- What is griseofulvin tablet, and how does it work (mechanism of action)?
- What are the side effects of griseofulvin tablet?
- What is the dosage for griseofulvin tablet?
- Which drugs or supplements interact with griseofulvin tablet?
- Is griseofulvin tablet safe to take if I'm pregnant or breastfeeding?
- What else should I know about griseofulvin tablet?
What is griseofulvin tablet, and how does it work (mechanism of action)?
Griseofulvin is an oral antibiotic that is used to treat fungal infections of the skin, body, hair/beard, or nails. Griseofulvin prevents fungal cells from dividing and multiplying. Griseofulvin also is deposited in keratin cells on the surface of the skin making it difficult for fungus to invade the skin and other tissues. Griseofulvin is effective against Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Trichophyton. It is not effective against bacteria. The FDA approved griseofulvin in 1959.
What brand names are available for griseofulvin tablet?
Gris-Peg, Grifulvin V, Griseofulvin Ultramicrosize
Is griseofulvin tablet available as a generic drug?
Yes
Do I need a prescription for griseofulvin tablet?
Yes
What are the side effects of griseofulvin tablet?
Reported side effects include:
- Hypersensitivity type reactions including rashes, itching, and redness
- Angioedema (swelling under the surface of the skin)
- Numbness of the hands and feet
- Oral thrush (fungal infection with Candida Albicans)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Upset stomach
- Loose stool (diarrhea)
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Dizziness
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Mental confusion
- Impairment of performance of routine activities
- Presence of abnormal quantities of protein in the urine (proteinuria)
- Reduced white blood cell count (leukopenia)

IMAGES
Eczema Browse our medical image collection of allergic skin disorders such as psoriasis and dermatitis and more caused by allergies See ImagesWhat is the dosage for griseofulvin tablet?
Adults
- The recommended dose is 375 mg daily or 250 mg three times daily of the ultramicrosize formulation depending on the type of infection.
- The dosing recommendation for the microsize formulation is 500 mg once or twice daily, or 1000 mg as a single dose depending on the type of fungal infection.
The duration of treatment varies and is generally continued until the fungal infection is completed eradicated. It is usually taken for
Which drugs or supplements interact with griseofulvin tablet?
Griseofulvin interacts with many drugs. Patients should consult the prescribing information for a complete list of drugs that interact with griseofulvin. Known drug interactions include:
- Griseofulvin increases the activity of CYP3A4 liver enzymes. Griseofulvin should not be combined with other drugs that are metabolized (broken down) by CYP3A4 enzymes because griseofulvin may decrease their blood concentrations, decreasing treatment effectiveness. Examples of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4 enzymes include atazanavir (Reyataz), bedaquiline (Sirturo), daclatasvir (Daklinza), darunavir (Prezista), gefitinib (Iressa), nilotinib (Tasigna), palbociclib (Ibrance), telithromycin (Ketek), and several other drugs.
- Use of griseofulvin with birth control pills may reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills and cause breakthrough bleeding. Patients should use an alternative or additional form of birth control (contraception) while on griseofulvin therapy and for up to 1 month after stopping treatment.
- The effectiveness of warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven) may be reduced by griseofulvin because griseofulvin may increase the breakdown warfarin by enzymes in the liver.
Health News
- Check Your Pantry, Lay's Classic Potato Chips Recalled Due to Milk Allergy Risk
- California Declares Bird Flu Emergency as Outbreak in Cows Continues
- Not Just Blabber: What Baby's First Vocalizations and Coos Can Tell Us
- Norovirus Sickens Hundreds on Three Cruise Ships
- FDA Updates Meaning of 'Healthy' on Food Labels
 More Health News »
More Health News »
Is griseofulvin tablet safe to take if I'm pregnant or breastfeeding?
Griseofulvin is known to cause birth defects and should be avoided during pregnancy. Women of child bearing potential must use appropriate forms of contraception (birth control) during treatment and for one month after completing griseofulvin therapy. Men are advised to wait six months after completing griseofulvin therapy before attempting to father a child.
It is not known whether griseofulvin is excreted into human milk. Due to the lack of conclusive safety data, the manufacturer recommends against the use of griseofulvin in nursing mothers.
What else should I know about griseofulvin tablet?
What preparations of griseofulvin tablet are available?
- Oral suspension (microsize): 125 mg/5ml
- Microsize: Oral tablets: 250 mg, 500 mg
- Ultramicrosize oral tablets: 125 mg, 250 mg,
How should I keep griseofulvin tablet stored?
Griseofulvin should be stored at room temperature, between 15 C and 30 C (59 F and 86 F).
Summary
Griseofulvin (Gris-Peg, Grifulvin V, Griseofulvin Ultramicrosize) is an antibiotic prescribed to treat fungal infections such as ringworm of the body, athlete's foot, barber's itch, and fungal or ringworm of the nails. Side effects, drug interactions, dosing, storage, and pregnancy and breastfeeding information should be reviewed prior to taking this medication.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
-

Rosacea, Acne, Shingles, Covid-19 Rashes: Common Adult Skin Diseases
Learn to spot and treat skin conditions commonly found in adults such as acne, Covid-19 rashes, eczema, shingles, psoriasis,...
-

