What is the hippocampus?
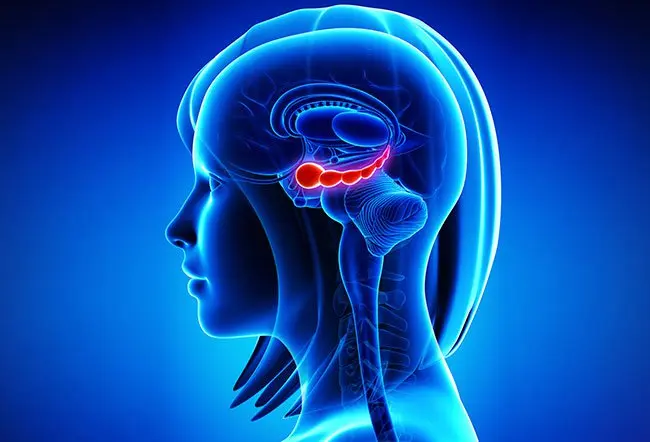
The hippocampus is part of the limbic system in the brain, the part of the brain that regulates our emotional and behavioral responses. The hippocampus contributes to learning and memory as well as emotion.
The hippocampus is one of the most studied parts of the brain. Scientists are particularly interested in the atrophy of the hippocampus, which shrinks in persons with Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and other disorders. Hippocampal atrophy is related to cognitive decline, particularly when it comes to the ability to access old memories or make new ones.
The hippocampus is crucial, and it is important to protect this vulnerable part of the brain and to see a doctor early if you suspect it may be atrophying in you or someone else.
Signs and symptoms of hippocampus atrophy
Because the hippocampus is involved in so many brain functions, hippocampus atrophy can produce multiple different symptoms, some of which are closely associated with particular conditions.
Symptoms that are particularly related to Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia include:
- Memory loss that disrupts daily life such as appointments or events
- Difficulty solving problems or planning
- Confusion about place or time
- Difficulty completing familiar tasks
- Difficulty with images and spatial relationships
- Problems with words, either speaking or writing
- Misplacing things and not being able to retrace steps
- Decreased judgment
- Social or professional withdrawal
- Changes in mood or personality
It can often be difficult to judge whether these symptoms are related to dementia or to typical age-related changes. However, early detection matters, so schedule a doctor’s visit if you’re concerned.
Causes of hippocampus atrophy
The vulnerability of the hippocampus has not been fully explained, nor have the biological mechanisms that might play a role in causing it to shrink. The following all appear to play a role in hippocampus health:
- Age
- Genetics
- Lifestyle
- Environment
Hippocampus atrophy is a consistent feature in the following conditions:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Depression
- Schizophrenia
- Epilepsy
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Cushing’s disease
- Trauma
Diagnosis for hippocampus atrophy
If your doctor suspects that your hippocampus has atrophied, they will base their diagnosis on multiple sources of information. These may include any or all of the following:
- A detailed personal and family medical history
- A physical exam
- A neurological exam to test basic functions
- Brain imaging with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT)
- Mental status tests on memory and the ability to solve simple problems
- Mood assessment

SLIDESHOW
Brain Food Pictures: What to Eat to Boost Focus See SlideshowTreatments for the hippocampus
While many of the problems associated with hippocampus deterioration have no absolute “cure,” there are things you can do to keep your hippocampus healthy.
Maintain a healthy diet
Limit your intake of saturated fat and stick to healthy fats, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Look for foods that are rich with antioxidants. You should also consume foods with omega-3 fatty acids such as fish or olive oil. Avoid alcohol, which has been associated with hippocampus atrophy.
Stay mentally and socially active
Both mental and social stimulation are important to hippocampus size. Keep your brain healthy with puzzles, games, and new challenges. Social relationships and interaction also play a role. They help ward off depression, which is associated with hippocampal atrophy. Studies of older people routinely demonstrate the importance of social activity to hippocampus function.
Exercise
Exercise may help you keep the hippocampus healthy through both direct and indirect means. Its indirect benefits come from exercise’s ability to lower blood pressure and prevent metabolic issues, both of which are linked to brain decay.
Aerobic exercise is particularly important and directly benefits the hippocampus. One study found that regular aerobic exercise boosts the size of the hippocampus.
