Because of the potential risk of toxicity from the large amount of the excipient, propylene glycol, contained in AGENERASE Oral Solution, that formulation is contraind icated in infants and children below the age of 4 years and certain other patient populations and should be used with caution in others. Consult the complete prescribing information for AGENERASE Oral Solution for full information.
Description for Agenerase Capsules
AGENERASE (amprenavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease. The chemical name of amprenavir is (3S)-tetrahydro-3-furyl N-[(1S,2R)-3-(4-amino-N-isobutylbenzenesulfonamido)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamate. Amprenavir is a single stereoisomer with the (3S)(1S,2R) configuration. It has a molecular formula of C25H35N3O6S and a molecular weight of 505.64. It has the following structural formula:
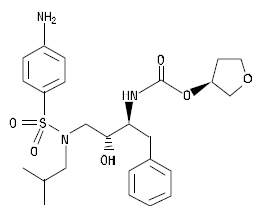 |
Amprenavir is a white to cream-colored solid with a solubility of approximately 0.04 mg/mL in water at 25°C.
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) are available for oral administration. Each 50- mg capsule contains the inactive ingredients d-alpha tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400) 246.7 mg, and propylene glycol 19 mg. The capsule shell contains the inactive ingredients d-sorbitol and sorbitans solution, gelatin, glycerin, and titanium dioxide. The soft gelatin capsules are printed with edible red ink. Each 50- mg AGENERASE Capsule contains 36.3 IU vitamin E in the form of TPGS. The total amount of vitamin E in the recommended daily adult dose of AGENERASE is 1,744 IU.
Uses for Agenerase Capsules
AGENERASE (amprenavir) is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
The following points should be considered when initiating therapy with AGENERASE:
In a study of NRTI-experienced, protease inhibitor-naive
patients, AGENERASE was found to be significantly less effective than indinavir
(see DESCRIPTION OF CLINICAL STUDIES).
Mild to moderate gastrointestinal adverse events led to discontinuation of AGENERASE
primarily during the first 12 weeks of therapy (see ADVERSE
REACTIONS).
There are no data on response to therapy with AGENERASE in protease inhibitor-experienced
patients.
Dosage for Agenerase Capsules
AGENERASE may be taken with or without food; however, a high- fat meal decreases the absorption of amprenavir and should be avoided (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Effects of Food on Oral Absorption). Adult and pediatric patients should be advised not to take supplemental vitamin E since the vitamin E content of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) exceeds the Reference Daily Intake (adults 30 IU, pediatrics approximately 10 IU) (see DESCRIPTION).
Adults: The recommended oral dose of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) for adults is 1,200 mg (twenty- four 50- mg capsules) twice daily in combination with other antiretroviral agents.
Concomitant Therapy: If AGENERASE and ritonavir are used in combination, the recommended dosage regimens are: AGENERASE 1,200 mg with ritonavir 200 mg once daily or AGENERASE 600 mg with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily.
Pediatric Patients: For adolescents (13 to 16 years), the recommended oral dose of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) is 1,200 mg (twenty- four 50- mg capsules) twice daily in combination with other antiretroviral agents. For patients between 4 and 12 years of age or for patients 13 to 16 years of age with weight of < 50 kg, the recommended oral dose of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) is 20 mg/kg twice daily or 15 mg/kg 3 times daily (to a maximum daily dose of 2,400 mg) in combination with other antiretroviral agents. The recommended dose of AGENERASE for use in combination with ritonavir has not been established in pediatric patients.
Before using AGENERASE Oral Solution, the complete prescribing information should be consulted.
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) and AGENERASE Oral Solution are not interchangeable on a milligram-per-milligram basis (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Patients with Hepatic Impairment: AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) should be used with caution in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. Patients with a Child-Pugh score ranging from 5 to 8 should receive a reduced dose of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) of 450 mg twice daily, and patients with a Child-Pugh score ranging from 9 to 12 should receive a reduced dose of AGENERASE Capsules of 300 mg twice daily (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Hepatic Insufficiency).
HOW SUPPLIED
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) , 50 mg, are oblong, opaque, off-white to cream-colored soft gelatin capsules printed with “GX CC1” on one side.
Bottles of 480 with child-resistant closures (NDC 0173-0679-00).
Store at controlled room temperature of 25°C (77°F) (see USP).
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) are manufactured by R.P. Scherer Beinheim, France for GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709. Licensed from: Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Cambridge, MA 02139. AGENERASE is a registered trademark of GlaxoSmithKline. May 2005. FDA rev date: 11/4/2005
Side Effects for Agenerase Capsules
In clinical studies, adverse events leading to amprenavir discontinuation occurred primarily during the first 12 weeks of therapy, and were mostly due to gastrointestinal events (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain/discomfort), which were mild to moderate in severity.
Skin rash occurred in 22% of patients treated with amprenavir in studies PROAB3001 and PROAB3006. Rashes were usually maculopapular and of mild or moderate intensity, some with pruritus. Rashes had a median onset of 11 days after amprenavir initiation and a median duration of 10 days. Skin rashes led to amprenavir discontinuation in approximately 3% of patients. In some patients with mild or moderate rash, amprenavir dosing was often continued without interruption; if interrupted, reintroduction of amprenavir generally did not result in rash recurrence.
Severe or life-threatening rash (Grade 3 or 4), including cases of Stevens -Johnson syndrome, occurred in approximately 1% of recipients of AGENERASE (see WARNINGS). Amprenavir therapy should be discontinued for severe or life-threatening rashes and for moderate rashes accompanied by systemic symptoms.
Table 9. Selected Clinical Adverse Events of All Grades Reported
in > 5% of Adult Patients
| Adverse Event | PROAB 3001 Therapy-Naive Patients | PROAB 3006 NRTI-Experienced Patients | ||
| AGENERASE/ Lamivudine/ Zidovudine (n = 113) |
Lamivudine/ Zidovudine (n = 109) |
AGENERASE/ NRTI (n = 245) |
Indinavir/ NRTI (n = 241) |
|
| Digestive | ||||
| Nausea | 74% | 50% | 43% | 35% |
| Vomiting | 34% | 17% | 24% | 20% |
| Diarrhea or loose stools | 39% | 35% | 60% | 41% |
| Taste disorders | 10% | 6% | 2% | 8% |
| Skin | ||||
| Rash | 27% | 6% | 20% | 15% |
| Nervous | ||||
| Paresthesia, oral/perioral | 26% | 6% | 31% | 2% |
| Paresthesia, peripheral | 10% | 4% | 14% | 10% |
| Psychiatric | ||||
| Depressive or mood disorders | 16% | 4% | 9% | 13% |
Among amprenavir-treated patients in Phase 3 studies, 2 patients developed de novo diabetes mellitus, 1 patient developed a dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), and 9 patients developed fat redistribution.
In studies PROAB3001 and PROAB3006, no increased frequency of Grade 3 or 4 AST, ALT, amylase, or bilirubin elevations was seen compared to controls.
Pediatric Patients: An adverse event profile similar to that seen in adults was seen in pediatric patients.
