- Definition
- Signs and Symptoms
- Types
- Causes
- When to See a Doctor
- Diagnosis
- Treatments
-
Comments
-
**COMMENTSTAGLIST**
-
More
-
**OTHERTAGLIST**
What is pneumonia?
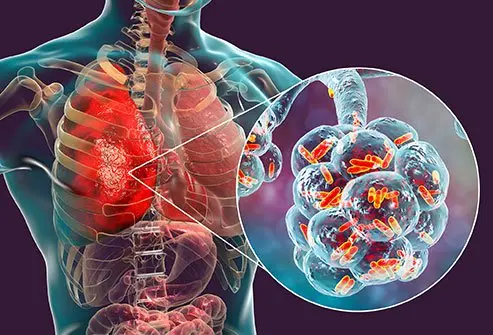
Pneumonia is a type of infection that affects your lungs. It can affect one or both lungs. It causes the air sacs in the lungs, called alveoli, to fill with pus or other liquid.
Pneumonia is caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or, more rarely, parasites. People of all ages can develop pneumonia. In some cases, it is mild and not much worse than a bad cold. In others, it can be life-threatening.
Older people and young children are most at risk of developing severe pneumonia. It can also be very serious for people with underlying chronic health problems or a weakened immune system.
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia may include any combination of the following:
Types of pneumonia
One way doctors classify pneumonia is based on where or how you got it. Knowing this can help your doctor decide on a course of treatment for your pneumonia.
Community-acquired pneumonia
This type of pneumonia occurs in a community setting, which is defined as somewhere other than a hospital, rehabilitation center, nursing home, or other types of healthcare facilities.
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
This type of pneumonia happens when you catch it while you're in a hospital or another type of healthcare facility, such as a nursing home. Hospital-acquired pneumonia develops in people at least 48 hours after being admitted. It does not include people who develop pneumonia while they are on a ventilator, as that is a separate type of pneumonia.
Ventilator-associated pneumonia
This occurs when people who are on a ventilator develop pneumonia. It occurs at least 48 hours after intubation, which is when the ventilator tube is placed in the airway so that a ventilator can assist with breathing.
Aspiration pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia happens when food, liquid, or vomit is inhaled into the lungs. When this happens, a healthy respiratory system can usually clear it up on its own, but in some cases, an infection develops

SLIDESHOW
How to Prevent the Common Cold See SlideshowCauses of pneumonia
Regardless of where it's acquired, pneumonia has three primary causes and a fourth, much rarer, cause:
Bacterial pneumonia
- Most commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Can also be caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, a bacterium that causes a milder form of pneumonia
- Can also be caused by Chlamydophila pneumoniae, which also causes milder pneumonia
- More rarely caused by Legionella pneumophila, also known as Legionnaires’ Disease, caused by exposure to contaminated water
Viral pneumonia
- Not as serious as bacterial pneumonia, but can be severe in pregnant women and people with existing heart and lung disease
- In adults, viral pneumonia is usually caused by the influenza virus
- In children, viral pneumonia is usually caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Fungal pneumonia
- Most common in people with chronic health problems or weakened immune systems, such as occurs with HIV/AIDS
- Also occurs in people who are exposed to large amounts of fungi in contaminated soil or bird droppings
Parasitic pneumonia
- Rare cause of pneumonia, almost always occurs in people with compromised immune systems
- Parasites get into the body through the skin or by being swallowed and travel to the lungs
When to see a doctor for pneumonia
You should call your doctor if you have a cough that doesn't improve, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, chest pain, fever, or you feel worse after having a cold.
Health News
- More of America's Pets Are Overdosing on Stray Coke, Meth
- GLP-1 Zepbound Is Approved As First Drug For Sleep Apnea
- Feeling Appreciated by Partner is Critical for Caregiver's Mental Health
- Tips for Spending Holiday Time With Family Members Who Live with Dementia
- The Most Therapeutic Kind of Me-Time
 More Health News »
More Health News »
Diagnosing pneumonia
Your doctor may be able to diagnose pneumonia by listening to your symptoms and doing a physical exam. Other tests may be done, including a chest X-ray, blood tests, sputum culture, which is testing the mucus you cough up, and pulse oximetry, which tests the oxygen level in your blood.
Treatments for pneumonia
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the cause.
Bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is generally treated with antibiotics.
Viral pneumonia
Antibiotics are not effective against viral pneumonia, so they usually get better on their own. Sometimes doctors prescribe antivirals for viral pneumonia.
Fungal pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is treated with an antifungal medication that is appropriate for the type of fungus causing pneumonia.
Parasitic pneumonia
Treatment for parasitic pneumonia will depend on the type of parasite involved and the underlying issues that weakened the immune system.
Symptomatic relief
Regardless of the cause or treatment of pneumonia, most people can find symptomatic relief with the following measures:
- Drink plenty of liquids, including hot liquids such as tea.
- Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen to control fever.
- Inhale the steam from a hot shower or use a humidifier.
- Get lots of rest.
- Don't take cough medicine without talking to your doctor. Coughing helps your body fight the infection.
- Take honey for a cough or sore throat, but don't give honey to children under the age of one.
American Lung Association: "Pneumonia."
Biomed Research International: "Parasitic Pneumonia and Lung Involvement."
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: "Causes of Pneumonia."
Craig Hospital: "Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) Prevention."
John Hopkins Medicine: "Pneumonia."
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: "Pneumonia."
Northwestern Medicine: "What is Aspiration Pneumonia?"
Pediatrics in Review: "Pneumonia."
StatPearls: "Bacterial Pneumonia."
StatPearls: "Pediatric Pneumonia."
