Generic Name: spironolactone
Brand Name: Aldactone
Drug Class: Aldosterone Antagonists, Selective, Diuretics, Potassium-Sparing
What is spironolactone, and what is it used for?
Aldactone (spironolactone) is a potassium-sparing diuretic that removes excess fluid from the body in congestive heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, and kidney disease. It also can be used in combination with other drugs to treat diuretic-induced low potassium (hypokalemia) and high blood pressure. Aldactone also is used to counteract the effects of excessive adrenal aldosterone production (hyperaldosteronism) that can occur from a tumor in the adrenal gland or enlarged adrenal glands (hyperplasia of the adrenal glands).
Aldactone and its active metabolites are specific pharmacologic antagonists of aldosterone, acting primarily through competitive binding of receptors at the aldosterone-dependent sodium-potassium exchange site in the distal convoluted renal tubule. Aldactone causes increased amounts of sodium and water to be excreted, while potassium is retained. Aldactone acts both as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive drug by this mechanism. It may be given alone or with other diuretic agents that act more proximally in the renal tubule.
- Aldactone removes excess fluid from the body in congestive heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, and kidney disease.
- It also can be used in combination with other drugs to treat elevated blood pressure, and for treating diuretic-induced low potassium (hypokalemia).
- Aldactone also is used to counteract the effects of excessive adrenal aldosterone production (hyperaldosteronism). Aldosterone overproduction can occur from a tumor in the adrenal gland or enlarged adrenal glands (hyperplasia of the adrenal glands).
What are the side effects of spironolactone?
Common side effects of Aldactone include:
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Cramps
- Drowsiness
- Rash
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Impotence
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Irregular hair growth
Enlargement of the male breasts (gynecomastia) may also occur and is related to dose and duration of therapy. It usually reverses upon discontinuation of Aldactone.
Possible serious side effects of Aldactone include:
- Liver dysfunction
- Kidney failure
- Anaphylaxis
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Low platelets
- Low white blood cells
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Vasculitis
- Risk of tumors in animal studies
Fluid and electrolytes imbalance (for example, low sodium, low magnesium, and high potassium) may occur, so patients should be monitored carefully.
What is the dosage for spironolactone?
- Aldactone may be taken with or without food. The dosage range is 25-400 mg daily in single or divided doses.
- The initial dose for treating edema in adults is 100 mg daily as a single dose or divided doses. The dose may be adjusted after 5 days based on response. The recommended dose range is 25 to 200 mg daily. The initial dose should be continued for at least 5 days before increasing the dose. If there is no adequate response after 5 days, a second diuretic may be added.
- The dose for treating high blood pressure (hypertension) is 50 to 100 mg daily in single or divided doses.
- The dose for treating hypokalemia is 25 to 100 mg daily.
QUESTION
In the U.S., 1 in every 4 deaths is caused by heart disease. See AnswerWhich drugs interact with spironolactone?
- Aldactone can lower blood sodium levels while raising blood potassium levels. Excessively high blood potassium levels can lead to potentially life-threatening abnormalities in the rhythm of the heart. Therefore, Aldactone usually is not administered with other agents that can raise blood potassium levels, such as potassium supplements, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors [for example, enalapril (Vasotec)], indomethacin (Indocin), or other potassium-sparing diuretics.
- Aldactone can cause elevation of blood digoxin (Lanoxin) to toxic levels, requiring adjustment of the digoxin dosage.
Is spironolactone safe to take if I'm pregnant or breastfeeding?
- There are no adequate studies in pregnant women. Aldactone may be harmful if used for treating gestational hypertension (high blood pressure during pregnancy).
- An active metabolite of Aldactone is secreted in breast milk. To avoid adverse effects in the newborn, mothers should avoid breastfeeding while taking Aldactone.
What else should I know about spironolactone?
What preparations of spironolactone are available?
- Tablets: 25, 50, and 100 mg
How should I keep spironolactone stored?
- Aldactone should be stored at room temperature, below 25 C (77 F).
Health News
- More of America's Pets Are Overdosing on Stray Coke, Meth
- GLP-1 Zepbound Is Approved As First Drug For Sleep Apnea
- Feeling Appreciated by Partner is Critical for Caregiver's Mental Health
- Tips for Spending Holiday Time With Family Members Who Live with Dementia
- The Most Therapeutic Kind of Me-Time
 More Health News »
More Health News »
Summary
Spironolactone is classified as a potassium-sparing diuretic. It is prescribed for the treatment of congestive heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, and kidney disease. It can also be used in combination with other drugs to treat diuretic induced low potassium and high blood pressure. Common side effects of Aldactone include headache, diarrhea, cramps, drowsiness, rash, nausea, vomiting, impotence, irregular menstrual periods, and irregular hair growth.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
-