Concomitant Therapy with Ritonavir: Tables 10 and 11 present adverse clinical events and laboratory abnormalities observed in subjects who received AGENERASE plus ritonavir. Since the trials were small, open- label, of varying duration, and often included different patient populations, direct comparisons to the frequency of events with AGENERASE alone (see Table 9) cannot be made.
Table 10. Selected Clinical Adverse Events of All Grades
Reported in Adult Patients in Open-Label Clinical Trials of AGENERASE in Combination
With Ritonavir
| Adverse Event | AGENERASE 1,200 mg plus Ritonavir 200 mg q.d.* (n = 101) |
AGENERASE 600 mg plus Ritonavir 100 mg b.i.d.† (n = 239) |
| Nausea | 31% | 23% |
| Diarrhea/loose stools | 30% | 28% |
| Headache | 16% | 12% |
| Abdominal symptoms | 14% | 14% |
| Vomiting | 11% | 9% |
| Rash | 10% | 9% |
| Paresthesias | 9% | 11% |
| Fatigue | 7% | 14% |
| Depressive & mood disorders | 4% | 9% |
| *Data from 2 open- label studies
in treatment- naive patients also receiving abacavir/lamivudine. †Data from 3 open- label studies in treatment- naive and treatment-experienced patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy. |
||
Table 11. Grade 3/4 Laboratory Abnormalities Reported in
≥ 2% of Adult Patients in Open-Label Clinical Trials of AGENERASE in Combination
With Ritonavir
| Laboratory Abnormality (non- fasting specimens) |
AGENERASE 1,200 mg plus Ritonavir 200 mg q.d.* (n = 101) |
AGENERASE 600 mg plus Ritonavir 100 mg b.i.d.† (n = 239) |
| Hypertriglyceridemia ( > 750 mg/dL) | 8% | 13% |
| Hyperglycemia ( > 251 mg/dL) | 2% | 3% |
| AST ( > 5 x ULN) | 3% | 5% |
| ALT ( > 5 x ULN) | 4% | 4% |
| Amylase ( > 2 x ULN) | 4% | 3% |
| *Data from 2 open- label studies
in treatment- naive patients also receiving abacavir/lamivudine. †Data from 3 open- label studies in treatment- naive and treatment-experienced patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy. |
||
Drug Interactions for Agenerase Capsules
See also CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interactions.
AGENERASE is an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A4 metabolism and therefore should not be administered concurrently with medications with narrow therapeutic windows that are substrates of CYP3A4. There are other agents that may result in serious and/or life-threatening drug interactions (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS).
Table 7. Drugs That Should Not Be Coadministered With AGENERASE
| Drug Class/Drug Name | Clinical Comment |
| Antimycobacterials: Rifampin* | May lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to AGENERASE or to the class of protease inhibitors. |
| Ergot derivatives: Dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine | CONTRAINDICATED due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as acute ergot toxicity characterized by peripheral vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues. |
| GI motility agents: Cisapride | CONTRAINDICATED due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. |
| Herbal products: St. John's wort (hypericum perforatum) | May lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to AGENERASE or to the class of protease inhibitors. |
| HMG Co-reductase inhibitors: Lovastatin, simvastatin | Potential for serious reactions such as risk of myopathy including rhabdomyolysis. |
| Neuroleptic: Pimozide | CONTRAINDICATED due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. |
| Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor: Delavirdine* | May lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to delavirdine. |
| Oral contraceptives: Ethinyl estradiol/norethindrone | May lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to AGENERASE. Alternative methods of non-hormonal contraception are recommended. |
| Sedative/hypnotics: Midazolam, triazolam | CONTRAINDICATED due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as prolonged or increased sedation or respiratory depression. |
| See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY for magnitude of interaction, Tables 3 and 4. | |
Table 8. Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug
Interactions: Alteration in Dose or Regimen May Be Recommended Based on Drug
Interaction Studies or Predicted Interaction
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration of Amprenavir or Concomitant Drug | Clinical Comment | |
| HIV-Antiviral Agents | |||
| Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Efavirenz, nevirapine | ↑Amprenavir | Appropriate doses of the combinations with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. | |
| Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor: Didanosine (buffered formulation only) | ↑Amprenavir | Take AGENERASE at least 1 hour before or after the buffered formulation of didanosine. | |
| HIV proteaseinhibitors: Indinavir*, lopinavir /ritonavir,nelfinavir* | ↓Amprenavir Amprenavir's effect on other protease inhibitors is not well established. | Appropriate doses of the combinations with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. | |
| HIV protease inhibitor:Ritonavir* | ↓Amprenavir | The dose of amprenavir should be reduced when used in combination with ritonavir (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Also, see the full prescribing information for NORVIR for additional drug interaction information. | |
| HIV protease inhibitor: Saquinavir* | ↑Amprenavir Amprenavir's effect on saquinavir is not well established. | Appropriate doses of the combination with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. | |
| Other Agents | |||
| Antacids | ↓Amprenavir | Take AGENERASE at least 1 hour before or after antacids. | |
| Antiarrhythmics: Amiodarone, lidocaine (systemic), and quinidine | ↑Antiarrhythmics | Caution is warranted and therapeutic concentration monitoring is recommended for antiarrhythmics when coadministered with AGENERASE, if available. | |
| Antiarrhythmic: Bepridil | ↑Bepridil | Use with caution. Increased bepridil exposure may be associated with life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. | |
| Anticoagulant: Warfarin | Concentrations of warfarin may be affected. It is recommended that INR (international normalized ratio) be monitored. | ||
| Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin | ↓ Amprenavir | Use with caution. AGENERASE may be less effective due to decreased amprenavir plasma concentrations in patients taking these agents concomitantly. | |
| Antidepressant: Trazodone | ↑ Trazodone | Concomitant use of trazodone and AGENERASE with or without ritonavir may increase plasma concentrations of trazodone. Adverse events of nausea, dizziness, hypotension, and syncope have been observed following coadministration of trazodone and ritonavir. If trazodone is used with a CYP3A4 inhibitor such as AGENERASE, the combination should be used with caution and a lower dose of trazodone should be considered. | |
| Antifungals: Ketoconazole, itraconazole | ↑ Ketoconazole ↑ Itraconazole |
Increase monitoring for adverse events due to ketoconazole or itraconazole. Dose reduction of ketoconazole or itraconazole may be needed for patients receiving more than 400 mg ketoconazole or itraconazole per day. | |
| Antimycobacterial: Rifabutin* | ↑ Rifabutin and rifabutin metabolite | A dosage reduction of rifabutin to at least half the recommended dose is required when AGENERASE and rifabutin are coadministered.* A complete blood count should be performed weekly and as clinically indicated in order to monitor for neutropenia in patients receiving amprenavir and rifabutin. | |
| Benzodiazepines: Alprazolam, clorazepate, diazepam, flurazepam | ↑ Benzodiazepines | Clinical significance is unknown; however, a decrease in benzodiazepine dose may be needed. | |
| Calcium channel blockers: Diltiazem, felodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine, nimodipine, verapamil, amlodipine, nisoldipine, isradipine | ↑ Calcium channel blockers | Caution is warranted and clinical monitoring of patients is recommended. | |
| Corticosteroid: Dexamethasone | ↓ Amprenavir | Use with caution. AGENERASE may be less effective due to decreased amprenavir plasma concentrations in patients taking these agents concomitantly. | |
| Erectile dysfunction agent: Sildenafil | ↑ Sildenafil | Use with caution at reduced doses of 25 mg every 48 hours with increased monitoring for adverse events. | |
| HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: Atorvastatin | ↑ Atorvastatin | Use lowest possible dose of atorvastatin with careful monitoring or consider other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors such as pravastatin or fluvastatin in combination with AGENERASE. | |
| Immunosuppressants: Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, rapamycin | ↑ Immunosup-pressants | Therapeutic concentration monitoring is recommended for immunosuppressant agents when coadministered with AGENERASE. | |
| Inhaled/nasal steroid: Fluticasone | AGENERASE ↑ Fluticasone |
Concomitant use of fluticasone propionate and AGENERASE (without ritonavir) may increase plasma concentrations of fluticasone propionate. Use with caution. Consider alternatives to fluticasone propionate, particularly for long-term use. | |
| AGENERASE/ ritonavir ↑ Fluticasone |
Concomitant use of fluticasone propionate and AGENERASE/ritonavir may increase plasma concentrations of fluticasone propionate, resulting in significantly reduced serum cortisol concentrations. Coadministration of fluticasone propionate and AGENERASE/ritonavir is not recommended unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk of systemic corticosteroid side effects (see WARNINGS). | ||
| Narcotic analgesics: Methadone* | ↓ Amprenavir | AGENERASE may be less effective due to decreased amprenavir plasma concentrations in patients taking these agents concomitantly. Alternative antiretroviral therapy should be considered. | |
| ↓ Methadone | Dosage of methadone may need to be increased when coadministered with AGENERASE. | ||
| Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline, imipramine | ↑ Tricyclics | Therapeutic concentration monitoring is recommended for tricyclic antidepressants when coadministered with AGENERASE. | |
| *See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY for magnitude of interaction, Tables 3 and 4. | |||
Warnings for Agenerase Capsules
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should not be taken with AGENERASE.
