Semantic SEO has marked a significant shift in how we approach search engine optimization. Gone are the days when keywords alone dictate the fate of web content’s visibility.
Today, semantic SEO has transformed the game, offering a more nuanced, context-driven, user-centric approach to ranking higher on search engines.
From the importance and benefits of semantic SEO, to the key elements of this SEO strategy, to the differences between traditional and semantic SEO practices, this article will equip you with the knowledge and tools to elevate your site’s rankings.
What Is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO refers to a strategy in search engine optimization that focuses on optimizing content by considering the intent and contextual meaning behind user search queries, not just keywords.
Rather than solely targeting specific keywords or phrases, semantic SEO aims to understand and address the broader topic and context of the content.
Key aspects of semantic SEO include:
👉 Semantic Keyword Research. This goes beyond traditional keyword research to identify not just direct keywords, but also related terms, synonyms and topics that offer a broader understanding of a subject.
👉 User Intent. Understanding what users are looking for when they enter specific queries helps you tailor your content to answer their questions, solve their problems or provide the information they seek.
👉 Topic Maps. These are comprehensive representations of content that cover a subject in a structured way. Topic maps include various sub-topics and connected concepts, which help make sure your content fully addresses a topic.
👉 Relevant Content. Semantic SEO emphasizes creating content that is not only keyword-rich but also contextually relevant and enriched with related concepts, synonyms, and varied linguistic structures. Topic clusters can help search engines understand the content more holistically.
👉 Entities and Context. An entity is anything that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable – this could be people, places, concepts or objects that are relevant to your content. Context refers to the environment in which these entities are discussed, which helps search engines grasp the meaning behind content more accurately.
👉 Structured Data and Schema Markup. Help search engines understand the context of your content by using schema markup to highlight entities, relationships and content types.
👉 Natural Language Processing (NLP). Use NLP tools to analyze your content’s language and ensure that it aligns naturally with how people speak and search.
👉 User Experience and Engagement. A key part of semantic SEO is creating a positive user experience, as search engines favor content that engages users effectively.
Incorporating these elements into your SEO strategy ensures a holistic approach that better aligns with how search engines operate. By focusing on semantics, entities, context and user intent, your content becomes not just discoverable, but also meaningful and valuable to your audience.
These are the main advantages of semantic SEO:
✅ Improved User Experience: By prioritizing content relevance and comprehensiveness, semantic SEO enhances user satisfaction.
✅ Resilience to Algorithm Updates: Semantic SEO is more aligned with the continuous updates in search engine algorithms, making it a more robust strategy.
✅ Broader Content Reach: Semantic SEO can capture a wider range of search queries, as it accounts for synonyms, related terms and varied user intents.
Semantic SEO vs Traditional SEO
The evolution from traditional SEO to semantic SEO marks a significant shift in how search engine optimization is approached. Understanding this transition will help you leverage the full potential of modern SEO practices.
Traditional SEO focuses heavily on the keywords that users would search for and to incorporate these into your web content. In the past, this approach often led to practices like keyword stuffing, where the main priority was to include as many keywords as possible, sometimes at the expense of content quality or relevance.
Semantic SEO emerged as a response to the limitations of traditional SEO. It’s based on understanding the intent and contextual meaning behind user searches. So instead of just matching keywords, semantic SEO provides comprehensive and relevant content that truly addresses user queries.
Key differences of traditional and semantic SEO summed up:

How to Implement Semantic SEO
Implementing semantic SEO requires a shift in approach from traditional keyword-centric strategies to a more comprehensive understanding of content and user intent. Here’s how to do it.
1) Conduct Comprehensive Semantic Keyword Research
Effective semantic keyword research is key for aligning your content with user intent and context. Go beyond simple keywords. Use tools to understand related topics, questions and long-tail phrases that encompass the broader scope of your subject.
Using a hypothetical business called “GreenGlow Yoga Studio,” let’s see a break-down of how to do semantic keyword research.

Step 1. Start with Core Topics: Identify the core topics that are relevant to your business or content. These topics are broader than keywords and represent the main ideas or services you offer.
- Core topics for GreenGlow Yoga Studio might include “Yoga Classes”, “Yoga for Wellness”, “Beginner Yoga Tips”, and “Yoga Retreats”.