Stay current with medical developments
Alzheimer’s disease affects many people and is a frequent subject of research. New information about brain health is continually emerging, leading to new medications and protocols. One current topic of research is neural stem cell grafting as a way to protect against some of the consequences of hippocampal atrophy.
Talk to your doctor about recent developments in the field and get updates as necessary.
Health News
- Check Your Pantry, Lay's Classic Potato Chips Recalled Due to Milk Allergy Risk
- California Declares Bird Flu Emergency as Outbreak in Cows Continues
- Not Just Blabber: What Baby's First Vocalizations and Coos Can Tell Us
- Norovirus Sickens Hundreds on Three Cruise Ships
- FDA Updates Meaning of 'Healthy' on Food Labels
 More Health News »
More Health News »
Alzheimer's Association: "Medical Tests."
The American Journal of Medicine: "Association of Long-Term Diet Quality with Hippocampal Volume: Longitudinal Cohort Study."
Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology: "Hippocampus in health and disease: An overview."
Epilepsy & Behavior: "Hippocampal Injury Induced Cognitive and Mood Dysfunction, Altered Neurogenesis and Epilepsy: Can Early Neural Stem Cell Grafting Intervention Provide Protection?"
Harvard Health Publishing: "Regular exercise changes the brain to improve memory, thinking skills."
University of California Irvine Health: "When to worry about memory loss."
Top What Is the Hippocampus and What Does It Do Related Articles
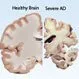
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is a common cause of dementia. Symptoms of Alzheimer's disease include memory loss, difficulty performing familiar tasks, disorientation to time and place, misplacing things, and more. The biggest risk factor for Alzheimer's disease is increased age. Treatment for Alzheimer's is often targeted toward decreasing the symptoms and progression of the disease.
Alzheimer's Quiz
Take the Alzheimer's Quiz to discover some of the mysteries behind this cognitive disorder. Learn causes, symptoms, treatments, diagnosis, and little-known facts about Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the brain disorders it can mimic.
Brain Foods Slideshow
Learn how to increase concentration and boost memory. Brain foods such as fish (omega 3 fatty acids), berries, fruits, nuts, chocolate, vitamins and more can help.
Dementia Foods: Foods that May Lower Dementia Risk
What foods are associated with Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia? Cognitive function is predicated on good nutrition. Learn how vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins like fish can lead to a healthier brain. Discover why foods that stave off heart disease are good for brain function.
10 Facts About the Amazing Brain Quiz
Take this brain quiz to learn about your amazing brain! It's the most complex part of your body, and is responsible for many functions, including how you behave!
The Stages of Dementia: Alzheimer's Disease and Aging Brains
What are the symptoms of dementia? What causes dementia? Dementia includes many disorders, such as Lewy Body dementia, Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, and more. Learn the warning signs of dementia.
How Conditions Change Your Brain
The brain doesn’t always stay the same. Mental disorders, health issues, and lifestyle habits can alter the way it looks and works.
How the Brain Works: Test Your Medical IQ
Take this quiz and test your knowledge of how the human brain works. You may be surprised!
Left Brain vs. Right Brain
Are left brain vs. right brain theories myth or fact? They actually are a little of both! Scientists and researchers have tried to answer this question since the 1800s. In the 1960s, neuroscientist Roger Sperry began to research the right brain vs. left brain theory. In 1981, together with neuroscientist Torsten Wiesel, he won the won the Nobel Prize for his "split-brain" theory. In the split-brain theory, the left and right sides of the brain are connected by the corpus callosum (where place each side of the brain meets and sends signals and communicates with other), and that both the left and right sides of the brain have specific functions.
What is an example of right-brain vs. left brain theory? Scientists now know that for most people who are right-handed, the language center of their brain is located in the Broca are of the left side of the brain. Moreover, research suggests that that emotions and creativity are located in the right-side of the brain. The medical field calls this "brain lateralization." While researchers and scientists don't fully understand the functions of the right-and -left sides of the brain or hemispheres, but through ongoing research there are endless possibilities in learning how the brain functions.
REFERENCE: Corballis, MC. "Left Brain, Right Brain: Facts and Fantasies." PLoS Biol. 2014 Jan; 12(1): e1001767.