Serious and/or life-threatening drug interactions could occur between amprenavir and amiodarone, lidocaine (systemic), tricyclic antidepressants, and quinidine. Concentration monitoring of these agents is recommended if these agents are used concomitantly with AGENERASE (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Rifampin should not be used in combination with amprenavir because it reduces plasma concentrations and AUC of amprenavir by about 90%.
A drug interaction study in healthy subjects has shown that ritonavir significantly increases plasma fluticasone propionate exposures, resulting in significantly decreased serum cortisol concentrations. Concomitant use of AGENERASE with ritonavir and fluticasone propionate is expected to produce the same effects. Systemic corticosteroid effects including Cushing's syndrome and adrenal suppression have been reported during postmarketing use in patients receiving ritonavir and inhaled or intranasally administered fluticasone propionate. Therefore, coadministration of fluticasone propionate and AGENERASE/ritonavir is not recommended unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk of systemic corticosteroid side effects (see PRECAUTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS).
Concomitant use of AGENERASE and St. John's wort (hypericum perforatum) or products containing St. John's wort is not recommended. Coadministration of protease inhibitors, including AGENERASE, with St. John's wort is expected to substantially decrease protease inhibitor concentrations and may result in suboptimal levels of amprenavir and lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to AGENERASE or to the class of protease inhibitors.
Concomitant use of AGENERASE with lovastatin or simvastatin is not recommended. Caution should be exercised if HIV protease inhibitors, including AGENERASE, are used concurrently with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors that are also metabolized by the CYP3A4 pathway (e.g., atorvastatin). The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, may be increased when HIV protease inhibitors, including amprenavir, are used in combination with these drugs.
Particular caution should be used when prescribing sildenafil in patients receiving amprenavir. Coadministration of AGENERASE with sildenafil is expected to substantially increase sildenafil concentrations and may result in an increase in sildenafil-associated adverse events, including hypotension, visual changes, and priapism (see PRECAUTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS and INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS, and the complete prescribing information for sildenafil).
Because of the potential toxicity from the large amount of the excipient, propylene glycol, contained in AGENERASE Oral Solution, that formulation is contraindicated in certain patient populations and should be used with caution in others. Consult the complete prescribing information for AGENERASE Oral Solution for full information.
Severe and life-threatening skin reactions, including Stevens -Johnson syndrome, have occurred in patients treated with AGENERASE (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). Acute hemolytic anemia has been reported in a patient treated with AGENERASE.
New onset diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus, and hyperglycemia have been reported during post- marketing surveillance in HIV- infected patients receiving protease inhibitor therapy. Some patients required either initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents for treatment of these events. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis has occurred. In those patients who discontinued protease inhibitor therapy, hyperglycemia persisted in some cases. Because these events have been reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made and causal relationships between protease inhibitor therapy and these events have not been established.
Precautions for Agenerase Capsules
General: AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) and AGENERASE Oral Solution are not interchangeable on a milligram-per-milligram basis(see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pediatric Patients).
Amprenavir is a sulfonamide. The potential for cross-sensitivity between drugs in the sulfonamide class and amprenavir is unknown. AGENERASE should be used with caution in patients with a known sulfonamide allergy.
AGENERASE is principally metabolized by the liver. AGENERASE, when used alone and in combination with low-dose ritonavir, has been associated with elevations of SGOT (AST) and SGPT (ALT) in some patients. Caution should be exercised when administering AGENERASE to patients with hepatic impairment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Appropriate laboratory testing should be conducted prior to initiating therapy with AGENERASE and at periodic intervals during treatment.
Formulations of AGENERASE provide high daily doses of vitamin E (see INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS, DESCRIPTION, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). The effects of long-term, high-dose vitamin E administration in humans is not well characterized and has not been specifically studied in HIV- infected individuals. High vitamin E doses may exacerbate the blood coagulation defect of vitamin K deficiency caused by anticoagulant therapy or malabsorption.
Patients with Hemophilia: There have been reports of spontaneous bleeding in patients with hemophilia A and B treated with protease inhibitors. In some patients, additional factor VIII was required. In many of the reported cases, treatment with protease inhibitors was continued or restarted. A causal relationship between protease inhibitor therapy and these episodes has not been established.
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome: Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including AGENERASE. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Fat Redistribution: Redistribution/accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and “cushingoid appearance,” have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
Lipid Elevations: Treatment with AGENERASE alo ne or in combination with ritonavir has resulted in increases in the concentration of total cholesterol and triglycerides. Triglyceride and cholesterol testing should be performed prior to initiation of therapy with AGENERASE and at periodic intervals during treatment. Lipid disorders should be managed as clinically appropriate. See PRECAUTIONS Table 8: Established and Other Potentially Significant DRUG INTERACTIONS for additional information on potential drug interactions with AGENERASE and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
Resistance/Cross-Resistance: Because the potential for HIV cross-resistance among protease inhibitors has not been fully explored, it is unknown what effect amprenavir therapy will have on the activity of subsequently administered protease inhibitors. It is also unknown what effect previous treatment with other protease inhibitors will have on the activity of amprenavir (see MICROBIOLOGY).