Step 2. Use Semantic Research Tools: Use tools like Google’s Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs. These tools provide insights into related queries, question patterns, and the language your audience uses.
- Using Google’s Keyword Planner, we input “Yoga Classes”. The tool suggests related queries like “online yoga classes”, “best yoga for beginners”, and “yoga classes near me”.
- Using Semrush, entering “Yoga for Wellness” might reveal phrases like “yoga for mental health” and “wellness through yoga”.
Step 3. Analyze ‘People Also Ask’ and ‘Related Searches’ on Google: Google’s “People Also Ask” and “Related Searches” sections are goldmines for uncovering semantically related queries. They help understand the different ways users search for similar topics.
A search for “Beginner Yoga Tips” on Google might show:
- People Also Ask questions like “What is the best yoga routine for beginners?” and “Essential yoga poses for beginners”.
- Related Searches might include “Yoga tips for flexibility” or “Yoga basics for all ages”.
Step 4. Explore Long-Tail Keywords: Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases. They often have lower search volume but higher relevance and conversion potential. Tools like AnswerThePublic can be useful for discovering these.
- Using AnswerThePublic with the phrase “Yoga Retreats”, we find long-tail keywords like “affordable yoga retreats for beginners” and “best yoga retreats in the world”.

Step 5. Study Competitors’ Keywords: Analyze keywords used by your competitors, especially those ranking well in your industry. Tools like Moz’s Keyword Explorer can help identify what your competitors are ranking for.
- Analyzing a top competitor’s website, we might find they rank well for “holistic yoga lifestyle” and “integrative yoga practice”.
Step 6. Incorporate Synonyms and Variations: Use synonyms and variations of your core topics. This broadens your reach and aligns with how different users might search for the same concept.
- Synonyms and variations for “Yoga Classes” could include “Yoga training sessions”, “Hatha yoga classes”, or “Group yoga practices”.
Step 7. Consider User Intent: For each keyword or phrase, consider the user intent behind it. Is the user looking for information, a product, a service or something else? Tailoring your content to match this intent is key. (More on this in the next section.)
- For “online yoga classes”, the intent might be to find accessible yoga instruction from home.
- For “yoga retreats”, users might be looking for immersive yoga experiences or vacation ideas.
Step 8. Regularly Update Your Research: Search trends and language evolve over time. Regular updates to your keyword research ensure that your content remains relevant and aligned with current user behaviors.
- Regularly revisiting these steps ensures the content remains aligned with the latest trends and user interests in the yoga space.
Follow these steps to conduct thorough semantic keyword research so that your content is not only rich in relevant keywords, but also aligned with the broader context and user intent.
Just want someone to do all the work for you? Single Grain’s Semantic SEO experts can help!👇
2) Optimize for User Intent
This involves understanding why someone is conducting a search, what kind of information they are seeking and anticipating what they might want to know next.
Whether they seek information, want to make a purchase, or find a specific website, your content should be tailored to address their questions, solve their problems or provide the information they seek.
This search intent could be informational (seeking knowledge), navigational (looking for a specific website or page), commercial (doing final research and reading reviews) or transactional (intending to make a purchase or engage in another specific online activity).