What Is High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)? Symptoms, Treatments
What causes high blood pressure (hypertension)? What is normal blood pressure? Know the warning signs and symptoms of high blood...
-

Heart Healthy Diet: 25 Foods You Should Eat
What foods are heart healthy? Learn what foods help protect your cardiovascular system from heart attack, coronary heart disease,...
-

Heart Disease: Causes of a Heart Attack
Heart disease prevention includes controlling risk factors like diet, exercise, and stress. Heart disease symptoms in women may...
-

Am I Having a Heart Attack? Symptoms of Heart Disease
Heart attacks symptoms vary greatly for men and women, from anxiety and fatigue to nausea and sweating. Learn the warning signs...
-

Heart Disease: Symptoms, Signs, and Causes
What is heart disease (coronary artery disease)? Learn about the causes of heart disease, arrhythmias and myopathy. Symptoms of...
-

Kidney Disease Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Kidney disease is common. Take this kidney disease quiz to test your knowledge and learn the symptoms, causes and types of kidney...
-

High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Quiz: Symptoms, Signs & Causes
Take this quiz and test your IQ of high blood pressure (hypertension), the cardiovascular disease that causes most strokes and...
-
Heart Disease Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Take our Heart Disease Quiz to get answers and facts about high cholesterol, atherosclerosis prevention, and the causes,...
-

Liver Disease Quiz: Fatty Liver Disease, Cirrhosis & Symptoms
What is liver disease? Take the Liver Disease Quiz and test your knowledge about this organ and its function.
-

Heart Failure Quiz
What is heart failure? Learn about this dangerous condition, as well as who is at risk, and what to do about it.
-
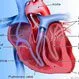
Picture of Heart Detail
The heart is composed of specialized cardiac muscle, and it is four-chambered, with a right atrium and ventricle, and an...
-

Picture of Liver
Front View of the Liver. The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly. See a picture of the Liver...
-

Picture of Kidneys
The kidneys are a pair of organs located in the back of the abdomen. See a picture of the Kidneys and learn more about the health...
-
Picture of Heart
The muscle that pumps blood received from veins into arteries throughout the body. See a picture of the Heart and learn more...
-

Heart Disease: Best and Worst Foods for Heart Failure
Learn which dietary changes help your heart, and which ones make it work harder.
-

Food Swaps for Meals and Snacks for Heart Health in Pictures
Explore 10 food swaps for heart-wise dining. Learn what food to buy and how to cook in order to make a big difference for your...
Related Disease Conditions
-

Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis of the liver refers to a disease in which normal liver cells are replaced by scar tissue caused by alcohol and viral hepatitis B and C. This disease leads to abnormalities in the liver's ability to handle toxins and blood flow, causing internal bleeding, kidney failure, mental confusion, coma, body fluid accumulation, and frequent infections. Symptoms include yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue. The prognosis is good for some people with cirrhosis of the liver, and the survival can be up to 12 years; however, the life expectancy is about 6 months to 2 years for people with severe cirrhosis with major complications.
-

