What is medical marijuana or medical cannabis?

Medical marijuana is the medical use of the Cannabis sativa or Cannabis indica plant to relieve symptoms of or treat diseases and conditions. The Cannabis plant was used medically for centuries around the world until the early 1900s. Medical marijuana facts can be difficult to find because strong opinions exist, both pros and cons. Medical uses and emerging research on off-label uses are summarized in this article.
What are THC and CBD?
THC or Tetrahydrocannabinol
THC or tetrahydrocannabinol is the psychoactive compound in marijuana. It is responsible for the "high" people feel. There are two man-made drugs called dronabinol (Marinol) and nabilone (Cesamet) which are synthetic forms of THC. They are FDA-approved to prevent nausea and vomiting in people receiving chemotherapy.
CBD or Cannabidiol
CBD or cannabidiol is another compound in marijuana that is not psychoactive. CBD is thought to be responsible for the majority of the medical benefits.
Epidiolex is a CBD oil extract that is undergoing clinical trials for epilepsy.
THC: CBD
Nabiximols (Sativex) is a specific plant extract with an equal ratio of THC: CBD. It is approved as a drug in the UK and elsewhere in Europe for the treatment of multiple sclerosis, spasticity, neuropathic pain, overactive bladder, and other indications.
Medical marijuana products are available with a huge range of THC and CBD concentrations. The expert opinion states that 10mg of THC should be considered "one serving" and a person new to medical marijuana should inhale or consume no more until they know their response.
What are the uses for medical marijuana?
Medical uses of marijuana include both studied and approved uses and off-label uses.
In a recent research survey, the most common reasons people use medical marijuana include:
- Pain
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Muscle spasticity
- Inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease
More research has been conducted on the compound CBD. Medical CBD is anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, antioxidant, neuroprotective, anxiolytic, antipsychotic, and anti-emetic. The CBD compound in medical marijuana appears to be neuroprotective in Huntington's, Parkinson's, and Alzheimer's disease, fetal hypoxia, and other neurodegenerative conditions and movement disorders.
What are the health benefits of medical marijuana?
There are over 60 peer-reviewed research studies examining the benefits of medical marijuana. Sixty-eight percent of these studies found benefit while 8% found no benefit. Twenty-three percent of the studies were inconclusive or neutral. Most research has been conducted on the compound CBD.
The benefits of medical marijuana can be attributed to binding to the endocannabinoid system and may include:
- Modulating the immune system
- Promoting neuroplasticity
- Emotional and cognitive modulation including learning and motivation, appetite, vascular function, and digestive function

SLIDESHOW
What Is Pot? Medical Marijuana Laws, Uses, Safety See SlideshowAre there any side effects of medical marijuana?
Medical marijuana side effects are minimal when used at low doses and include:
At higher doses, side effects include:
- Dizziness
- Paranoia
- Psychoactive effects include mood changes and hallucinations
There are concerns about the adverse effects of cannabis among adolescents because the risks are greater to the immature brain and neurological system. Concerns include an increased risk of schizophrenia and loss of IQ.
There are public health concerns about the safety of driving under the influence of medical marijuana. A JAMA study found lower rates of opioid overdose deaths in states with legal medical marijuana.
Is medical marijuana legal?
At the time this article was written, 23 states had legalized medical marijuana with varying restrictions. However, it is classified as a Schedule I substance by the Federal Drug Administration (FDA) and thus is illegal at the Federal level. In most states with legal medicinal marijuana, a prescription, authorization, or medical recommendation is required, and a card or license is issued. This allows a person to buy medical marijuana.
How do you get medical marijuana?
In states where medical marijuana is legal, shops, often called dispensaries, sell marijuana products in a variety of forms, such as:
- Edible forms (candies or cookies)
- Oils
- Extracts
- As the plant which can be smoked or otherwise inhaled
Dispensaries require a medical marijuana card before they will sell products. How people can get a medical marijuana card varies by state. It requires a prescription from a licensed healthcare professional.
Is medical marijuana "addictive?"
Most research suggests a very low risk of addiction and very low toxicity of medical marijuana when taken as recommended in low therapeutic doses. There is concern about psychological dependence in heavy users and whether this constitutes marijuana abuse. Some research has suggested CBD oil might be useful in the treatment of marijuana addiction or marijuana abuse.
Fernández-Ruiz, J. et al. "Cannabidiol for neurodegenerative disorders: important new clinical applications for this phytocannabinoid." Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;75(2):323-33.
Sexton, M., et al. "A Cross-Sectional Survey of Medical Cannabis Users: Patterns of Use and Perceived Efficacy." (Under Review 2016: Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research).