Information for Patients: A statement to patients and healthcare providers is included on the product's bottle label: ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with AGENERASE. A Patient Package Insert (PPI) for AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) is available for patient information. Patients treated with AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) should be cautioned against switching to AGENERASE Oral Solution because of the increased risk of adverse events from the large amount of propylene glycol in AGENERASE Oral Solution. Please see the complete prescribing information for AGENERASE Oral Solution for full information.
Patients should be informed that AGENERASE is not a cure for HIV infection and that they may continue to develop opportunistic infections and other complications associated with HIV disease. The long-term effects of AGENERASE (amprenavir) are unknown at this time.
Patients should be told that there are currently no data demonstrating that therapy with AGENERASE can reduce the risk of transmitting HIV to others through sexual contact. Patients should remain under the care of a physician while using AGENERASE. Patients should be advised to take AGENERASE every day as prescribed. AGENERASE must always be used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. Patients should not alter the dose or discontinue therapy without consulting their physician. If a dose is missed, patients should take the dose as soon as possible and then return to their normal schedule. However, if a dose is skipped, the patient should not double the next dose.
Patients should inform their doctor if they have a sulfa allergy. The potential for cross-sensitivity between drugs in the sulfonamide class and amprenavir is unknown.
AGENERASE may interact with many drugs; therefore, patients should be advised to report to their doctor the use of any other prescription or nonprescription medication or herbal products, particularly St. John's wort.
Patients taking antacids (or the buffered formulation of didanosine) should take AGENERASE at least 1 hour before or after antacid (or the buffered formulation of didanosine) use.
Patients receiving sildenafil should be advised that they may be at an increased risk of sildenafil-associated adverse events, including hypotension, visual changes, and priapism, and should promptly report any symptoms to their doctor.
Patients taking AGENERASE should be instructed not to use hormonal contraceptives because some birth control pills (those containing ethinyl estradiol/norethindrone) have been found to decrease the concentration of amprenavir. Therefore, patients receiving hormonal contraceptives should be instructed to use alternate contraceptive measures during therapy with AGENERASE.
High- fat meals may decrease the absorption of AGENERASE and should be avoided. AGENERASE may be taken with meals of normal fat content.
Patients should be informed that redistributio n or accumulation of body fat may occur in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy and that the cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known at this time.
Adult and pediatric patients should be advised not to take supplemental vitamin E since the vitamin E content of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) and Oral Solution exceeds the Reference Daily Intake (adults 30 IU, pediatrics approximately 10 IU).
Laboratory Tests: The combination of AGENERASE and low-dose ritonavir has been associated with elevations of cholesterol and triglycerides, SGOT (AST), and SGPT (ALT) in some patients. Appropriate laboratory testing should be considered prior to initiating combination therapy with AGENERASE and ritonavir and at periodic intervals or if any clinical signs or symptoms of hyperlipidemia or elevated liver function tests occur during therapy. For comprehensive information concerning laboratory test alterations associated with ritonavir, physicians should refer to the complete prescribing information for NORVIR® (ritonavir).
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis: Amprenavir was evaluated for carcinogenic potential by oral gavage administration to mice and rats for up to 104 weeks. Daily doses of 50, 275 to 300, and 500 to 600 mg/kg/day were administered to mice and doses of 50, 190, and 750 mg/kg/day were administered to rats. Results showed an increase in the incidence of benign hepatocellular adenomas and an increase in the combined incidence of hepatocellular adenomas plus carcinoma in males of both species at the highest doses tested. Female mice and rats were not affected. These observations were made at systemic exposures equivalent to approximately 2 times (mice) and 4 times (rats) the human exposure (based on AUC0-24 hr measurement) at the recommended dose of 1,200 mg twice daily. Administration of amprenavir did not cause a statistically significant increase in the incidence of any other benign or malignant neoplasm in mice or rats. It is not known how predictive the results of rodent carcinogenicity studies may be for humans. However, amprenavir was not mutagenic or genotoxic in a battery of in vitro and in vivo assays including bacterial reverse mutation (Ames), mouse lymphoma, rat micronucleus, and chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes.
Fertility: The effects of amprenavir on fertility and general reproductive performance were investigated in male rats (treated for 28 days before mating at doses producing up to twice the expected clinical exposure based on AUC comparisons) and female rats (treated for 15 days before mating through day 17 of gestation at doses producing up to 2 times the expected clinical exposure). Amprenavir did not impair mating or fertility of male or female rats and did not affect the development and maturation of sperm from treated rats. The reproductive performance of the F1 generation born to female rats given amprenavir was not different from control animals.
Pregnancy and Reproduction: Pregnancy Category C. Embryo/fetal development studies were conducted in rats (dosed from 15 days before pairing to day 17 of gestation) and rabbits (dosed from day 8 to day 20 of gestation). In pregnant rabbits, amprenavir administration was associated with abortions and an increased incidence of 3 minor skeletal variations resulting from deficient ossification of the femur, humerus trochlea, and humerus. Systemic exposure at the highest tested dose was approximately one twentieth of the exposure seen at the recommended human dose. In rat fetuses, thymic elongation and incomplete ossification of bones were attributed to amprenavir. Both findings were seen at systemic exposures that were one half of that associated with the recommended human dose.
Pre- and post- natal developmental studies were performed in rats dosed from day 7 of gestation to day 22 of lactation. Reduced body weights (10% to 20%) were observed in the offspring. The systemic exposure associated with this finding was approximately twice the exposure in humans following administration of the recommended human dose. The subsequent development of these offspring, including fertility and reproductive performance, was not affected by the maternal administration of amprenavir.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. AGENERASE should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
AGENERASE Oral Solution is contraindicated during pregnancy due to the potential risk of toxicity to the fetus from the high propylene glycol content.
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry: To monitor maternal- fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to AGENERASE, an Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry has been established. Physicians are encouraged to register patients by calling 1-800-258-4263.
Nursing Mothers: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV. Although it is not known if amprenavir is excreted in human milk, amprenavir is secreted into the milk of lactating rats. Because of both the potential for HIV transmission and the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers should be instructed not to breastfeed if they are receiving AGENERASE.
Pediatric Use: Two hundred fifty-one patients aged 4 and above have received amprenavir as single or multiple doses in studies. An adverse event profile similar to that seen in adults was seen in pediatric patients.
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) have not been evaluated in pediatric patients below the age of 4 years (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
AGENERASE Oral Solution is contraindicated in infants and children below the age of 4 years due to the potential risk of toxicity from the large amount of the excipient, propylene glycol. Please see the complete prescribing information for AGENERASE Oral Solution for full information.
Geriatric Use: Clinical studies of AGENERASE did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger adults. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Overdose Information for Agenerase Capsules
There is no known antidote for AGENERASE. It is not known whether amprenavir can be removed by peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis. If overdosage occurs, the patient should be monitored for evidence of toxicity and standard supportive treatment applied as necessary.
Contraindications for Agenerase Capsules
Coadministration of AGENERASE is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A4 for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events. These drugs are listed in Table 6.