What Is Considered Stroke-Level High Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure readings above 180/120 mmHg are considered stroke-level and require immediate medical attention. Check out the center below for more medical references on hypertension, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related diseases, treatment, diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
-

High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
High blood pressure (hypertension) occurs due to the tightening or stiffness of very small arteries called arterioles. As a result, the heart pumps harder through the stiff or narrow arterioles, leading to elevated pressure inside the vessels. Hypertension is known as 'the silent killer' because it often goes unnoticed and may cause serious complications such as kidney diseases, heart diseases, heart failure, and stroke.
-

Liver Disease
Liver disease can be cause by a variety of things including infection (hepatitis), diseases, for example, gallstones, high cholesterol or triglycerides, blood flow obstruction to the liver, and toxins (medications and chemicals). Symptoms of liver disease depends upon the cause and may include nausea, vomiting, upper right abdominal pain, and jaundice. Treatment depends upon the cause of the liver disease.
-

Kidney Failure
Kidney failure can occur from an acute event or a chronic condition or disease. Prerenal kidney failure is caused by blood loss, dehydration, or medication. Some of the renal causes of kidney failure include sepsis, medications, rhabdomyolysis, multiple myeloma, and acute glomerulonephritis. Post-renal causes of kidney failure include bladder obstruction, prostate problems, tumors, or kidney stones. Treatment options included diet, medications, or dialysis.
-
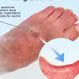
Edema
Edema is swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the tissues of the body and occurs most often in the legs, feet, ankles, or hands. Learn about the different types, causes, symptoms, and treatments to alleviate fluid retention.
-

Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Congestive heart failure (CHF) refers to a condition in which the heart loses the ability to function properly. Heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, myocarditis, and cardiomyopathies are just a few potential causes of congestive heart failure. Symptoms of congestive heart failure may include fatigue, breathlessness, palpitations, angina, and edema.
-

How the Heart Works
The heart is a very important organ in the body. It is responsible for continuously pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood throughout your body to sustain life. It is a fist-sized muscle that beats (expands and contracts) 100,000 times per day, pumping a total of five or six quarts of blood each minute, or about 2,000 gallons per day.
-
Ascites
Ascites (fluid retention) are an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, often caused by liver disease or cirrhosis, cancers, or heart failure. Learn about symptoms, types, and treatment.
-

Liver
The liver is the largest gland and organ in the body. There are a variety of liver diseases caused by liver inflammation, scarring of the liver, infection of the liver, gallstones, cancer, toxins, genetic diseases, and blood flow problems. Symptoms of liver disease generally do not occur until the liver disease is advanced. Some symptoms of liver disease include jaundice, nausea and vomiting, easy bruising, bleeding excessively, fatigue, weakness, weight loss, shortness of breath, leg swelling, impotence, and confusion. Treatment of diseases of the liver depends on the cause.
-

Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)
Heart disease (coronary artery disease) occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, the vessels that supply blood to the heart. Heart disease can lead to heart attack. Treatment of heart disease involves control of heart disease risk factors through lifestyle changes, medications, and/or stenting or bypass surgery. Heart disease can be prevented by controlling heart disease risk factors.
-

Can You Be Physically Fit and Have High Blood Pressure?
It is entirely possible and common for physically fit people to have high blood pressure (hypertension). Check out the center below for more medical references on high blood pressure, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
-
Low Potassium (Hypokalemia)
Low potassium or hypokalemia is a decrease in blood potassium levels, which is caused by colon polyps, vomiting, diarrhea, medications, and laxatives. Foods in the diet are how the body absorbs potassium. Symptoms of low potassium in the blood include palpitations, muscle cramps, and muscle aches. Treatment for low potassium is low potassium through diet IV.
-

