- What Is an IUD?
- Moved IUD
- Symptoms
-
Comments
-
**COMMENTSTAGLIST**
-
More
-
**OTHERTAGLIST**
What is an IUD?

An intrauterine device or IUD is a popular birth control device. It is placed inside the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It is a reversible contraceptive. You can remove it anytime if you wish to get pregnant. Modern day IUDs are one of the safest and most effective birth control methods available. IUDs are of two main types: copper and hormonal IUDs. They work in either of the two ways:
- They release a hormone (progesterone) or the copper in them changes the nature of the sticky fluid in the cervix (cervical mucus). This makes the survival of sperm inside the uterus difficult.
- They cause changes in the lining of the uterus that prevents attachment or implantation of a zygote if fertilization occurs.
What does it mean to have a moved IUD?
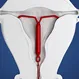
For effective contraception, IUD must be properly positioned inside the uterus. This is ensured by a healthcare professional when inserting the IUD. An IUD is said to be correctly positioned when it is in the uterine cavity near the fundus (the dome-shaped upper part of the uterus). The stem of the IUD should extend toward the cervix (neck of the uterus). The two arms of the IUD must be fully unfolded (forming a “T” shape with the stem) during insertion, reaching laterally toward the two uterine cornua (the points where the uterus meets the fallopian tubes). An IUD is said to be displaced if any of the following three things occur:
- The IUD moved out of the uterus (expulsion).
- The IUD is not positioned correctly inside the uterus (displacement).
- The IUD got buried or embedded in the walls of the uterus (embedment).
- The IUD pierced through the walls of the uterus and entered inside the abdomen (perforation).
Doctors generally schedule a follow-up visit a month after IUD insertion to make sure the IUD is in its place. IUD movement is rare and if it happens at all, it is usually during the first few months after the IUD insertion.
What are the symptoms of a moved IUD?
A misplaced IUD may not work effectively as a contraceptive. Hence, you must know how to find out if the IUD has moved. IUDs come with a thin string attached at their end which can be felt through the vagina. To feel the string
- Wash your hands well. Make sure your nails are trimmed.
- Sit or squat and insert one finger into the vagina.
- Feel your cervix (It feels firm like the tip of the nose).
- Try to feel the string coming out of the cervix. Do not pull or tug on the string.
You may check this every month after your period. While feeling the string you may notice
- The string length seems the same as before. This may mean that your IUD is in its place.
- The string feels shorter or could not be felt. This may either mean the string has curled up or the IUD has moved. Contact your doctor.
- The string feels longer than usual. This may mean that the IUD has moved. Contact your doctor.
Besides the change in the string length, a moved IUD may cause the following signs and symptoms:
- You can feel the IUD with your fingers (normally only the string is felt).
- Your partner may feel the IUD during sex.
- You have excessive bleeding during your period or bleeding or spotting between periods.
- Painful intercourse.
- Excessive pain or cramps in the abdomen.
- Foul-smelling or unusual vaginal discharge.
- Fever.
If you think your IUD has moved, do not try correcting it yourself. Contact your doctor right away.

SLIDESHOW
Sex-Drive Killers: The Causes of Low Libido See SlideshowUltrasonography: "Ultrasonography of Intrauterine Devices." https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4484292/
Top What Are the Symptoms of a Moved IUD Related Articles

Birth Control Options
Birth control is available in a variety of methods and types. The method of birth control varies from person to person, and their preferences to either become pregnant or not. Examples of barrier methods include barrier methods (sponge, spermicides, condoms), hormonal methods (pill, patch), surgical sterilization (tubal ligation, vasectomy), natural methods, and the morning-after pill. Side effects and risks of each birth control option should be reviewed before using any birth control method.
How Painful Is Getting an IUD?
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small T-shaped birth control device, about the size of a quarter, that is placed inside a woman’s uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one of the most popular contraceptive options for women. It is a reversible contraceptive, meaning it can be removed if pregnancy is desired. Modern-day IUDs are one of the safest and most effective birth control methods.
Is It Painful to Have an IUD Inserted?
Gynecologists insert a T-shaped device into the woman’s uterus (womb). This process is quick and not very painful. However, some pain is inevitable, and pain experience is different for every woman. It is normal to feel some discomfort when the opening of the womb (cervix) is stretched. For most women, this only lasts for a few seconds and may be felt as a sharp pain.
Is It Painful to Remove an IUD?
Removing an IUD when you aren't having complications shouldn’t take very long and shouldn’t be very painful. Most people say that IUD insertion is more painful than its removal.
IUD (Intrauterine Device)
An IUD (intrauterine device) is a birth control method designed for a woman. The IUD is a small "T" made of molded polyethylene plastic coated with barium so that, if need be, it can be seen on X-ray. Side effects of the IUD include spotting, infection, infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and heavy menstrual bleeding. Risks and complications of the IUD are miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased menstrual bleeding.
levonorgestrel-releasing 5 year system - intrauterine, Mirena
Mirena Weight Gain: Do IUDs Cause Weight Gain?
Nonhormonal IUDs generally do not cause any weight gain. Hormonal IUDs cause weight gain in about 5% of patients. As Mirena is a hormonal IUD, there are chances of weight gain. This weight gain is mainly due to the hormone progestin that causes water retention and bloating.
What Are Intrauterine Devices?
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a method of contraception that requires the placement of a small, T-shaped device inside the uterus. Contraception or birth control refers to precautionary measures to prevent vaginal intercourse from resulting in pregnancy.