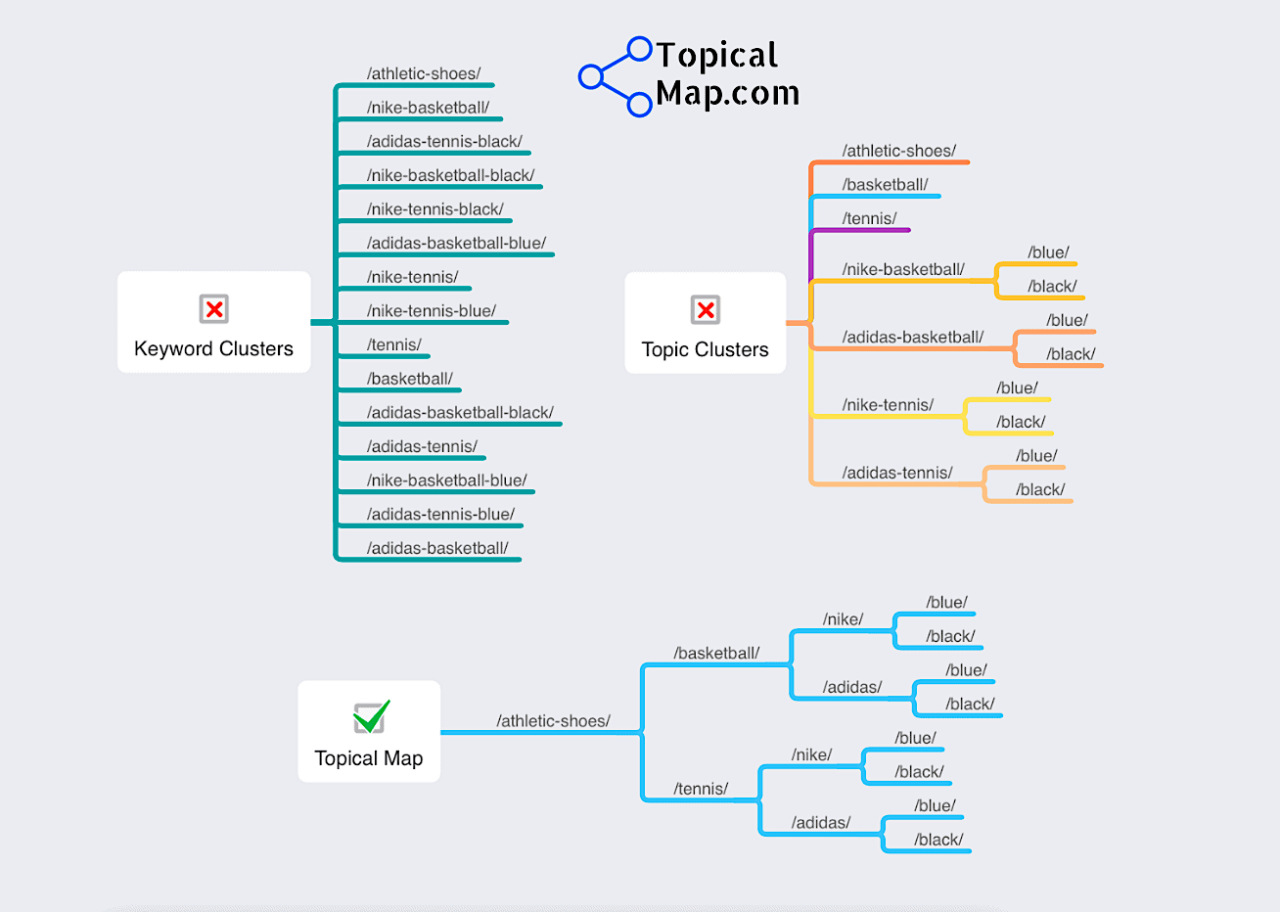
3) Create Topic Maps
Semantic SEO leverages topic maps as part of a broader strategy to organize and clarify the content on a website. They function as a visual and conceptual representation of how various topics and subtopics interconnect, providing a clear structure for both content creators and search engines.
Here’s how topic maps play a role in Semantic SEO:
- Comprehensive Topic Coverage: Topic maps ensure that all relevant subtopics and related areas are covered, providing a thorough understanding of the subject matter.
- Identifying Content Gaps and Opportunities: By visually laying out the relationships between various topics, you can easily identify areas where your content might be lacking, which is beneficial for SEO.
- Enhancing User Experience and Navigation: Topic maps can guide the structure of your website, making it easier for users to find related content. This improved navigation and user experience can lead to longer session durations and lower bounce rates.
- Improving Content Relevance and Context: By clearly mapping out the relationships between different pieces of content, you help search engines understand the context and relevance of your content. This is crucial in semantic SEO, where the focus is on the meaning and relationships between words and topics, rather than just keywords.
- Supporting Long-Tail Keyword Strategy: Topic maps can reveal long-tail keywords and phrases that are semantically related to your main topics. By targeting these in your content, you can capture more niche search queries.