Things to Know About High Blood Pressure Treatment
High blood pressure (hypertension) means high pressure (tension) in the arteries. Treatment for high blood pressure include lifestyle modifications (alcohol, smoking, coffee, salt, diet, exercise), drugs and medications such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta blockers, diuretics, calcium channel blockers (CCBs), alpha blockers, clonidine, minoxidil, and Exforge.
-
High Potassium (Hyperkalemia)
Hyperkalemia is an abnormally high level of potassium in the blood. Hyperkalemia symptoms include nausea, fatigue, tingling sensations, or muscle weakness. Hyperkalemia may also cause no symptoms. Hyperkalemia treatment may include a low-potassium diet, medications, and intravenous glucose and insulin. Causes of hyperkalemia include kidney dysfunction, certain medications, adrenal gland diseases, and potassium shifts.
-
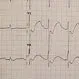
Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmias)
Heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias) occur when the heart's electrical system malfunctions. Discover the different types (like atrial fibrillation), causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prevention tips.
-

Acne
Acne is a localized skin inflammation as a result of the overactivity of oil glands at the base of hair follicles. This inflammation, depending on its location, can take the form of a superficial pustule (contains pus), a pimple, a deeper cyst, congested pores, whiteheads, or blackheads. Treatments vary depending on the severity of the acne.
-
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), also known by the name Stein-Leventhal syndrome, is a hormonal problem that causes women to have a variety of symptoms including irregular or no menstrual periods, acne, obesity, and excess hair growth. Treatment of PCOS depends partially on the woman's stage of life and the symptoms of PCOS.
-

Cystic Acne
Cystic acne is distinguished by painful nodules on the chest, face, neck, and back. This form of acne is known to scar. Treatment may incorporate the use of hormonal therapies, oral antibiotics, and prescription medications.
-

How Long Can You Live With Heart Failure?
What is the life expectancy of people with heart failure? Learn about survival rates, determining factors, and lifestyle changes that may help increase your life expectancy.
-
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) Treatment
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is thought to be an autoimmune disorder that involves the deterioration of the liver's small bile ducts. These ducts are crucial to transport bile to the small intestine, digesting fats, and removing wastes. Symptoms of PBC are edema, itching, elevated cholesterol, malabsorption of fat, liver cancer, gallstones, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and hypothyroidism. Treatments include ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA); colchicine (Colcrys); and immunosuppressive medications, such as corticosteroids; obeticholic acid (Ocaliva); and medications that treat PBC symptoms. For PBC that is associated with cirrhosis of the liver, liver transplantation may be indicated in extreme cases.
-

What Is High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)?
High blood pressure or hypertension is when the blood pressure readings consistently range from 140 or higher for systolic or 90 or higher for diastolic. Blood pressure readings above 180/120 mmHg are dangerously high and require immediate medical attention.
-

How Do You Strengthen Your Heart After Heart Failure?
You can strengthen your heart after heart failure by making recommended changes to your diet, exercising regularly, and adopting healthy habits.
Treatment & Diagnosis
- High Blood Pressure FAQs
- Heart Disease FAQs
- Kidney Disease FAQs
- Liver Disease FAQs
- Heart Failure FAQs
- Drugs: Buying Prescription Drugs Online Safely
- Drugs: The Most Common Medication Errors
- Medication Disposal
- Heart Failure: What Killed George Carlin?
- Pharmacy Visit, How To Get The Most Out of Your Visit
- Indications for Drugs: Approved vs. Non-approved
- Generic Drugs, Are They as Good as Brand-Names?
Medications & Supplements
- spironolactone - oral, Aldactone
- Drugs: Questions to Ask Your Doctor or Pharmacist about Your Drugs
- Drug Interactions
- Types of High Blood Pressure Medications
- triamterene and hydrochlorothiazide
- Congestive Heart Failure Medications
- Why Are Diuretics Used in Heart Failure?
- Types of High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Medications
- spironolactone/hydrochlorothiazide
- Aldactone (spironolactone) Side Effects, Interactions, and Warnings
- Carospir (spironolactone)
Prevention & Wellness

Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.