Menopause comes to all women. At this time, your body reduces the production of estrogen and progesterone, the hormones that manage your reproductive cycle. The reduced hormone levels in the blood often bring several unpleasant problems. These include night sweats, hot flashes, weight gain, reduced sex drive, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
The reduced hormone levels are also believed to cause calcium loss from your bones. This loss leaves your bones weak, often causing fractures. Hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) helps reduce the troublesome symptoms and prevents bone demineralization. But hormone replacement therapy length is a critical concern.
What is hormone replacement therapy?
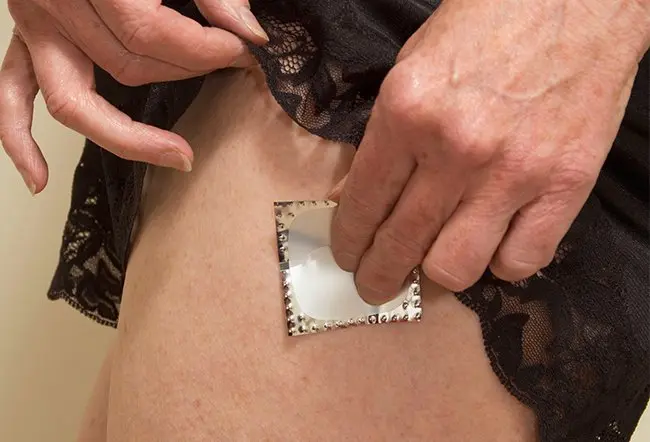
Your doctor will prescribe HRT if you're having an uncomfortable time with the symptoms of menopause. Hormonal replacement therapy consists of pills, sprays, gels, or vaginal products that contain estrogen alone or combinations of estrogen and progesterone (combination HRT).
The symptoms of menopause can last for several years and can significantly reduce your quality of life. Hormonal replacement therapy relieves the symptoms of menopause. Other measures like yoga, hypnosis, acupuncture, stress reduction, dietary supplements, Chinese herbs, and botanical products do not provide the same relief.
If you experience these symptoms with your menopause, you should talk to your doctor. Usually, no tests are needed. Your doctor will prescribe HRT if your symptoms affect you significantly. HRT can be taken continuously or in cycles.
You can take estrogen by itself if you've had a hysterectomy (surgery to remove your uterus). With an intact uterus, your doctor will prescribe a combination of estrogen and progesterone. You can use vaginal creams, pessaries, and rings for local effect. Pills or skin patches are used for systemic effects and the long-term prevention of chronic conditions.
What is the optimal duration of HRT?
The (Food and Drug Administration) FDA recommends that hormonal replacement therapy, whether estrogen-only or in combination with progesterone, should be used at the lowest dose that is effective, and for the shortest duration that fulfills treatment goals.
In general, there isn't a definite duration for HRT. You and your doctor should decide how long you should take it. Once your menopause symptoms pass (which may be several years), you can stop treatment. Stopping hormonal replacement therapy gradually reduces the odds of your symptoms becoming troublesome again. If your symptoms do return, your doctor may restart HRT.
The benefits of HRT
About 70% of women have hot flashes during menopause. As pills or skin patches, estrogen, alone or in combination with progesterone, is the most effective therapy for menopausal hot flashes. HRT also reduces hip fractures, total fractures, and colorectal cancers in women taking it.
About half of all women have genitourinary problems during menopause. These include urinary infections, incontinence (loss of bladder control), painful sex, vaginal dryness, and bleeding during intercourse. Vaginal preparations of estrogen (creams, tablets, or rings) can treat these problems.

QUESTION
If menopause occurs in a woman younger than ___ years, it is considered to be premature. See AnswerThe risks of HRT
Breast cancer. Women who have taken HRT for a year or more have a higher risk of breast cancer than those who have never taken it. This risk is reduced once you stop taking the treatment.
Endometrial cancer. This malignancy of the uterus lining is more common in women given estrogen-only HRT. The risk increases with larger doses and longer durations of treatment. Women given combinations of estrogen and progesterone do not have a higher risk of this cancer.
Stroke. Both estrogen-only and combination HRT increases your likelihood of strokes.
Blood clots. Hormonal replacement therapy is associated with blood clots in the veins (thrombosis). These clots can travel to the heart and block the arteries to the lungs (pulmonary embolism). Transdermal gels (estrogen preparations applied to, and absorbed from, the skin) have a lower risk of venous clots.
On average, women live for 30 years after their menopause. At one time, HRT was expected to prevent several disorders associated with old age, including heart disease, dementia, fractures, and cancers. However, we now know that HRT does not have significant benefits in these areas. The US Preventive Task Force no longer recommends long-term hormonal replacement therapy for prevention of these chronic conditions.
