- Definition/Uses
- Side Effects
- Thiazide Diuretics List
- Drug Interactions
-
Comments
-
**COMMENTSTAGLIST**
-
More
-
**OTHERTAGLIST**
What are thiazide diuretics, and what are they used for?
Thiazide diuretics (water pills) are medications that are used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and congestive heart failure as well as the accumulation of fluid and swelling (edema) of the body caused by conditions such as heart failure, cirrhosis, chronic kidney failure, corticosteroid medications, and nephrotic syndrome.
Thiazides work by reducing the ability of the kidneys to reabsorb salt and water from the urine and into the body thereby increasing the production and output of urine (diuresis).
Thiazide diuretics are similar in effectiveness and usually are not effective in people with severe renal impairment.
What are the side effects of thiazide diuretics?
Side effects of thiazide diuretics are dose related and include:
- dizziness and lightheadedness,
- blurred vision,
- loss of appetite,
- itching,
- stomach upset,
- headache, and
- weakness.
Other side effects and adverse reactions are:
- An increased sensitivity to sunlight (prolonged sun exposure should be avoided)
- Owing to their ability to increase the production of urine, these drugs may lower levels in the body of potassium and magnesium which also are present in urine.
- Thiazide diuretics may increase uric acid levels in blood.
- Like other antihypertensive medications, thiazides cause sexual dysfunction.
What are some examples thiazide diuretics?
- chlorthalidone (Thalitone)
- hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
- methyclothiazide
What drugs interact with thiazide diuretics?
- Thiazide diuretics can lower potassium and magnesium blood levels since they are both eliminated in urine. Low levels of potassium and magnesium in the blood can result in abnormal heart rhythms, particularly in those who are also taking digoxin (Lanoxin) in addition to a thiazide. Thiazide diuretics can increase the risk of lithium (Eskalith, Lithobid) toxicity by reducing the kidney's ability to eliminate lithium in the urine.
- Drugs known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Motrin), naproxen (Naprosyn), and nabumetone (Relafen) can reduce the effectiveness of thiazide diuretics in lowering blood pressure because they may reduce the ability of the kidneys to make urine, particularly in patients who have reduced kidney function.
- People who have diabetes may have increased blood sugar levels when taking thiazide diuretics.
- It is not recommended to use thiazide diuretics with dofetilide (Tikosyn), a drug used for treating abnormal heart rhythms, as this may increase the blood levels of dofetilide (Tikosyn) and cause abnormal heart rhythms. Thiazide diuretics can reduce how the body responds to norepinephrine and render norepinephrine less effective.

SLIDESHOW
How to Lower Blood Pressure: Exercise and Tips See SlideshowSummary
Thiazide diuretics are drugs prescribed to treat high blood pressure and reduce edema (fluid accumulation) in the body. Side effects of thiazide diuretics include dizziness and lightheadedness, blurred vision, loss of appetite, itching, stomach upset, headache, and weakness. Diuretic drug names include chlorthalidone (Thalitone), hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide), and methyclothiazide. Thiazide diuretics are similar in effectiveness and usually are not effective in people with severe renal impairment.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
-

What Is High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)? Symptoms, Treatments
What causes high blood pressure (hypertension)? What is normal blood pressure? Know the warning signs and symptoms of high blood...
-

Hypertension: What High Blood Pressure Can Do to Your Body
High blood pressure puts you at risk for a number of other conditions. Here's what to look out for.
-

Hypertension: 15 Surprising Things That Raise Your Blood Pressure
Salt, worry, and anger aren't the only things that can raise your blood pressure. Risk factors like loneliness and birth control...
-

Hypertension: Worst Foods for High Blood Pressure
Diagnosed with high blood pressure or trying to avoid it? Stay away from these foods.
-

Foot Health: Causes of Swollen Feet and Ankles
Swollen feet and ankles may be associated with conditions like pregnancy, injury, heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease,...
-

High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Quiz: Symptoms, Signs & Causes
Take this quiz and test your IQ of high blood pressure (hypertension), the cardiovascular disease that causes most strokes and...
-

Liver Disease Quiz: Fatty Liver Disease, Cirrhosis & Symptoms
What is liver disease? Take the Liver Disease Quiz and test your knowledge about this organ and its function.
-