- Enhancing Internal Linking: A well-structured topic map can guide your internal linking strategy. By linking related pieces of content as indicated in your topic map, you reinforce the semantic relationships between different pages, helping search engines crawl and index your site more effectively.
- Influencing Content Creation and Marketing Strategies: Understanding how different topics are interrelated can inform your content creation and marketing strategies, ensuring that all your content efforts contribute cohesively towards establishing topical authority in your domain.
For a deeper understanding of building topic maps, take a look at this guide What Is a Topical Map in SEO?:
4) Write Rich and Relevant Content
Semantic SEO emphasizes creating content that is not only keyword-rich but also contextually relevant and enriched with related concepts, synonyms and varied linguistic structures. This helps search engines understand the content more holistically.
Focus on content depth and quality. Create content that thoroughly covers topics. This includes addressing related subtopics and questions and providing detailed, valuable information.

Create topic clusters. Rather than creating isolated articles or pages targeting individual keywords, semantic SEO focuses on building comprehensive content that covers a topic in depth. This can involve creating ‘pillar’ pages that provide a broad overview of a topic and ‘cluster’ content that delves into specific aspects of that topic in detail.
5) Entities and Context
An entity is anything that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable. In semantic SEO, entities could be people, places, concepts or objects that are relevant to your content. And context simply refers to the environment in which these entities are discussed.
Imagine that you’re writing an article about “Apple.” In semantic SEO, “Apple” is an entity.
However, it’s a unique entity that can have different meanings based on the context:
- If the context is technology: Here, “Apple” refers to the multinational technology company known for products like the iPhone and MacBook. When your content discusses aspects like “Apple’s latest iPhone release” or “Apple’s iOS updates,” the search engine understands that the entity “Apple” relates to the technology sector.
- If the context is nutrition or food: In this scenario, “Apple” refers to the fruit. Content discussing “health benefits of eating an apple” or “apple farming techniques” places the entity “Apple” within the context of food and nutrition.