Hot flashes and other symptoms may persist for ten years or more during and after your menopause. However, continuing combination hormone replacement therapy for more than 3 to 5 years increases your risk for breast cancer. Be aware of the dangers of HRT, and discuss carefully with your doctor if you need to continue for longer. If your symptoms make it necessary to take prolonged treatment, use the smallest doses that give you adequate relief.
Journal of the American Medical Association: "Hormone Therapy for the Primary Prevention of Chronic Conditions in Postmenopausal Women. US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement"
National Health Service: "Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)"
Obstetrics and Gynecology: "Management of Menopausal Symptoms"
Top How Long Stay on Hormone Replacement Therapy HRT Related Articles

Tips to Ease Menopause Symptoms
What happens during menopause? At what age do menopause symptoms start? Women in their 40s or 50s may begin to have hot flashes, night sweats, and sleep problems as they enter menopause. See what triggers some menopause symptoms. Get tips for relief through treatment.
15 Things Women Should Know About Menopause
Menopause is a phase in a woman's life that challenges her physically and emotionally. Many women deal with menopause without any medical treatments, whereas some women with severe symptoms require therapies.
9 Signs of Perimenopause
Perimenopause occurs before menopause as estrogen levels begin to change. This can cause menopause like symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, heavy bleeding, weight gain, vaginal dryness, and changes to libido. Pregnancy is still possibly during perimenopause.
Can Hormonal Imbalance Cause Weight Gain?
Hormonal imbalance is a common issue that affects many people. Learn the signs of hormonal imbalance, how it can cause weight gain and other symptoms, how doctors diagnose it, and what you can do to treat it.
What Are the Causes and Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalances in Women?
The main causes of hormonal imbalances are issues with the thyroid, stress, and eating disorders. Some symptoms include irregular periods, low sex-drive, unexplained weight gain, and mood swings. Getting rid of hormonal belly fat involves treating the underlying cause along with diet changes, regular exercise, and stress management.
estradiol/norethindrone acetate
Estradiol/norethindrone acetate is a combination hormone replacement therapy used to relieve menopausal symptoms. Estradiol/norethindrone acetate is used to supplement the fall in secretion of these hormones in menopausal women. Common side effects of estradiol/norethindrone acetate include vaginal bleeding, endometrial thickening, post-menopausal bleeding, uterine fibroid, ovarian cyst, breast pain, headache, back pain, pain in extremity, upper respiratory tract infection, nose and throat inflammation (nasopharyngitis), sinus inflammation (sinusitis), nausea, diarrhea, and others.
25 Hormone Imbalance Symptoms and Signs
Hormone imbalance involves changes in estrogen, progesterone, and other hormone levels. Hormonal imbalance in women may cause symptoms like weight gain, hot flashes, fatigue, and acne. Hormonal changes happen in menopause and at other times. Women with hormone imbalances can seek treatment from medications like triptans and SSRIs.
Does Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) Cause Weight Gain or Loss?
Hormone replacement therapy can help with the symptoms of menopause. Learn more about the potential effects, including how it might impact weight loss or weight gain.
Can Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) Help You Lose Weight and Make You Look Younger?
Research has found that there's no difference in weight gain between women taking HRT and those not taking it. HRT can improve the appearance of the skin, contributing to a younger look.
Menopause
Menopause is the time in a woman's life when menstrual periods permanently stop, also called the "change of life." Menopause symptoms and signs include hot flashes, night sweats, irregular vaginal bleeding, vaginal dryness, painful intercourse, urinary incontinence, weight gain, and emotional symptoms such as mood swings. Treatment of menopausal symptoms varies and should be discussed with your physician.
Menopause Quiz
The Menopause Quiz challenges your knowledge about the time in a woman’s life when menstruation ceases. Menopause can bring many physical, mental and sexual challenges to maturing women, but they don’t have to be limiting. Take the Menopause Quiz to learn the causes, symptoms and treatments of what’s known as "the change of life."
Menopause & Perimenopause: Symptoms, Signs
What is menopause? What are the signs of menopause? What age does menopause start? Learn about menopause and perimenopause symptoms. Find the latest treatments for menopause.
Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the time in a woman's life when she is approaching menopause. During this time a woman starts to develop symptoms of declining estrogen levels that may include mood swings, painful sex, night sweats, hot flashes, and weight gain. Every adult woman eventually will experience perimenopause.
What Are the Signs That You Need Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)?
What is hormone replacement therapy (HRT)? Learn the signs you might need hormone replacement therapy and the different types of therapies.
Sogroya
Sogroya is a prescription medicine that contains human growth hormone, the same growth hormone made by the human body. Sogroya is indicated for the replacement of endogenous growth hormone (GH) in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD). Sogroya is given by injection under the skin (subcutaneous) and is used to treat adults who do not make enough growth hormone.
What Are the 40 Symptoms of Menopause?
Menopause is the end of the reproductive era of a woman's life that is characterized by drastic changes in her emotional and physical aspects. Studies have identified around 40 signs and symptoms of menopause, but not every woman gets all of them.