Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Inverted axis#
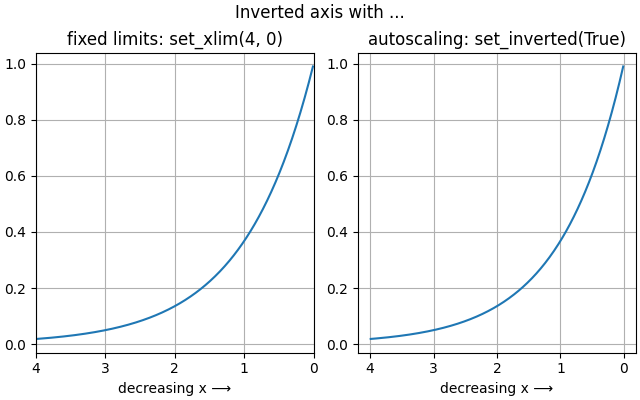
This example demonstrates two ways to invert the direction of an axis:
If you want to set explicit axis limits anyway, e.g. via
set_xlim, you can swap the limit values:set_xlim(4, 0)instead ofset_xlim(0, 4).Use
Axis.set_invertedif you only want to invert the axis without modifying the limits, i.e. keep existing limits or existing autoscaling behavior.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(0.01, 4.0, 0.01)
y = np.exp(-x)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(6.4, 4), layout="constrained")
fig.suptitle('Inverted axis with ...')
ax1.plot(x, y)
ax1.set_xlim(4, 0) # inverted fixed limits
ax1.set_title('fixed limits: set_xlim(4, 0)')
ax1.set_xlabel('decreasing x ⟶')
ax1.grid(True)
ax2.plot(x, y)
ax2.xaxis.set_inverted(True) # inverted axis with autoscaling
ax2.set_title('autoscaling: set_inverted(True)')
ax2.set_xlabel('decreasing x ⟶')
ax2.grid(True)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.530 seconds)