StatPearls: "Viral Pneumonia."
World Health Organization: "Pneumonia."
Top What are the Three Major Causes of Pneumonia Related Articles

Respiratory Illnesses: 13 Types of Lung Infections
Is your cough caused by a cold, flu, pneumonia or something else? Learn causes of respiratory infection like bronchitis, pneumonia, SARS, Coronavirus COVID-19 bird flu, and more.
Augmentin (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, Augmentin XR, Augmentin ES-600, Amoclan)
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid (Augmentin Amoclan, Augmentin XR, Augmentin ES-600) is an antibiotic used to treat middle ear infections, sore throat, sinus infection, bronchitis, pneumonia, and urinary tract infections. Side effects include abdominal discomfort, bloating, diarrhea, gas, headache, heartburn, nausea, and vomiting.
amoxicillin/clavulanate
Amoxicillin/clavulanate is a combination antibacterial medication used to treat various types of bacterial infections, including lower respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, acute otitis media, sinusitis, acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, skin and skin structure infections, urinary tract infection, and others. Common side effects of amoxicillin/clavulanate include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distress, gas (flatulence), Candida yeast infection (candidiasis), diaper rash, Candidal diaper rash, skin rash, hives (urticaria), vaginal fungal infection (mycosis), vaginal inflammation (vaginitis), headache, and excessive platelet production (thrombocytosis).
Can Pneumonia Go Away On Its Own?
Mild pneumonia may be healed by body’s defense system. However severe cases of pneumonia require medical attention especially viral pneumonia.
cefuroxime
Cefuroxime is an antibiotic used to treat infections of the middle ear, sinuses, skin, tonsils, and throat, and to treat laryngitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, gonorrhea, COPD, and early Lyme disease. Common side effects of cefuroxime include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headache, rash, hives, vaginitis, and mouth ulcers.
cephalexin
Cephalexin is a prescription antibiotic used for treating middle ear infections (otitis media), tonsillitis, laryngitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections (UTIs), skin infections, bone infections, throat infections, bronchitis, and bone infections. Common side effects of cephalexin include diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, headaches, and vaginitis. Dosage of cephalexin depends on the type of infection.
clindamycin
Clindamycin is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections including septicemia, pelvic inflammatory disease, abdominal, gynecological, respiratory tract, bone and joint, and skin and skin structure infections. Common side effects of clindamycin include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, skin reactions, jaundice, abnormal liver function test results, and others. Use clindamycin during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Avoid use when breastfeeding if possible.
How Long Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Pneumonia may be contagious for 2-14 days. Usually, the goal of medications given for pneumonia is to limit the spread of the disease.
Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial lung disease refers to a variety of diseased that thicken the tissue between the lungs' air sacks. Symptoms of interstitial lung disease include shortness of breath, cough, and vascular problems, and their treatment depends on the underlying cause of the tissue thickening. Causes include viruses, bacteria, tobacco smoke, environmental factors, cancer, and heart or kidney failure.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Pneumonia is inflammation of the lung usually caused by bacterial or viral infection (rarely, also by fungi) that causes the air sacs to fill with pus. If inflammation affects both lungs, the infection is termed double pneumonia. If it affects one lung, it is termed single pneumonia. If it affects only a certain lobe of a lung it's termed lobar pneumonia. Most pneumonias are caused by bacteria and viruses, but some pneumonias are caused by inhaling toxic chemicals that damage lung tissue.
Reasons You're Short of Breath
Have you ever found yourself gasping for air after just a short flight of stairs? You may just need to do a bit more exercise, or it could be something more serious.
ofloxacin
Ofloxacin is an antibiotic medication prescribed for the treatment of pneumonia, bronchitis, staph infections, STDs (gonorrhea, chlamydia), urinary tract infections, and prostate infections caused by E. coli. The most common side effects of ofloxacin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, insomnia, headache, dizziness, itching, and vaginitis in women. Do not take ofloxacin if pregnant or breastfeeding.
Penicillin (Antibiotics)
Penicillin antibiotics are prescribed to treat a variety of types of infections. For example, middle ear and sinus infections; bladder, stomach, intestines, and kidney; pneumonia; sepsis; meningitis; endocarditis; and many other serious infections. Examples of penicillin antibiotics, side effects, drug interactions, and pregnancy and breastfeeding safety information should be reviewed prior to taking any medication.
Pneumococcal Vaccination
Pneumococcal vaccination prevents one of the most common and severe forms of pneumonia. It is usually given only once in a lifetime, usually after the age of 55, to someone with ongoing lung problems (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma) or other chronic diseases (including those involving the heart and kidneys).
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs caused by fungi, bacteria, or viruses. Symptoms and signs include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chills. Antibiotics treat pneumonia, and the choice of the antibiotic depends upon the cause of the infection.
Do I Have Pneumonia Quiz
Pneumonia can be deadly. Take the Pneumonia Quiz on MedicineNet to learn more about this highly contagious, infectious disease.
Surprising Causes of Lung Damage
Carpets, fireworks, and hot tubs are some of the unexpected things that can hurt your lungs. Find out what you can do to prevent problems from these and other culprits.
What Are the Side Effects of the Pneumonia Vaccine?
The pneumonia vaccine can help protect against pneumococcal infections. Learn what the pneumonia vaccine is all about, and what to do if you experience side effects. Pneumonia is an infection in your lungs that is usually caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi.
What Is the Most Common Cause of Bronchiectasis?
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition in which the bronchi (tube-like passageways that transfer air within the lungs) get permanently damaged and widened. The most common causes of bronchiectasis are pneumonia, pertussis, tuberculosis and non-tuberculosis mycobacterium.