Heart Failure Quiz
What is heart failure? Learn about this dangerous condition, as well as who is at risk, and what to do about it.
-

Picture of Hypertension
High blood pressure, defined as a repeatedly elevated blood pressure exceeding 140 over 90 mmHg -- a systolic pressure above 140...
-

Heart Disease: Best and Worst Foods for Heart Failure
Learn which dietary changes help your heart, and which ones make it work harder.
Related Disease Conditions
-

What Are the 4 Stages of Cirrhosis of the Liver?
Stages of cirrhosis of the liver include steatosis, scarring (fibrosis), cirrhosis, and liver failure (hepatic failure).
-

Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis of the liver refers to a disease in which normal liver cells are replaced by scar tissue caused by alcohol and viral hepatitis B and C. This disease leads to abnormalities in the liver's ability to handle toxins and blood flow, causing internal bleeding, kidney failure, mental confusion, coma, body fluid accumulation, and frequent infections. Symptoms include yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue. The prognosis is good for some people with cirrhosis of the liver, and the survival can be up to 12 years; however, the life expectancy is about 6 months to 2 years for people with severe cirrhosis with major complications.
-

What Level of BUN Indicates Kidney Failure?
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is one of the parameters measured to ascertain kidney function. BUN indicates the urea nitrogen produced in the body during protein breakdown. There is no definite value of BUN that would diagnose kidney failure.
-

What Is Considered Stroke-Level High Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure readings above 180/120 mmHg are considered stroke-level and require immediate medical attention. Check out the center below for more medical references on hypertension, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related diseases, treatment, diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
-

How Long Can You Live With Cirrhosis?
The life expectancy of people with liver cirrhosis is typically predicted through the following variables.
-

High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
High blood pressure (hypertension) occurs due to the tightening or stiffness of very small arteries called arterioles. As a result, the heart pumps harder through the stiff or narrow arterioles, leading to elevated pressure inside the vessels. Hypertension is known as 'the silent killer' because it often goes unnoticed and may cause serious complications such as kidney diseases, heart diseases, heart failure, and stroke.
-

Is Turmeric OK to Take With High Blood Pressure?
Turmeric is an ancient remedy, a perennial plant in the ginger family. Turmeric may help lower blood pressure, but talk to your doctor if you take medication to make sure it doesn't interact with it.
-

Kidney Failure
Kidney failure can occur from an acute event or a chronic condition or disease. Prerenal kidney failure is caused by blood loss, dehydration, or medication. Some of the renal causes of kidney failure include sepsis, medications, rhabdomyolysis, multiple myeloma, and acute glomerulonephritis. Post-renal causes of kidney failure include bladder obstruction, prostate problems, tumors, or kidney stones. Treatment options included diet, medications, or dialysis.
-

Can Drinking Water Stop Kidney Failure?
While drinking more water can help boost kidney function, there is no evidence that suggests that it can prevent the progress of kidney failure.
-
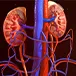
How Long Can a Person Live With Stage V Kidney Failure Without Dialysis?
Life expectancy for stage V kidney failure without dialysis varies from person to person. However, death is inevitable within a few weeks.
-

How Is Diastolic Hypertension Treated?
Diastolic hypertension, where only your diastolic blood pressure is elevated, may be treated with lifestyle changes such as weight loss, reducing your sodium intake or alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking. Medications may be prescribed in more severe cases.
-
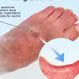
Edema
Edema is swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the tissues of the body and occurs most often in the legs, feet, ankles, or hands. Learn about the different types, causes, symptoms, and treatments to alleviate fluid retention.
-

Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Congestive heart failure (CHF) refers to a condition in which the heart loses the ability to function properly. Heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, myocarditis, and cardiomyopathies are just a few potential causes of congestive heart failure. Symptoms of congestive heart failure may include fatigue, breathlessness, palpitations, angina, and edema.
-

Which ACE Inhibitor Is the Best for Hypertension?
The best ACE inhibitors for hypertension include Trandolapril, Enalapril, and Ramipril.
-

