What is mental nerve block?
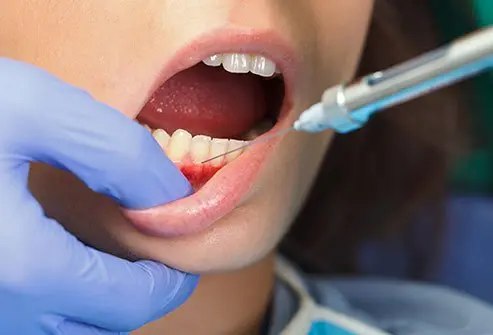
A mental nerve block is a type of anesthesia used for numbing parts of the face. This type of anesthetic nerve block is mainly used for wound repair to the lip and chin.
The sensory area of the mental nerve is a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve located on the face, below the lower lip, on the side of the chin. The mental nerve is a branch of the 5th cranial nerve (called the trigeminal nerve), which provides sensory input to the face.
The trigeminal nerve divides into the inferior alveolar nerve, and exits the jaw and enters the face through the mental canal (mental foramen) and supplies sensation to the skin of the chin and the mucus membranes of the lower lip.
This type of nerve block does not numb the teeth and is not used for dental procedures.
What is mental nerve block used for?
Mental nerve block is used for the following:
- To repair lacerations and wounds of the lower lip, especially if the cosmetic edge of the lip (vermillion border) is involved
- To repair lacerations and wounds to the soft tissue of the chin that extends from the lip
- To surgically remove facial tumors/lesions
- To relieve chronic nerve pain from shingles (postherpetic neuralgia)
How do you give a mental nerve block?
There are two ways to numb the mental nerve and perform a mental nerve block: through the mouth (intraoral) and outside the mouth (extraoral).
For a mental nerve block performed through the mouth (intraoral):
- Topical anesthetic is applied to the inner part of the lower lip and gums below the tooth line
- The doctor feels for the mental canal (foramen) on the side of the chin, on the jawline
- An anesthetic is injected into the area around the mental foramen using a small needle from inside the lower lip
- After a few minutes, the area of the mental nerve becomes numb and the procedure can be performed
For a mental nerve block performed from outside the mouth (extraoral):
- The skin over the chin is cleansed with antiseptic
- The doctor feels for the mental canal (foramen) on the side of the chin, over the jawline
- An anesthetic is injected through the skin of the chin into the area around the mental foramen using a small needle
- The doctor firmly massages the area for 10-15 seconds
- After a few minutes, the area of the mental nerve becomes numb and the procedure can be performed
For either the intraoral or extraoral approach, the local anesthetic’s (usually lidocaine) effect lasts between 30 minutes and two hours.
What are the risks and complications of mental nerve block?
Complications of mental nerve block can include the following:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Needle fracture
- Intravascular injection
- Nerve damage (neurapraxia) secondary to direct injection into the mental foramen

SLIDESHOW
Rheumatoid Arthritis Exercises: Joint-Friendly Workouts See SlideshowTop How Do You Give a Mental Nerve Block Related Articles

Bupivacaine
Bupivacaine is a local anesthetic used to prevent pain during dental procedures and as nerve blocks for regional anesthesia during various medical procedures including during labor and delivery. Common side effects of bupivacaine include visible bruising, postprocedural contusion, surgical site bleeding, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dizziness, somnolence, slow heart rate (bradycardia), headache, generalized itching (pruritus), abnormal skin sensation (paresthesia), reduced skin sensation (hypoesthesia), taste perversion (dysgeusia), and others.
bupivacaine liposome
Bupivacaine liposome is a local anesthetic used for post-surgical pain relief (analgesia) in patients 6 years and older, who have had a superficial or invasive surgical procedure. Bupivacaine liposome is also used as a nerve block in adults for pain relief after shoulder surgery. Common side effects of bupivacaine liposome used as postsurgical local analgesia include nausea, vomiting, constipation, fever (pyrexia), dizziness, fainting (syncope), muscle twitching or spasms, back pain, low blood pressure (hypotension), rapid heart rate (tachycardia), low red blood cell count (anemia), postoperative anemia, itching (pruritus), and fungal infection.
Burns
Burn types are based on their severity: first-degree burns, second-degree burns, and third-degree burns. First-degree burns are similar to painful sunburns. The damage is more severe with second-degree burns, leading to blistering and more intense pain. The skin turns white and loses sensation with third-degree burns. Burn treatment depends upon the burn location, total burn area, and intensity of the burn.
First Aid: Why You Need a First Aid Kit and CPR
First aid is providing medical assistance to someone a sick or injured person. The type of first aid depends on their condition. Preparedness is key to first aid, like having basic medical emergency kits in your home, car, boat, or RV. Many minor injuries may require first aid, including cuts, puncture wounds, sprains, strains, and nosebleeds. Examples of more critical first aid emergencies include heart attacks, strokes, seizures, and heatstroke.
When to Call 911: Serious Symptoms to Never Ignore
It’s not always easy to tell the difference between a minor bump on the head and a serious head injury. Here are some situations that need medical help right away.
First Aid: Bandaging Injuries and Wounds From Head to Toe
Bandaging a wound like a burn, cut, or scrape requires different techniques depending on which part of the body was hurt. Ace bandages, liquid bandages, bandage wraps, waterproof bandages, elastic bandages, and other types are available to cover and protect your wound from dirt and water.
First Aid: Wound Care for Cuts and Scrapes
Wound care treatment at home involves performing cuts and scrapes first aid including cleaning the injury and applying antibiotic ointment and a bandage. Use wound care products like adhesive bandages, hypoallergenic bandages, sprays, tape, and gauze. If cuts and scrapes don’t heal, see your doctor.
8 First Aid Kit Essentials for Scrapes, Cuts, Bug Bites, and More
Are you always prepared for a first aid crisis? See which basic first aid items to pack to treat minor scrapes, cuts, and stings when you're on the go.
How Dangerous Is General Anesthesia?
General anesthesia drugs induce unconsciousness to prevent the patient from feeling any sensations at all while surgeons perform procedures that would otherwise cause unbearable pain. It is generally safe, but comes with risks like breathing problems and inhaling fluid in the lungs, blood pressure and heart function issues and allergic reactions to the medications.
How Long Does A Supratrochlear Nerve Block Last?
A supratrochlear nerve block is a procedure to anesthetize the lower middle portion of the forehead and the bridge of the nose. An anesthetic injection is administered below the eyebrow on the edge close to the nasal bridge, where the supratrochlear nerve comes out of the skull and runs up the forehead.
lidocaine anesthetic
Lidocaine anesthetic is a local anesthetic injection administered to numb specific parts of the body before painful medical procedures. Side effects of lidocaine anesthetic include irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), slow heartbeat (bradycardia), cardiovascular collapse, low blood pressure (hypotension), heart block, swelling (edema), shortness of breath (dyspnea), respiratory depression, respiratory arrest, anxiety, agitation, confusion, euphoria, and others. Lidocaine is safe to use in pregnancy, and in labor and delivery. Consult your doctor if you are breastfeeding.
mepivacaine
Mepivacaine is a prescription medication used for infiltration anesthesia and nerve blocks such as an epidural or spinal block. Common side effects of mepivacaine include anxiety, restlessness, excitement, depression, dizziness, tremors, blurred vision, and ringing in your ears. Consult your doctor if pregnant or breastfeeding.
Trauma/First Aid Quiz
What should be in your first-aid kit? Take this quiz to understand trauma and learn the truth about how to administer first aid.