- Definition
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Types
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- Complications
-
Comments
-
**COMMENTSTAGLIST**
-
More
-
**OTHERTAGLIST**
What is tendonitis in the foot?
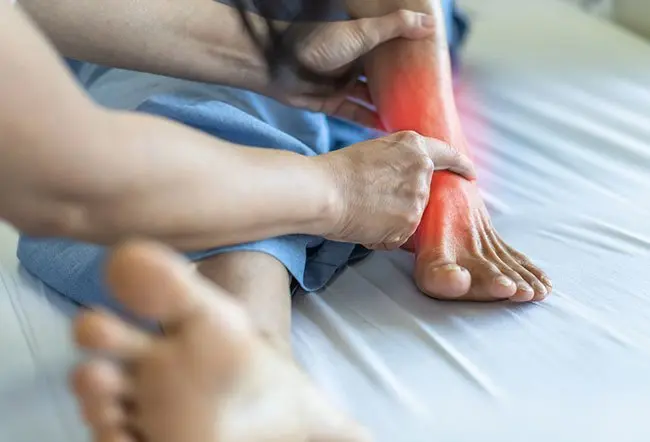
Tendons are tissue cords in your body that attach muscles to bones. When your tendons become damaged and cause irritation or inflammation, it’s called tendonitis. Tendonitis causes acute pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area. This can make it painful or difficult for you to move.
Tendonitis most commonly happens after the repeated incorrect use of a part of the body. In the case of foot tendonitis, your Achilles tendon and other tendons that connect your foot to the bones in your lower leg become injured.
Symptoms of tendonitis in the foot
Tendonitis foot symptoms include pain, tenderness, and soreness around your ankle joint. It may be difficult and painful to move and painful to the touch. Sometimes the affected joint can swell.
Causes of tendonitis in the foot
There are many causes of tendonitis of the foot and ankle. These include, but are not limited to:
- Abnormal foot structure
- Medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout
- Trauma caused by injury or accident
- Improper overuse of the foot and ankle
Types of tendonitis in the foot
The most common types of foot tendonitis are:
Achilles tendonitis
The Achilles tendon is the large tendon that attaches the back of your heel to your calf muscle. Achilles tendonitis usually occurs one to four inches above the area where your Achilles attaches to your heel bone. This is the weakest part of the tendon and the location where tendon tears typically occur.
Extensor tendonitis
Extensor tendons run along the top of your foot. Tendonitis in this location is often caused by your foot rubbing against your shoe. It can also be caused by less common inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. If your feet have high arches, they are more vulnerable to the shoe friction that causes this type of tendonitis.
Flexor tendonitis
Flexor Tendonitis usually causes a profound pain deep in the back of your ankle near the inside of your foot. This type of tendonitis is common in dancers or those who are required to do a lot of balancing on their toes.
Peroneal tendinosis
The tendons of the peroneal muscle wrap around the outside of your foot and down towards your ankle. Pain and possibly swelling can occur here and in the area just below and above it.
Posterior tibial tendonitis
This type of tendonitis is usually associated with people who have flat feet. The tendon of your tibialis posterior muscle wraps around the inside of your foot. That area of your foot is where pain and swelling can be felt.
Diagnosis for tendonitis in the foot
Only a licensed healthcare professional can diagnose tendonitis. Your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical evaluation of the affected foot. They may order X-rays or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to see whether you have a broken bone or a tendon rupture.
If you frequently experience tendonitis symptoms in the foot, your doctor may recommend that you go see a specialist. A podiatrist can help you identify what the underlying cause of your tendonitis is.

SLIDESHOW
Pictures of the 7 Riskiest Workout Moves, and How to Improve Them See SlideshowTreatments for tendonitis in the foot
When you begin to feel pain in your foot, the first recommendation is to follow R.I.C.E., which stands for:
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
In other words, you should stop any physical activities. Apply ice to the affected area. Use a compress to keep the pressure on it. Lie down and raise your foot to a level that is above your heart.
The general idea behind treating your foot and ankle tendonitis is to rest so that your body can heal the injury. This takes time, usually a couple of days, but may last as long as a couple of weeks or even months.
If you need to move around, your doctor may give you a walking boot to keep your foot and ankle immobilized. They may also instruct you to stay off the foot completely with the use of crutches or a wheelchair.
To help ease the pain of your foot tendonitis, your doctor will likely prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). You may also be referred to do some physical therapy to help strengthen the muscles around the tendon and reduce the stress on it.
Complications of tendonitis in the foot
There is the potential to injure other parts of your body, like your other foot or leg, for example, by relying on it to reduce the strain of your injured foot caused by foot tendonitis.
It is important to take precautions to not put too much pressure or strain on your healthy leg or foot when treating the foot affected with tendonitis.
Medications that you take for pain or inflammation may have different side effects. Consult your healthcare provider about possible complications of any medications you might take for your tendonitis.
How do you know you have tendonitis?
Tendons are thick cords of tissue that attach muscles to bones. When these tendons become irritated or inflamed, it’s called tendonitis. Tendonitis causes acute pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected joint, making it painful to move.
Any tendon can develop tendonitis, but you’re more likely to develop it in joints that are most active during physical activities, like your elbow, heel, knee, shoulder, or wrist.
