
-
Vendor Management DirectorManages relationships with IT vendors providing legal solutions.
-
Legal Vendor ManagersOversee relationships with vendors of legal software and services.
-
Legal Systems Analysts (Vendor Relations)Analyze and optimize relationships with legal systems vendors.
-
-
-
-
Mental Health Services Provider
Click here for an image version.

-
Executive Director or CEOOverall responsibility for the mental health services provider.
-
Chief Information Officer (CIO)Drives the IT strategy aligning with mental health service goals.
-
Health IT Operations DirectorOversees day-to-day IT operations for mental health services.
-
Clinical Systems ManagerManages clinical information systems, such as Electronic Health Records (EHR) for mental health.
-
Health IT Support TeamsProvides technical support for healthcare systems with a focus on mental health services.
-
-
-
Health IT Development DirectorManages development of mental health applications and integrations.
-
Mental Health Applications Development ManagersOversee development teams for mental health applications.
-
Mental Health Integration SpecialistsFocus on integrating various health IT systems for mental health services.
-
-
Database Administration DirectorManages databases supporting mental health systems.
-
Mental Health Database Administrators (DBAs)Specialized roles managing databases for mental health applications.
-
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)Oversees IT security strategy, emphasizing patient confidentiality and HIPAA compliance.
-
Mental Health Security ManagersManage security measures specific to mental health operations.
-
-
HIPAA Compliance OfficerEnsures IT compliance with HIPAA regulations and other mental health standards.
-
QA DirectorManages testing and quality assurance processes for mental health applications.
-
Mental Health QA ManagersOversee QA teams focusing on mental health software.
-
Mental Health Testing AnalystsConduct testing for mental health systems and applications.
-
-
-
Governance and Risk Management DirectorOversees IT governance and risk management, tailored for mental health services.
-
Mental Health Risk ManagersManage IT-related risks specific to mental health operations.
-
Mental Health Compliance AnalystsFocus on compliance related to mental health and healthcare regulations.
-
-
Training and Support Services DirectorManages IT training and support services for mental health staff.
-
Mental Health IT TrainersProvide training on mental health systems and applications.
-
Mental Health Support SpecialistsProvide specialized IT support for mental health applications.
-
-
Vendor Management DirectorManages relationships with IT vendors providing mental health solutions.
-
Mental Health Vendor ManagersOversee relationships with vendors of mental health software and services.
-
Mental Health Systems Analysts (Vendor Relations)Analyze and optimize relationships with mental health systems vendors.
-
-
-
-
Conclusion: The Importance of IT Organizational Charts
The importance of effective IT planning cannot be overstated in today's technology-dependent businesses. Because of this, the need for well-structured IT organizations becomes more important. The factors influencing the planning of an IT organizational structure are diverse. This underscores the complexity involved in designing IT teams that align with an organization's goals and adapt to its unique circumstances.
Giva Can Meet All of Your ITSM Needs
Giva's IT Service Desk and Help Desk software applications can help you take your IT ticket tracking to the next level. ITIL® aligned but easy to use and configure, with robust reporting capabilities.