Table 6. Drugs That Are Contraindicated With AGENERASE
| Drug Class | Drugs Within Class That Are CONTRAINDICATED with AGENERASE |
| Ergot derivatives | Dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine |
| GI motility agent | Cisapride |
| Neuroleptic | Pimozide |
| Sedatives/hypnotics | Midazolam, triazolam |
If AGENERASE is coadministered with ritonavir, the antiarrhythmic agents flecainide and propafenone are also contraindicated.
Because of the potential toxicity from the large amount of the excipient, propylene glycol, contained in AGENERASE Oral Solution, that formulation is contraindicated in certain patient populations and should be used with caution in others. Consult the complete prescribing information for AGENERASE Oral Solution for full information.
AGENERASE is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated clinically significant hypersensitivity to any of the components of this product.
Clinical Pharmacology for Agenerase Capsules
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action: Amprenavir is an inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. Amprenavir binds to the active site of HIV-1 protease and thereby prevents the processing of viral gag and gag-pol polyprotein precursors, resulting in the formation of immature non- infectious viral particles.
Antiviral Activity in Vitro: The in vitro antiviral activity of amprenavir was evaluated against HIV-1 IIIB in both acutely and chronically infected lymphoblastic cell lines (MT-4, CEM-CCRF, H9) and in peripheral blood lymphocytes. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of amprenavir ranged from 0.012 to 0.08 μM in acutely infected cells and was 0.41 μM in chronically infected cells (1 μM = 0.50 mcg/mL). Amprenavir exhibited synergistic anti-HIV-1 activity incombination with abacavir, zidovudine, didanosine, or saquinavir, and additive anti-HIV-1 activity in combination with indinavir, nelfinavir, and ritonavir in vitro. These drug combinations have not been adequately studied in humans. The relationship between in vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of amprenavir and the inhibition of HIV-1 replication in humans has not been defined.
Resistance: HIV-1 isolates with a decreased susceptibility to amprenavir have been selected in vitro and obtained from patients treated with amprenavir. Genotypic analysis of isolates from amprenavir-treated patients showed mutations in the HIV-1 protease gene resulting in amino acid substitutions primarily at positions V32I, M46I/L, I47V, I50V, I54L/M, and I84V as well as mutations in the p7/p1 and p1/p6 gag cleavage sites. Phenotypic analysis of HIV-1 isolates from 21 nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor- (NRTI-) experienced, protease inhibitor- naive patients treated with amprenavir in combination with NRTIs for 16 to 48 weeks identified isolates from 15 patients who exhibited a 4- to 17-fold decrease in susceptibility to amprenavir in vitro compared to wild-type virus. Clinical isolates that exhibited a decrease in amprenavir susceptibility harbored one or more amprenavir-associated mutations. The clinical relevance of the genotypic and phenotypic changes associated with amprenavir therapy is under evaluation.
Cross-Resistance: Varying degrees ofHIV-1 cross-resistance among protease inhibitors have been observed. Five of 15 amprenavir-resistant isolates exhibited 4- to 8-fold decrease in susceptibility to ritonavir. However, amprenavir-resistant isolates were susceptible to either indinavir or saquinavir.
Pharmacokinetics in Adults: The pharmacokinetic properties of amprenavir have been studied in asymptomatic, HIV- infected adult patients after administration of single oral doses of 150 to 1,200 mg and multiple oral doses of 300 to 1,200 mg twice daily.
Absorption and Bioavailability: Amprenavir was rapidly absorbed after oral administration in HIV-1-infected patients with a time to peak concentration (Tmax) typically between 1 and 2 hours after a single oral dose. The absolute oral bioavailability of amprenavir in humans has not been established.
Increases in the area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (AUC) after single oral doses between 150 and 1,200 mg were slightly greater than dose proportional. Increases in AUC were dose proportional after 3 weeks of dosing with doses from 300 to 1,200 mg twice daily. The pharmacokinetic parameters after administration of amprenavir 1,200 mg twice daily for 3 weeks to HIV- infected subjects are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Average (%CV) Pharmacokinetic Parameters After 1,200
mg Twice Daily of Amprenavir Capsules (n = 54)
| Cmax (mcg/mL) |
Tmax (hours) |
AUC0-12 (mcg•hr/mL) |
Cavg (mcg/mL) |
Cmin (mcg/mL) |
CL/F (mL/min/kg) |
| 7.66 | 1.0 | 17.7 | 1.48 | 0.32 | 19.5 |
| (54%) | (42%) | (47%) | (47%) | (77%) | (46%) |
The relative bioavailability of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) and Oral Solution was assessed in healthy adults. AGENERASE Oral Solution was 14% less bioavailable compared to the capsules.
Effects of Food on Oral Absorption: The relative bioava ilability of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) was assessed in the fasting and fed states in healthy volunteers (standardized high- fat meal: 967 kcal, 67 grams fat, 33 grams protein, 58 grams carbohydrate). Administration of a single 1,200- mg dose of amprenavir in the fed state compared to the fasted state was associated with changes in Cmax (fed: 6.18 ± 2.92 mcg/mL, fasted: 9.72 ± 2.75 mcg/mL), Tmax (fed: 1.51 ± 0.68, fasted: 1.05 ± 0.63), and AUC0-∞ (fed: 22.06 ± 11.6 mcg•hr/mL, fasted: 28.05 ± 10.1 mcg•hr/mL). AGENERASE may be taken with or without food, but should not be taken with a high- fat meal (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Distribution: The apparent volume of distribution (Vz/F) is approximately 430 L in healthy adult subjects. In vitro binding is approximately 90% to plasma proteins. The high affinity binding protein for amprenavir is alpha1-acid glycoprotein (AAG). The partitioning of amprenavir into erythrocytes is low, but increases as amprenavir concentrations increase, reflecting the higher amount of unbound drug at higher concentrations.
Metabolism: Amprenavir is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzyme system. The 2 major metabolites result from oxidation of the tetrahydrofuran and aniline moieties. Glucuronide conjugates of oxidized metabolites have been identified as minor metabolites in urine and feces.
Elimination: Excretion of unchanged amprenavir in urine and feces is minimal. Approximately 14% and 75% of an administered single dose of 14C-amprenavir can be accounted for as radiocarbon in urine and feces, respectively. Two metabolites accounted for > 90% of the radiocarbon in fecal samples. The plasma elimination half- life of amprenavir ranged from 7.1 to 10.6 hours.
Special Populations: Hepatic Insufficiency: AGENERASE has been studied in adult patients with impaired hepatic function using a single 600- mg oral dose. The AUC0-∞ was significantly greater in patients with moderate cirrhosis (25.76 ± 14.68 mcg•hr/mL) compared with healthy volunteers (12.00 ± 4.38 mcg•hr/mL). The AUC0-∞ and Cmax were significantly greater in patients with severe cirrhosis (AUC0-∞: 38.66 ± 16.08 mcg•hr/mL; Cmax: 9.43 ± 2.61 mcg/mL) compared with healthy volunteers (AUC0-∞: 12.00 ± 4.38 mcg•hr/mL; Cmax: 4.90 ± 1.39 mcg/mL). Patients with impaired hepatic function require dosage adjustment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Renal Insufficiency: The impact of renal impairment on amprenavir elimination in adult patients has not been studied. The renal elimination of unchanged amprenavir represents < 3% of the administered dose.