Health News
- More of America's Pets Are Overdosing on Stray Coke, Meth
- GLP-1 Zepbound Is Approved As First Drug For Sleep Apnea
- Feeling Appreciated by Partner is Critical for Caregiver's Mental Health
- Tips for Spending Holiday Time With Family Members Who Live with Dementia
- The Most Therapeutic Kind of Me-Time
 More Health News »
More Health News »
Types of tendonitis
Most common forms of tendonitis are named after the sports that increase their risk. They include:
Golfer's elbow
This type of tendonitis is when the tendons that attach your forearm muscles to the inside bone at your elbow become inflamed.
Jumper's knee
Also known as Patellar Tendonitis, jumper’s knee is characterized by an inflammation in the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the shin bone. Continued activity on jumper’s knee could lead to a tear in the tendon.
Pitcher's shoulder
Overhand throwing places extreme stress on the shoulder, particularly the tendons that keep the shoulder stable. While most common among baseball players, this tendonitis can also be seen in other types of sports that require repetitive overhand motions like volleyball, tennis, and some track and field events.
Swimmer's shoulder
Similar to pitcher’s shoulder, this form of tendonitis affects the shoulder ligaments from continuous improper overhead motions of the arm. Freestyle or backstroke are the most common swim strokes to cause tendonitis.
Tennis elbow is inflammation or sometimes a micro-tear of the tendons that join the forearm muscles on the outside of the elbow. The forearm muscles and tendons are damaged from repeating the same motions over and over. This leads to pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow.
American Family Physician: "Tendinopathies of the foot and ankle."
BioMed Research International: "Achilles Tendinopathy: Current Concepts about the Basic Science and Clinical Treatments."
EFORT Open Reviews: "Peroneal tendon disorders."
Journal of Athletic Training: "What is the Evidence for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation Therapy in the Treatment of Ankle Sprains in Adults?"
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care: "Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction: An overlooked cause of foot deformity."
Journal of Orthopaedic Research: "Mechanisms of tendon injury and repair."
OrthoInfo: "Achilles Tendinitis."
Pediatric Rheumatology: "Review for the Generalist: Evaluation of Pediatric Foot and Ankle Pain."
Radiology Case Reports: "Imaging Findings in Two Cases of Fluoroquinolone-Induced Achilles Tendinopathy."
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, OrthoInfo: "Golf Injury Prevention."
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, OrthoInfo: "Shoulder Injuries in the Throwing Athlete."
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, OrthoInfo: "Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)."
American College of Rheumatology: "Tendinitis (Bursitis)."
Harvard Health Publishing: "Tendonitis."
Johns Hopkins Medicine: "Patellar Tendonitis (Jumper's Knee)."
North American Journal of Sports Physical Therapy: "Prevention and Treatment of Swimmer's Shoulder."
National Institute of Health, News in Health: "Protect Your Tendons: Preventing the Pain of Tendinitis."
Top How Do You Treat Tendonitis in the Foot Related Articles
Ankle Pain (Tendonitis)
Ankle pain is commonly due to a sprain or tendonitis. The severity of ankle sprains ranges from mild (which can resolve within 24 hours) to severe (which can require surgical repair). Tendonitis of the ankle can be caused by trauma or inflammation.
What Is the Fastest Way to Heal Tendonitis in the Wrist?
Learn what medical treatments can help ease your wrist tendonitis symptoms and help you manage this condition.
Foot Health: Causes of Swollen Feet and Ankles
Swollen feet and ankles may be associated with conditions like pregnancy, injury, heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease, chronic venous insufficiency, and lymphedema. Treatment may include home remedies, exercise, magnesium, and certain medications.
Foot Pain
Foot pain may be caused by many different diseases, deformities, biomechanical conditions, improper footwear, or injuries. Pain and tenderness may be accompanied by joint looseness, swelling, weakness, discoloration, and loss of function.
Foot Pain Slideshow
Learn about common causes of foot pain such as bunions, corns, athlete's foot, plantar warts and more. Get the latest information on treatments for foot pain.
How Do You Treat Tendonitis in the Ankle?
Learn about the causes and symptoms of tendonitis in the ankle and treatment options.
How Do You Treat Tendonitis in the Elbow?
Learn what medical treatments can help ease your elbow tendonitis symptoms and help you manage tendonitis in the elbow.
Sprains and Strains
An injury to a ligament is called a sprain, and an injury to muscle or tendon is called a strain. Sprains and strains may be caused by repetitive movements or a single stressful incident. Symptoms and signs include pain and swelling. Though treatment depends upon the extent and location of the injury, rest, ice, compression, and elevation are key elements of treatment.
Tendinitis Causes
If your tendons get irritated and swollen, you might have tendinitis. Learn the symptoms and find out how you can prevent and treat the condition.
What Is the Best Treatment for Knee Tendonitis?
Learn what medical treatments can help ease your knee tendonitis symptoms and speed up your recovery.
What Is the Best Treatment for Shoulder Tendonitis?
Learn what medical treatments can help ease your shoulder tendonitis symptoms and help you manage this condition.
The Worst Shoes for Your Feet
Stilettos, platforms or flip-flops... which are the worst shoes for your feet? See how some of the hottest styles can be torture on your feet, learn how damage and foot pain can occur, and discover how to stop foot pain.