Childhood Diseases: Measles, Mumps, & More
Is your child at risk for these childhood diseases? Know when to call the doctor for conditions such as measles, mumps, ringworm,...
-

Hair Loss: Alopecia, Thinning Hair in Men and Women
Learn about hair loss (alopecia) in women and men. Discover hair loss causes and treatments like shampoos and drugs, as well as...
-

Burning or Swollen Feet? What Foot Pain Symptoms Say About Your Health
Foot pain and heel pain can be signs of serious health problems. Discover information about cold feet, itchy feet, burning feet...
-
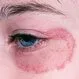
Picture of Ringworm Tinea Corporis (Faciei)
Ringworm infection on a 51-year-old woman's skin. Ringworm (tinea) is a disease caused by a fungal infection of the skin. It can...
-

Picture of Ringworm Tinea Pedis
Close-up of athlete's foot (tinea pedis) on the foot of a 66year old man. See a picture of Ringworm Tinea Pedis and learn more...
-
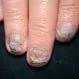
Picture of Ringworm Tinea Unguium (Onychomycosis)
Ringworm - Tinea unguium or onchomycosis is a chronic fungal infection of the nails. It is normally caused by the dermatophyte...
-

Common Childhood Skin Disorders
What are the most common skin rashes in children? Learn about childhood eczema, ring worm, chicken pox and more. Get the facts on...
-

Is It Contagious? What Diseases Are Contagious?
Is it contagious? Take this quiz to learn about contagious diseases, how contagious diseases are spread, and myths and facts...
-

Skin Conditions Quiz: Common Skin Diseases
Could you identify a scabies infestation? Take the Skin Diseases Pictures Quiz and learn to identify common conditions that...
-

Feet Facts Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Did you know that certain shoes and common diseases can wreak havoc on your feet? If you've been having problems with your feet,...
-
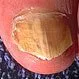
Picture of Ringworm of the Nails
This is the most common fungal infection of the nails, also called onychomycosis. See a picture of Ringworm of the Nails and...
-
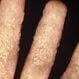
Picture of Ringworm of the Hand
Ringworm may involve the hands, particularly the palms and the spaces between the fingers. See a picture of Ringworm of the Hand...
-

Picture of Pet Ringworm
Ringworm is an example of a zoonotic disease (transmitted from animals to humans). See a picture of Pet Ringworm and learn more...
-
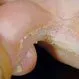
Picture of Athlete's Foot 2
Athlete's foot is a fungus that causes itching, redness, and cracking. See a picture of Athlete's Foot and learn more about the...
-
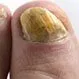
Picture of Fungal Nail Infection
Nails that are infected with a fungus may become discolored (yellowish-brown or opaque), thick and brittle, and may separate from...
-

Picture of Types of Ringworm
Ringworm is a common skin disorder otherwise known as tinea. See a picture of Types of Ringworm and learn more about the health...
-
Picture of Ringworm Illustration
Ringworm is a fungal infection of the skin previously thought to be due to a parasite (worm). See a picture of Ringworm and learn...
-

Picture of Ringworm
This superficial skin infection, also known as tinea, is caused by fungi called dermatophytes. See a picture of Ringworm and...
-
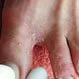
Picture of Athlete's Foot 1
Athlete's foot is caused by a fungus that grows on or in the top layer of skin. See a picture of Athlete's Foot and learn more...
-

19 Health Problems in Men: Snoring, Hair Loss, and More
What are the biggest body health issues that plague men? Most men struggle with belly fat, back hair, sweating, erectile...
Related Disease Conditions
-

Ringworm
The term "ringworm" refers to a fungal infection on the surface of the skin. A physical examination of the affected skin, evaluation of skin scrapings under the microscope, and culture tests can help doctors make the appropriate distinctions. A proper diagnosis is essential to successful treatment. The different types of ringworm include the following: tinea barbae, tinea capitis, tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea faciei, tinea manus, tinea pedis, and tinea unguium.
-
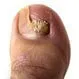
Fungal Nails
Fungal nails (onychomycosis) may be caused by many species of fungi, but the most common is Trichophyton rubrum. Distal subungal onychomycosis starts as a discolored area at the nail's corner and slowly spreads toward the cuticle. In proximal subungal onychomycosis, the infection starts at the cuticle and spreads toward the nail tip. Yeast onychomycosis is caused by Candida and may be the most common cause of fungal fingernails.
-

Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot (tinea pedis) is a skin infection caused by the ringworm fungus. Symptoms include itching, burning, cracking, peeling, and bleeding feet. Treatment involves keeping the feet dry and clean, wearing shoes that can breathe, and using medicated powders to keep your feet dry.
-

Ringworm vs. Eczema
While ringworm is a fungal infection, and eczema is a skin condition, both are characterized by itchiness. Eczema patches are leathery while ringworm involves ring formation on the skin. Over-the-counter antifungals treat ringworm. Topical creams and ointments treat eczema.
Treatment & Diagnosis
Medications & Supplements
Subscribe to MedicineNet's Skin Care & Conditions Newsletter
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from MedicineNet and I understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet subscriptions at any time.

Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
REFERENCE:
FDA Prescribing Information