Pediatric Patients: The pharmacokinetics of amprenavir have been studied after either single or repeat doses of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) or Oral Solution in 84 pediatric patients. Twenty HIV-1- infected children ranging in age from 4 to 12 years received single doses from 5 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg using 25- mg or 150- mg capsules. The Cmax of amprenavir increased less than proportionally with dose. The AUC0-∞ increased proportionally at doses between 5 and 20 mg/kg. Amprenavir is 14% less bioava ilable from the liquid formulation than from the capsules; therefore AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) and AGENERASE Oral Solution are not interchangeable on a milligram-per-milligram basis.
AGENERASE Oral Solution is contraindicated in infants and children below the age of 4 years due to the potential risk of toxicity from the large amount of the excipient, propylene glycol. Please see the complete prescribing information for AGENERASE Oral Solution for full information.
Table 2. Average (%CV) Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Children
Ages 4 to 12 Years Receiving 20 mg/kg Twice Daily or 15 mg/kg Three Times Daily
of AGENERASE Oral Solution
| Dose | n | Cmax (mcg/mL) |
Tmax (hours) |
AUCss* (mcg•hr/mL) |
Cavg (mcg/mL) |
Cmin (mcg/mL) |
CL/F (mL/min/kg) |
| 20 mg/kg b.i.d. | 20 | 6.77 (51%) |
1.1 (21%) |
15.46 (59%) |
1.29 (59%) |
0.24 (98%) |
29 (58%) |
| 15 mg/kg t.i.d. | 17 | 3.99 (37%) |
1.4 (90%) |
8.73 (36%) |
1.09 (36%) |
0.27 (95%) |
32 (34%) |
| *AUC is 0 to 12 hours for b.i.d. and 0 to 8 hours for t.i.d., therefore the Cavg is a better comparison of the exposures. | |||||||
Geriatric Patients: The pharmacokinetics of amprenavir have not been studied in patients over 65 years of age.
Gender: The pharmacokinetics of amprenavir do not differ between males and females.
Race: The pharmacokinetics of amprenavir do not differ between blacks and non-blacks.
Drug Interactions: See also CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS.
Amprenavir is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Amprenavir inhibits CYP3A4. Caution should be used whe n coadministering medications that are substrates, inhibitors, or inducers of CYP3A4, or potentially toxic medications that are metabolized by CYP3A4. Amprenavir does not inhibit CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2E1, or uridine glucuronosyltransferase (UDPGT).
Drug interaction studies were performed with amprenavir capsules and other drugs likely to be coadministered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions. The effects of coadministration of amprenavir on the AUC, Cmax, and Cmin are summarized in Table 3 (effect of other drugs on amprenavir) and Table 4 (effect of amprenavir on other drugs). For information regarding clinical recommendations, see PRECAUTIONS.
Table 3. Drug Interactions: Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Amprenavir in the Presence of the Coadministered Drug
| Co-administered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug | Dose of AGENERASE | n | % Change in Amprenavir Pharmacokinetic Parameters* (90% CI) | ||
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| Abacavir | 300 mg b.i.d. for 3 weeks | 900 mg b.i.d. for 3 weeks | 4 | ↑47 (↓15 to ↑154) |
↑29 (↓18 to ↑103) |
↑27 (↓46 to ↑197) |
| Clarithromycin | 500 mg b.i.d. for 4 days | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 4 days | 12 | ↑15 (↑1 to ↑31) |
↑18 (↑8 to ↑29) |
↑39 (↑31 to ↑47) |
| Delavirdine | 600 mg b.i.d. for 10 days | 600 mg b.i.d. for 10 days | 9 | ↑40‡ | ↑130‡ | ↑125‡ |
| Ethinyl estradiol/Norethindrone | 0.035 mg/1 mg for 1 cycle | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 28 days | 10 | ⇔ (↓20 to ↑3) |
↓22 (↓35 to ↓8) |
↓20 (↓41 to ↑8) |
| Indinavir | 800 mg t.i.d. for 2 weeks (fasted) | 750 or 800 mg t.i.d. for 2 weeks (fasted) | 9 | ↑18 (↓13 to ↑58) |
↑33 (↑2 to ↑73) |
↑25 (↓27 to ↑116) |
| Ketoconazole | 400 mg single dose | 1,200 mg single dose | 12 | ↓16 (↓25 to ↓6) |
↑31 (↑20 to ↑42) |
NA |
| Lamivudine | 150 mg single dose | 600 mg single dose | 11 | ⇔ (↓17 to ↑9) |
⇔ (↓15 to ↑14) |
NA |
| Nelfinavir | 750 mg t.i.d. for 2 weeks(fed) | 750 or 800 mg t.i.d. for 2 weeks(fed) | 6 | ↓14 (↓38 to ↑20) |
⇔ (↓19 to ↑47) |
↑189 (↑52 to ↑448) |
| Rifabutin | 300 mg q.d. for 10 days | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 10 days | 5 | ⇔ (↓21 to ↑10) |
↓15 (↓28 to 0) |
↓15 (↓38 to ↑17) |
| Rifampin | 300 mg q.d. for 4 days | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 4 days | 11 | ↓70 (↓76 to ↓62) |
↓82 (↓84 to ↓78) |
↓92 (↓95 to ↓89) |
| Ritonavir | 100 mg b.i.d. for 2 to 4 weeks | 600 mg b.i.d. | 18 | ↓30† (↓44 to ↓14) |
↑64† (↑37 to ↑97) |
↑508† (↑394 to ↑649) |
| Ritonavir | 200 mg q.d. for 2 to 4 weeks | 1,200 mg q.d. | 12 | ⇔† (↓17 to ↑30) |
↑62† (↑35 to ↑94) |
↑319† (↑190 to ↑508) |
| Saquinavir | 800 mg t.i.d. for 2 weeks(fed) | 750 or 800 mg t.i.d. for 2 weeks(fed) | 7 | ↓37 (↓54 to ↓14) |
↓32 (↓49 to ↓9) |
↓14 (↓52 to ↑54) |
| Zidovudine | 300 mg single dose | 600 mg single dose | 12 | ⇔ (↓5 to ↑24) |
↑13 (↓2 to ↑31) |
NA |
| *Based on total-drug concentrations.