Murnion, B. "Medical Cannabis." Aust Prescr. 2015 Dec; 38(6): 212–215.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4674028/
Bachhuber, MA., et al. "Medical cannabis laws and opioid analgesic overdose mortality in the United States." 1999-2010. JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Oct;174(10):1668-73. Erratum in: JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Nov;174(11):1875.
Allsop, DJ., et al. "Nabiximols as an agonist replacement therapy during cannabis withdrawal: a randomized clinical trial." JAMA Psychiatry 2014;71:281-91.
Brunt, TM., et al. "Therapeutic satisfaction and subjective effects of different strains of pharmaceutical-grade cannabis." J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014 Jun;34(3):344-9.
Top Medical Marijuana (Medical Cannabis) Related Articles
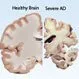
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is a common cause of dementia. Symptoms of Alzheimer's disease include memory loss, difficulty performing familiar tasks, disorientation to time and place, misplacing things, and more. The biggest risk factor for Alzheimer's disease is increased age. Treatment for Alzheimer's is often targeted toward decreasing the symptoms and progression of the disease.
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety is a feeling of apprehension and fear characterized by symptoms such as trouble concentrating, headaches, sleep problems, and irritability. Anxiety disorders are serious medical illnesses that affect approximately 19 million American adults. Treatment for anxiety may incorporate medications and psychotherapy.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism in children and adults is a developmental disorder, characterized by impaired development in communication, social interaction, and behavior. Autism is classified as a pervasive developmental disorder (PDD), which is part of a broad spectrum of developmental disorders affecting young children and adults. There are numerous theories and studies about the cause of autism. The treatment model for autism is an educational program that is suitable to an individual's developmental level of performance. There is no "cure" for autism.
Arterial Chemotherapy Infusion & Chemoembolization of Liver
Arterial chemotherapy infusion of the liver and chemoembolization of the liver (TACE) are used in the treatment of liver cancer. Chemotherapy is directly injected into the hepatic artery so that a higher concentration of chemotherapy agents reach the tumors without subjecting the patient to the toxicity of the chemotherapy. Intra-arterial chemotherapy can cause the following side effects:- inflammation of the gallbladder(cholecystitis),
- intestinal and stomach ulcers, and
- inflammation of the pancreas(pancreatitis).
Drug Abuse and Addiction
Drug abuse and addiction is a chronic disease that causes drug-seeking behavior and drug use despite negative consequences to the user and those around him. Though the initial decision to use drugs is voluntary, changes in the brain caused by repeated drug abuse can affect a person's self-control and ability to make the right decisions and increase the urge to take drugs. Drug abuse and addiction are preventable.
What Is Pot? Medical Marijuana Laws, Uses, Safety
What is medical marijuana? Learn about THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids, learn about marijuana scheduling, state laws for medical marijuana, marijuana addiction, the use of medical marijuana in treatment of seizures in children, edibles, topicals, smoke, and vape, and more.
Marijuana Addiction and Abuse
Cannabis use disorder is when you're addicted to marijuana. Learn more about this condition and how to treat it.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis or MS is an autoimmune disorder in which brain and spinal cord nerve cells become demyelinated. This damage results in symptoms that may include numbness, weakness, vertigo, paralysis, and involuntary muscle contractions. Different forms of MS can follow variable courses from relatively benign to life-threatening. MS is treated with disease-modifying therapies. Some MS symptoms can be treated with medications.
Muscle Spasms
Muscle spasms are involuntary muscle contractions that come on suddenly and are usually quite painful. Dehydration, doing strenuous exercise in a hot environment, prolonged muscle use, and certain diseases of the nervous system may cause muscle spasms. Gently stretching the muscle usually resolves a muscle spasm.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are symptoms of many conditions including motion sickness, pregnancy, emotional stress, gallbladder disease, and other illnesses. Learn about causes, treatment, and when to be concerned.
Pain Management
The goal of pain management for each patient is to minimize suffering and improve quality of life. This goal may be different depending on the patient’s circumstances and disease or injury.
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a slowly progressive neurological disease characterized by a fixed inexpressive face, a tremor at rest, slowing of voluntary movements, a gait with short accelerating steps, peculiar posture and muscle weakness, caused by degeneration of an area of the brain called the basal ganglia, and by low production of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Most patients are over 50, but at least 10 percent are under 40.
Smoking Quiz
You know it's time you quit smoking. Learn the myths and facts about quitting smoking with the Smoking Quiz. When it comes to smoking, quitters always win!