Things to Know About High Blood Pressure Treatment
High blood pressure (hypertension) means high pressure (tension) in the arteries. Treatment for high blood pressure include lifestyle modifications (alcohol, smoking, coffee, salt, diet, exercise), drugs and medications such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta blockers, diuretics, calcium channel blockers (CCBs), alpha blockers, clonidine, minoxidil, and Exforge.
-
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia is a condition in which calcium levels in the blood are elevated. Hypercalcemia is associated with other conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, lung cancer, breast cancer, kidney failure, and elevated levels of vitamin D. Symptoms of hypercalcemia include constipation, nausea, abdominal pain, and kidney stones. Treatment depends on the cause of hypercalcemia.
-
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC)
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBS) is a liver disease in which bile building up in the organ damages bile ducts. Ultimately, this can cause liver failure. Several drugs are available to treat this disease of unknown cause, but the only ultimate cure is a liver transplant.
-

What Are the 4 Stages of Hypertension?
Learn the four stages of hypertension, which include normal, elevated blood pressure, stage I hypertension, and stage II hypertension.
-

Can High Blood Pressure (HBP) Cause Blood in Urine?
Blood in your urine is also known as hematuria. Very rarely, it is caused by high blood pressure (HBP) — also known as hypertension.
-

How Long Can You Live With Heart Failure?
What is the life expectancy of people with heart failure? Learn about survival rates, determining factors, and lifestyle changes that may help increase your life expectancy.
-

What Are the First Signs of Cirrhosis?
Here are ten early signs of liver cirrhosis, as well as other symptoms that may manifest as the condition worsens.
-

Can a Person Recover From Kidney Failure?
Recovery from kidney failure varies, depending on whether the condition is chronic or acute. Learn about renal failure treatment options.
-

Why Does Alcohol Cause Hypertension?
Alcoholic beverages are regular drinks in most parts of the world. No one knows how alcohol causes hypertension, but it may be due to the effects of alcohol endothelium, nervous system, cortisol levels or other body systems.
-
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) Treatment
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is thought to be an autoimmune disorder that involves the deterioration of the liver's small bile ducts. These ducts are crucial to transport bile to the small intestine, digesting fats, and removing wastes. Symptoms of PBC are edema, itching, elevated cholesterol, malabsorption of fat, liver cancer, gallstones, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and hypothyroidism. Treatments include ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA); colchicine (Colcrys); and immunosuppressive medications, such as corticosteroids; obeticholic acid (Ocaliva); and medications that treat PBC symptoms. For PBC that is associated with cirrhosis of the liver, liver transplantation may be indicated in extreme cases.
-

What Is High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)?
High blood pressure or hypertension is when the blood pressure readings consistently range from 140 or higher for systolic or 90 or higher for diastolic. Blood pressure readings above 180/120 mmHg are dangerously high and require immediate medical attention.
-

What Can Patients With Kidney Failure Eat?
If you have kidney failure, you need to be even more careful about your diet. Learn about what foods to avoid with kidney disease.
-

How Do You Strengthen Your Heart After Heart Failure?
You can strengthen your heart after heart failure by making recommended changes to your diet, exercising regularly, and adopting healthy habits.
-

Is There a Cure for Cirrhosis of the Liver?
Liver cirrhosis results from disease- or chemical-induced injury to the liver over a sustained period. The injury kills liver cells, and your body attempts to rebuild the damage. In the process, the existing cells are inflamed and scar tissue results, compromising the structure of the liver and hampering its function.
Treatment & Diagnosis
- High Blood Pressure FAQs
- Liver Disease FAQs
- Heart Failure FAQs
- High Blood Pressure Symptoms
- High Blood Pressure: Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Inherited High Blood Pressure in a Teenager
- Hypertension In The Elderly - Deserves More Attention
- High Blood Pressure and Exercise
- Drugs: Buying Prescription Drugs Online Safely
- Drugs: The Most Common Medication Errors
- Medication Disposal
- Can I Lift Weights with High Blood Pressure?
- Pain Relievers and High Blood Pressure
- Generic Drugs, Are They as Good as Brand-Names?
- Blood Pressure Elevation Established as Risk for Kidney Failure
Medications & Supplements
- Corticosteroids
- furosemide
- Types of High Blood Pressure Medications
- ammonium chloride
- mannitol
- Congestive Heart Failure Medications
- Why Are Diuretics Used in Heart Failure?
- Types of High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Medications
- goldenrod
- beta-blockers w/thiazide diuretics-oral
- What Conditions Are Diuretics Used For?
Prevention & Wellness

Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
REFERENCE:
FDA Prescribing Information