†Compared to amprenavir 1,200 mg b.i.d. in the same patients. ‡Median percent change; confidence interval not reported. ↑ = Increase; ↓ = Decrease; ⇔ = No change (↑ or ↓ < 10%); NA = Cmin not calculated for single-dose study. |
||||||
Table 4. Drug Interactions: Pharmacokinetic Parameters for
Coadministered Drug in the Presence of Amprenavir
| Co-administered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug | Dose of AGENERASE | n | % Change in Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Coadministered Drug (90% CI) | ||
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| Clarithromycin | 500 mg b.i.d. for 4 days | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 4 days | 12 | ↓10 (↓24 to ↑7) |
⇔ (↓17 to ↑11) |
⇔ (↓13 to ↑20) |
| Delavirdine | 600 mg b.i.d. for 10 days | 600 mg b.i.d. for 10 days | 9 | ↓47* | ↓61* | ↓88* |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.035 mg for 1 cycle | 1,200 mg b.i.d for 28 days | 10 | ⇔ (↓25 to ↑15) |
⇔ (↓14 to ↑38) |
↑32 (↓3 to ↑79) |
| Norethindrone | 1.0 mg for 1 cycle | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 28 days | 10 | ⇔ (↓20 to ↑18) |
↑18 (↑1 to ↑38) |
↑45 (↑13 to ↑88) |
| Ketoconazole | 400 mg single dose | 1,200 mg single dose | 12 | ↑19 (↑8 to ↑33) |
↑44 (↑31 to ↑59) |
NA |
| Lamivudine | 150 mg single dose | 600 mg single dose | 11 | ⇔ (↓17 to ↑3) |
⇔ (↓11 to 0) |
NA |
| Methadone | 44 to 100 mg q.d. for > 30 days | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 10 days | 16 | R-Methadone (active) | ||
| ↓25 (↓32 to ↓18) |
↓13 (↓21 to ↓5) |
↓21 (↓32 to ↓9) |
||||
| S-Methadone (inactive) | ||||||
| ↓48 (↓55 to ↓40) |
↓40 (↓46 to ↓32) |
↓53 (↓60 to ↓43) |
||||
| Rifabutin | 300 mg q.d. for 10 days | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 10 days | 5 | ↑119 (↑82 to ↑164) |
↑193 (↑156 to ↑235) |
↑271 (↑171 to ↑409) |
| Rifampin | 300 mg q.d. for 4 days | 1,200 mg b.i.d. for 4 days | 11 | ⇔ (↓13 to ↑12) |
⇔ (↓10 to ↑13) |
ND |
| Zidovudine | 300 mg single dose | 600 mg single dose | 12 | ↑40 (↑14 to ↑71) |
↑31 (↑19 to ↑45) |
NA |
| *Median percent change; confidence
interval not reported. ↑= Increase; ↓ = Decrease; ⇔ = No change (↑ or ↓ < 10%); NA = Cmin not calculated for single-dose study; ND = Interaction cannot be determined as Cmin was below the lower limit of quantitation. |
||||||
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs): There was no effect of amprena vir on abacavir in subjects receiving both agents based on historical data.
HIV Protease Inhibitors: The effect of amprenavir on total drug concentrations of other HIV protease inhibitors in subjects receiving both agents was evaluated using comparisons to historical data. Indinavir steady-state Cmax, AUC, and Cmin were decreased by 22%, 38%, and 27%, respectively, by concomitant amprenavir. Similar decreases in Cmax and AUC were seen after the first dose. Saquinavir steady-state Cmax, AUC, and Cmin were increased 21%, decreased 19%, and decreased 48%, respectively, by concomitant amprenavir. Nelfinavir steady-state Cmax, AUC, and Cmin were increased by 12%, 15%, and 14%, respectively, by concomitant amprenavir.
Methadone: Coadministration of amprenavir and methadone can decrease plasma levels of methadone. Coadministration of amprenavir and methadone as compared to a non- matched historical control group resulted in a 30%, 27%, and 25% decrease in serum amprenavir AUC, Cmax, and Cmin , respectively.
For information regarding clinical recommendations, see PRECAUTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS.
Description of Clinical Studies
Therapy-Naive Adults: PROAB3001, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study, compared treatment with AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) (1,200 mg twice daily) plus lamivudine (150 mg twice daily) plus zidovudine (300 mg twice daily) versus lamivudine (150 mg twice daily) plus zidovudine (300 mg twice daily) in 232 patients. Through 24 weeks of therapy, 53% of patients assigned to AGENERASE/zidovudine/lamivudine achieved HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL. Through week 48, the antiviral response was 41%. Through 24 weeks of therapy, 11% of patients assigned to zidovudine/lamivudine achieved HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL. Antiviral response beyond week 24 is not interpretable because the majority of patients discontinued or changed their antiretroviral therapy.
NRTI-Experienced Adults: PROAB3006, a randomized, open-label multicenter study, compared treatment with AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) (1,200 mg twice daily) plus NRTIs versus indinavir (800 mg every 8 hours) plus NRTIs in 504 NRTI-experienced, protease inhibitor- naive patients, median age 37 years (range 20 to 71 years), 72% Caucasian, 80% male, with a median CD4 cell count of 404 cells/mm³ (range 9 to 1,706 cells/mm³) and a median plasma HIV-1 RNA level of 3.93 log10 copies/mL (range 2.60 to 7.01 log10 copies/mL) at baseline. Through 48 weeks of therapy, the median CD4 cell count increase from baseline in the amprenavir group was significantly lower than in the indinavir group, 97 cells/mm³ versus 144 cells/mm³, respectively. There was also a significant difference in the proportions of patients with plasma HIV-1 RNA levels < 400 copies/mL through 48 weeks (see Figure 1 and Table 5).
Figure 1. Virologic Response Through Week 48, PROAB3006*,†
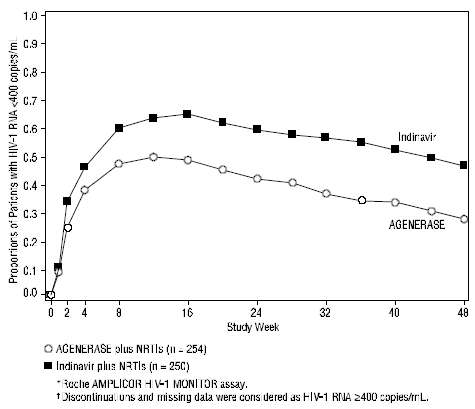 |
HIV-1 RNA status and reasons for discontinuation of randomized treatment at 48 weeks are summarized (Table 5).
Table 5. Outcomes of Randomized Treatment Through Week 48
(PROAB3006)
| Outcome | AGENERASE (n = 254) |
Indinavir (n = 250) |
| HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL* | 30% | 49% |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥ 400 copies/mL†,‡ | 38% | 26% |
| Discontinued due to adverse events*,‡ | 16% | 12% |
| Discontinued due to other reasons‡, § | 16% | 13% |
| *Corresponds to rates at Week
48 in Figure 1. †Virological failures at or before Week 48. ‡Considered to be treatment failure in the analysis. §Includes discontinuations due to consent withdrawn, loss to follow- up, protocol violations, non-compliance, pregnancy, never treated, and other reasons. |
||
Patient Information for Agenerase Capsules
AGENERASE®
(amprenavir) Capsules
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should not be taken with AGENERASE. Read the section: “What important information should I know about taking AGENERASE with other medicines?”
Read this information carefully before you start taking AGENERASE (ah-GEN-er-ase). Read the information each time you get more medicine. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talks with your healthcare provider when you start this medicine and at checkups.
What is the most important information I should know about AGENERASE?
AGENERASE can cause serious and life-threatening side effects if you take it with certain other medicines. For information about these medicines, see the section “What important information should I know about taking AGENERASE with other medicines?”
What is AGENERASE?
AGENERASE is a medicine you take by mouth to treat HIV infection. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome.) AGENERASE belongs to a class of anti-HIV medicines called protease inhibitors.
