- Things to Know
- Is It Contagious?
- Symptoms & Signs
- Transmission
- Contagious Period
-
Comments
-
**COMMENTSTAGLIST**
-
More
-
**OTHERTAGLIST**
What is hepatitis C (hep C)?
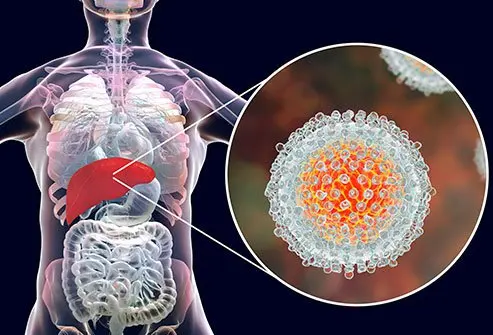
Hepatitis (hep C) is a form of viral hepatitis. Hepatitis C causes acute and chronic liver disease. Hepatitis C is transmitted when the virus in infected blood from one person infects another person. Hepatitis C disease is caused by a virus termed HCV (a single strand RNA virus) that infects liver cells. Hepatitis C was referred to in older scientific publications as non-A or non-B hepatitis.
Is hepatitis C contagious?
Hepatitis C is contagious. It is mainly transmitted via blood-to-blood transfer. This transmission can occur by
- sharing needles,
- acupuncture,
- tattoo needles,
- surgical or diagnostic instruments,
- sexual contact, and
- organ transplants.
Casual contact (including exposure to saliva and skin to skin such as with a handshake or) rarely, if ever, can transmit hepatitis C virus.
How long before I know I'm infected and have hepatitis C?
The incubation period (time from exposure to the virus to symptom development) for hep C is variable. The time period may vary from about 2 weeks to 6 months with 6-10 weeks being the average time span. However, about 80% of those infected may not develop acute symptoms.
Symptoms of hepatitis C develop slowly and include
About 70%-90% of infected people do not clear the virus and become chronic carriers. Tests for diagnosing the hepatitis C virus include detecting antibodies to the virus and a PCR test that detects virus antigens.

QUESTION
Hepatitis C virus causes an infection of the ______________. See AnswerHow does hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C spreads from person to person, usually by direct contact with another person's blood who is infected with hepatitis C virus. Individuals who share needles are at a high risk to become infected. Surgical and other instruments that are not properly decontaminated can also spread hepatitis C to others. Moreover, some patients that receive organ transplants from individuals that have the virus, but no symptoms, can transmit the disease to the organ transplant recipient.
How will you know when you are no longer contagious and cured of hepatitis C?
Treatments are usually long-term (for example, 12-24 weeks ) and a person is not considered "cured" until 6 months have passed with no virus detected in their blood samples. Treatments are varied according to the individual's disease.
When should you call a doctor if you think you may have hepatitis C?
If a person develops one or more of the following symptoms, they should seek medical care:
- About 1-3 days of nausea and vomiting that is not improving
- Yellowish color to the skin and/or the eyes
- Dark urine
- Abdominal pain
Let your doctor know if you shared needles with someone or you have had contact with anyone who has been diagnosed with hepatitis C.
If a person is known to have hepatitis C and develops severe nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, and/or mental status changes (confusion or unresponsiveness, for example), they should be evaluated in an emergency department immediately.
Health News
- More of America's Pets Are Overdosing on Stray Coke, Meth
- GLP-1 Zepbound Is Approved As First Drug For Sleep Apnea
- Feeling Appreciated by Partner is Critical for Caregiver's Mental Health
- Tips for Spending Holiday Time With Family Members Who Live with Dementia
- The Most Therapeutic Kind of Me-Time
 More Health News »
More Health News »
Top Is Hepatitis C Contagious Related Articles

Bilirubin Test
Bilirubin is a waste product of the normal breakdown of red blood cells in the liver. Normal bilirubin levels vary from lab to lab, and range from around 0.2 to 1.2 mg/dL. High levels of bilirubin can be diagnosed with a bilirubin blood test. Causes of elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood can be caused by infections, viral hepatitis, anemia, genetic diseases, and liver problems. Symptoms of elevated bilirubin levels depend on the cause; however, jaundice is a common sign. Treatment for elevated bilirubin levels depends on the cause.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis of the liver refers to a disease in which normal liver cells are replaced by scar tissue caused by alcohol and viral hepatitis B and C. This disease leads to abnormalities in the liver's ability to handle toxins and blood flow, causing internal bleeding, kidney failure, mental confusion, coma, body fluid accumulation, and frequent infections.Symptoms include yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue. The prognosis is good for some people with cirrhosis of the liver, and the survival can be up to 12 years; however, the life expectancy is about 6 months to 2 years for people with severe cirrhosis with major complications.