With semantic SEO, it’s crucial to establish clear context for entities to ensure search engines accurately understand and categorize your content. Establishing clear context for entities is all about the surrounding context, related keywords and the overall thematic coherence of your content:
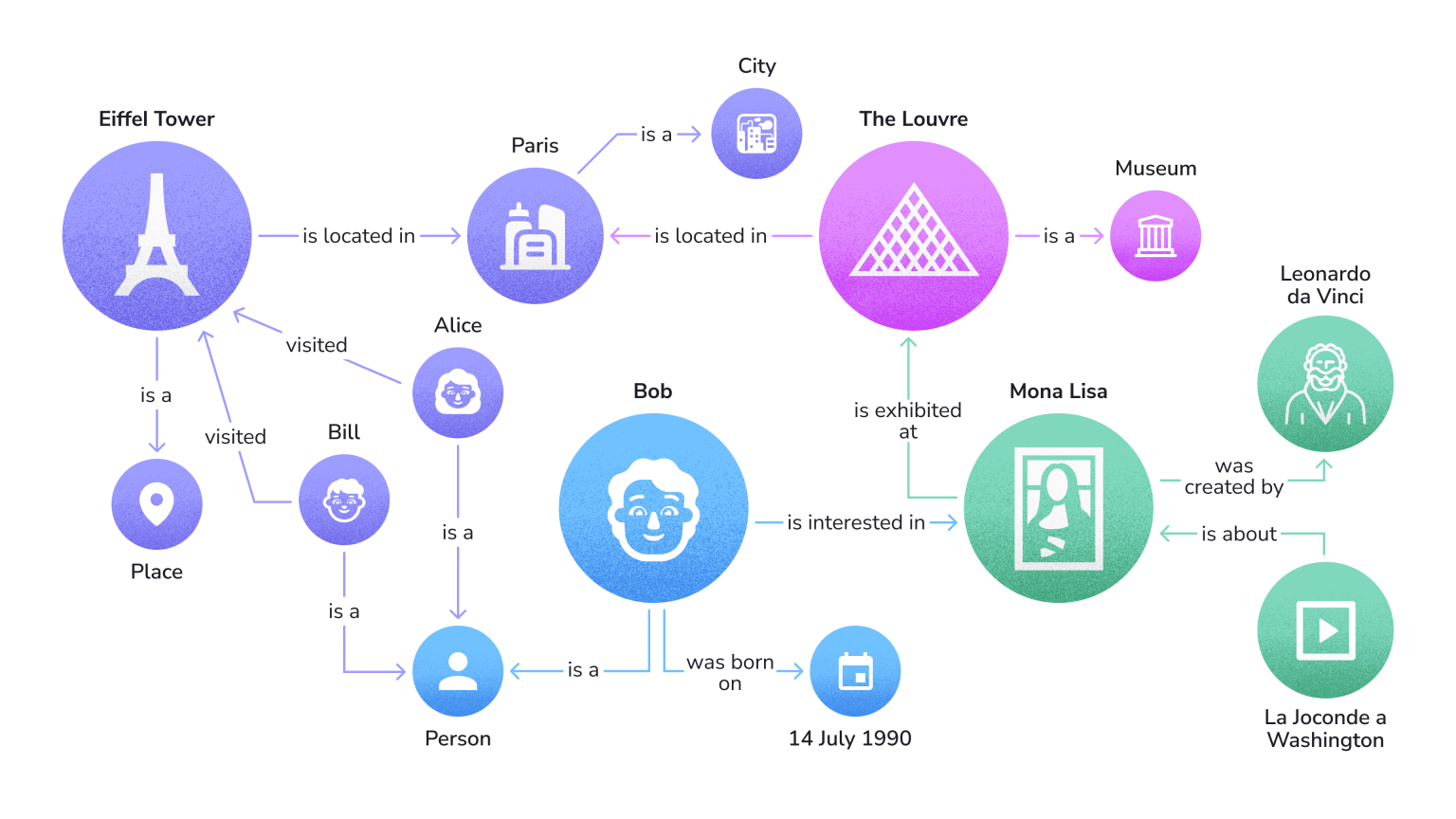
By doing so, your content is more likely to appear in relevant searches, aligned with the correct interpretation of the entity. This clarity enhances the chances of reaching your target audience effectively.
6) Use Structured Data and Schema Markup
Implementing structured data through schema markup helps search engines understand the context and meaning of the content on your pages. This is the language of search engines; it helps them understand the content and context of web pages.
Structured data (also known as “schema markup”) can enhance your SERPs listings with rich snippets, such as this example of schema markup for events:
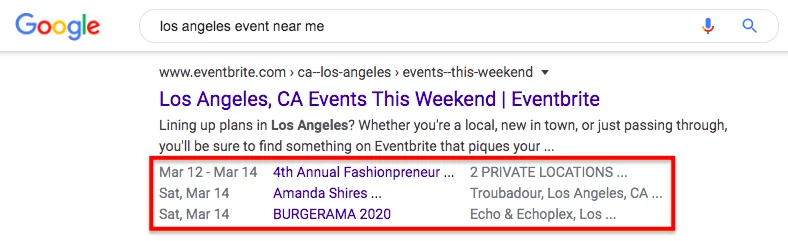
Here are a few more common and helpful schema markups:
- The organization schema can be useful, especially if your site is already established and often ranks well.
- The author schema is also a good one, because it tells Google exactly who has written the content.
- The person schema is a good one here. It allows you to add author information like credentials or awards earned, occupation and job title, and their brand for Google to read.
You can learn more about how to add schema markup here.
Single Grain’s Semantic SEO experts can help you!👇
7) Leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) Tools
Natural Language Processing helps search engines understand and interpret human language, and with advancements in NLP, search engines are getting better at understanding natural language queries.
By optimizing content with natural, conversational language and voice search, it aligns better with how people actually speak and search.
You’re probably already using some of these NLP tools for content optimization:
Google’s Natural Language API: This tool can analyze text and provide insights into categories, sentiment, entities and syntax. You can use it to understand how Google interprets the language in your content. It’s particularly useful for identifying the salience of different entities in your text, helping you understand which aspects of your content are seen as most relevant to the overall topic.
OpenAI’s GPT-3: GPT-3 (or GPT-4, but that’s a paid version) can generate human-like text, making it useful for creating content that is both rich in natural language and diverse in terms of vocabulary and style. It can also be used to improve existing content by making it more engaging and readable.