AGENERASE is used only in combination with other anti-HIV medicines. When used in combination therapy, AGENERASE may help lower the amount of HIV found in your blood, raise CD4 (T) cell counts, and keep your immune system as healthy as possible, so it can help fight infection. However, AGENERASE does not have these effects in all patients.
AGENERASE does not cure HIV infection or AIDS. We do not know if AGENERASE will help you live longer or have fewer of the medical problems (opportunistic infections) that people get with HIV or AIDS. Therefore, be sure to see your healthcare provider regularly. The long-term effects of AGENERASE are not known.
AGENERASE has not been shown to reduce the risk of passing HIV to others through sexual contact or blood. Continue to practice safe sex and do not use or share dirty needles.
Children from 4 to 12 years of age can take AGENERASE. Your healthcare provider will tell you if the oral solution (liquid) or capsule is best for your child. Your child's healthcare provider will decide the right dose based on your child's weight and age.
AGENERASE has not been studied in people who have taken anti-HIV medicine combinations before that included a protease inhibitor.
Who should not take AGENERASE?
Do not take AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) if
- you are taking certain medicines. Read the section entitled “What important information should I know about taking AGENERASE with other medicines?”
- you have had an allergic reaction to AGENERASE or any of its ingredients.
Children younger than age 4 should not take AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) or AGENERASE Oral Solution.
Tell your healthcare provider if
- you are pregnant, AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) may not be right for you.
- you are breastfeeding. Your baby can get HIV from your milk. Also, AGENERASE can pass through your milk and harm the baby.
Tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions . AGENERASE may not be right for you, or you may need a dosage change in AGENERASE. Be sure to tell your healthcare provider if you
- have liver or kidney problems.
- have hemophilia.
- are allergic to sulfa medicines. AGENERASE may cause problems for you.
What important information should I know about taking AGENERASE with other medicines? Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and supplements. Some of them may cause dangerous and life-threatening side effects if you take them during treatment with AGENERASE. For other medicines, you may need to change your dose to avoid problems.
- If you are on methadone therapy, talk to your doctor about possible interactions.
Do NOT take the following medicines* with AGENERASE. You could develop serious or life-threatening problems.
- HALCION® (triazolam; used for insomnia)
- CAFERGOT® and other ergot medicines (used for migraine headaches)
- PROPULSID® (cisapride, used for certain stomach problems)
- VERSED® (midazolam; used for sedation)
- ORAP® (pimozide; used for Tourette's disorder)
You will need to be monitored with regular blood tests if you take the following medicines* with AGENERASE.
- CORDARONE® (amiodarone; used for certain abnormal heart rhythms)
- Quinidine (used for certain abnormal heart rhythms)
- COUMADIN® (warfarin; used for blood thinning)
- Lidocaine (used for certain abnormal heart rhythms)
- ELAVIL® (amitriptyline), TOFRANIL® (imipramine) (tricyclic antidepressants)
- SANDIMMUNE® or NEORAL® (cyclosporine), PROGRAF® (tacrolimus), RAPAMUNE® (rapamycin or sirolimus) (immunosuppressants)
You will need to have your dose adjusted if you take the following medicines* with AGENERASE.
- MYCOBUTIN® (rifabutin; used to prevent Mycobacterium avium complex [MAC])
- NORVIR® (ritonavir; used to treat HIV infection)
- VIAGRA® (sildenafil; used for impotence). You may get increased side effects such as low blood pressure, changes in vision, or erections that last more than 4 hours. If an erection lasts more than 4 hours, get medical help right away.
The following medicines* may cause serious problems if you take them with AGENERASE. Tell your healthcare provider if you are taking any of these medicines.
- RESCRIPTOR® (delavirdine; used for HIV) and certain other anti-HIV medicines
- St. John's wort (hypericum perforatum) or products containing St. John's wort
- VASCOR® (bepridil; used for chronic stable angina)
- RIFADIN® , RIFAMATE® , RIFATER® , or RIMACTANE® (rifampin, used for tuberculosis)
- MEVACOR® (lovastatin), ZOCOR® (simvastatin), and LIPITOR® (atorvastatin) (cholesterol- lowering medicines)
- Phenobarbital (used for seizures)
- TEGRETOL® , CARBATROL® (carbamazepine; used for seizures and trigeminal neuralgia)
- DILANTIN® (phenytoin; used for seizures)
- DECADRON® (dexamethasone, used to reduce inflammation)
- Hormonal contraceptives (e.g., birth control pills) because the effectiveness of one or both drugs may be decreased. Talk to your doctor about choosing a different typ e of contraceptive.
- Vitamin E. AGENERASE contains high daily doses of vitamin E that could interfere with medicines that help you stop bleeding.
This list is not complete. Be sure to tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take.
How should I take AGENERASE?
- Take AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) every day exactly as your healthcare provider has prescribed it, so it will be as effective as possible. Your healthcare provider will decide the right dose for you.
- If you miss a dose by more than 4 hours , wait and take the next dose at the regular time.However, if you miss a dose by fewer than 4 hours, take your missed dose right away. Then take your next dose at the regular time.
- Do not take more or less than your prescribed dose of AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) at any one time. Do not change your dose or stop taking AGENERASE without talking with your healthcareprovider.
- You can take AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) with or without food. However, do not take AGENERASE with a high-fat meal. This could reduce the effectiveness of the medicine.
- If you take AGENERASE with the buffered form of VIDEX® (didanosine, ddI), take them at least 1 hour apart.
- If you take AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) with antacids, take them at least 1 hour apart.
- When your supply of AGENERASE or other anti-HIV medicine starts to run low, arrange to get more from your healthcare provider or pharmacy. The amount of virus in your blood may increase if one or more of the drugs are stopped, even for a short time.
- Stay under the care of a healthcare provider while using AGENERASE.
What should I avoid while taking AGENERASE? Do not
- switch from AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) to AGENERASE Oral Solution without talking to your healthcare provider. You may get increased side effects if you switch.
- take vitamin E while taking AGENERASE. It contains large amounts of vitamin E.
- take AGENERASE with a high- fat meal. It could reduce the effectiveness of the medicine.
What are the possible side effects of AGENERASE?
AGENERASE can cause a severe or life-threatening rash. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have a rash. Your healthcare provider will advise you whether your symptoms can be managed on therapy or whether AGENERASE should be stopped.
Common side effects of AGENERASE are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and a tingling feeling, especially around the mouth, and change in taste. These are usually mild to moderate. Depression and mood problems have also been reported in patients taking AGENERASE.
Changes in body fat have been seen in some patients taking antiretroviral therapy. These changes may include increased amount of fat in the upper back and neck (“buffalo hump”), breast, and around the trunk. Loss of fat from the legs, arms, and face may also happen. The cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known at this time.
Other side effects include high blood sugar or diabetes, diabetes complications, high cholesterol, or high triglycerides.
This list of side effects is not complete. Your healthcare provider or pharmacist can give you a more complete list of possible side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider about any concerns about the way you are feeling while you are taking AGENERASE.
How should I store AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) ?
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) should be stored at room temperature and should no t be refrigerated.
General advice about prescription medicines
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use AGENERASE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give AGENERASE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about AGENERASE. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about AGENERASE that is written for health professionals.
From 
Resources for Staying Well

Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.