Hepatitis C Slideshow
What is hepatitis C (Hep C, HVC)? Learn about hepatitis C symptoms, how you get Hep C, contagiousness, and treatment for hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C Quiz
How many Americans have hepatitis C? Take this quiz to learn the facts about this chronic disease.
Hepatitis C, Hep B, Hep A: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Hepatitis C, B, and A are viruses that cause liver inflammation. Hepatitis B vaccines and hepatitis A vaccines are available. Hepatitis symptoms may not appear for weeks to months after infection. Hepatitis A transmission occurs most often via contaminated food. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C transmission require contact with infected bodily fluids or blood.
What Is Viral Hepatitis? How You Catch Hepatitis A, B, and C
Hepatitis C virus and hepatitis B can make an infected person very sick and they are risk factors for liver cancer, liver disease, liver failure, and liver damage. Prior to 1992, blood transfusion was a risk for contracting hepatitis C infection. Hepatitis B and C are blood-borne infections, while hepatitis A is easier to catch, but less serious.
How Does a Person Get Hepatitis?
There are various types of hepatitis, which a person can get by food or water contaminated with the fecal matter of an infected person, sexual contact, blood transfusion, sharing needles, direct contact with an infected person’s blood or body fluid, transfer from mother to the fetus, tattoo needles, or needle prick.
Jaundice in Adults
Jaundice or hyperbilirubinemia in adults is caused by an underlying disease or condition. Learn about when to worry about jaundice in adults, symptoms, treatment, causes, diagnosis, and prevention.
Liver Blood Tests
An initial step in detecting liver damage is a simple blood test to determine the presence of certain liver enzymes in the blood. Under normal circumstances, these enzymes reside within the cells of the liver. But when the liver is injured, these enzymes are spilled into the bloodstream and can lead to diseases like fatty liver, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and hepatitis. Several medications also can increase liver enzyme test results.
Liver Disease
Liver disease can be cause by a variety of things including infection (hepatitis), diseases, for example, gallstones, high cholesterol or triglycerides, blood flow obstruction to the liver, and toxins (medications and chemicals). Symptoms of liver disease depends upon the cause and may include nausea, vomiting, upper right abdominal pain, and jaundice. Treatment depends upon the cause of the liver disease.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a method to analyze a short sequence DNA or RNA. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) has many uses, for example, it is used to diagnose genetic diseases, establish paternity or biological relationships, DNA fingerprinting, DNA forensics, and finding bacteria and viruses.
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is a bacterial infection inside the abdomen. Some doctors choose to group the causes of peritonitis into five categories; 1) primary peritonitis, 2) secondary peritonitis, 3) tertiary peritonitis, 4) chemical (sterile) peritonitis, and 5) peritoneal abscess. Others do not categorize peritonitis, they use a term to describe the disease in front or behind the word peritonitis. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Treatment is generally with antibiotics.
Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis is most often viral, due to infection with one of the hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, E, F (not confirmed), and G) or another virus (such as those that cause infectious mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus disease). The main nonviral causes of hepatitis are alcohol and drugs. Many patients infected with hepatitis A, B, and C have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms. Treatment of viral hepatitis is dependent on the type of hepatitis.
What Does it Mean If You Have Urobilinogen in Your Urine?
Urobilinogen is a substance that is produced when bilirubin, a waste product produced by the breakdown of red blood cells, is processed in the liver and released into the intestine. Excess urobilinogen in urine may indicate liver diseases, such as viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver damage. It is caused by drugs, toxic substances, or conditions associated with increased red blood cell destruction (hemolytic anemia). In a person with low urine urobilinogen and/or signs of liver dysfunction, it can be indicative of hepatic or biliary obstruction.