Semrush Writing Assistant: This tool offers SEO recommendations based on NLP analysis. It can help you optimize your content for search engines by providing suggestions on readability, tone, and SEO best practices.
MarketMuse: MarketMuse uses AI and NLP to analyze content and compare it against existing top-ranking pages. Input your content into MarketMuse to see how it stacks up against competitors. It provides insights on how to improve content depth and breadth for better SEO performance.

When you use these NLP tools, your content is optimized not just for keywords, but also for the nuances of natural language, which is increasingly important for SEO as search engines become more sophisticated in understanding and interpreting user queries.
8) User Experience and Engagement
A key part of semantic SEO (or traditional SEO, for that matter) is ensuring a positive user experience.
Search engines, particularly Google, place a high emphasis on how users interact with content, favoring websites that not only provide relevant information but also ensure a pleasant and engaging user journey.
Here are the key aspects to focus on to give your site visitors a good experience:
- Site Speed: Users typically expect a website to load within a couple of seconds. Slow-loading sites lead to higher bounce rates and lower engagement, negatively impacting SEO.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Your site must be optimized for mobile users. This includes responsive design that adapts to various screen sizes and easy-to-use interfaces on mobile devices.
- Intuitive Navigation: A clear menu, logical page hierarchy, and easy-to-find search functions on your website make it easier for users to find the information they need.
- Engaging Content Layout: Use headers, bullet points, images, and short paragraphs to make content easily readable.
- Interactive Elements: Incorporating elements like polls, quizzes, or interactive infographics can significantly increase user engagement, keeping visitors on your site longer.
- Clear Calls-to-Action: Your CTA should guide users on what to do next, whether it’s to read another article, sign up for a newsletter, or make a purchase. Here’s an example of a CTA we use:

- Accessibility: Make sure your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This includes using alt text for images, providing text transcripts for videos, and ensuring navigability via keyboard.
- Personalized Experiences: To increase engagement, personalize content and recommendations based on user behavior.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement ways to gather user feedback, such as surveys or comment sections. This feedback can be invaluable in further optimizing the user experience.
9) Monitor and Adapt to Algorithm Updates
And, finally, monitoring and adapting to algorithm updates is crucial for SEO success – traditional or semantic. It’s important to stay updated with the latest in search engine algorithms and adjust your strategies accordingly to maintain and improve your SEO performance.
Track your performance with various analytics tools that provide insights into your website’s traffic, user behavior and search engine rankings. Then, when you know what’s been working and what hasn’t, you can methodically update and optimize your content to keep it relevant and effective.
Here are some of the best analytics tools for this purpose:
- Google Analytics: This is one of the most widely used tools for tracking website performance. It offers comprehensive data on website traffic, user engagement, demographics, and behavior patterns. You can track specific goals, see which pages are performing best, and understand where your traffic is coming from.
- Google Search Console: This tool provides direct insights into how Google views your website. It shows which queries bring users to your site, how your site appears in search results, and provides information on site errors, mobile usability, and other key metrics that influence SEO.
- Semrush: Semrush is a powerful tool for tracking keyword rankings, analyzing backlinks, and researching competitors. It also offers detailed audits of your website to identify SEO issues and provides suggestions for improvement.
- Ahrefs: Known for its backlink analysis capabilities, Ahrefs also offers comprehensive tools for SEO auditing, keyword research, and competitive analysis. It’s particularly useful for tracking your site’s performance in terms of backlinks and ranking for specific keywords.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future with Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO is not just a trend, but a fundamental shift in the approach to search engine optimization. By focusing on the meaning behind words and user intent, semantic SEO offers a path to create more relevant, engaging and valuable online experiences.
This approach to SEO aligns with the evolving algorithms of search engines, ensuring that your website not only ranks higher, but remains resilient to future changes in the digital landscape. As we move forward, this SEO strategy will become increasingly integral to successful online strategies, offering a competitive edge to those who adopt them early and effectively.
By implementing the strategies and best practices outlined in this article, you can transform your site for better rankings and ensure its long-term success in the ever-evolving world of search engine optimization!
If you’re ready to improve your site’s content for better ranking, Single Grain’s Semantic SEO experts can help!👇