What is pyloroplasty?
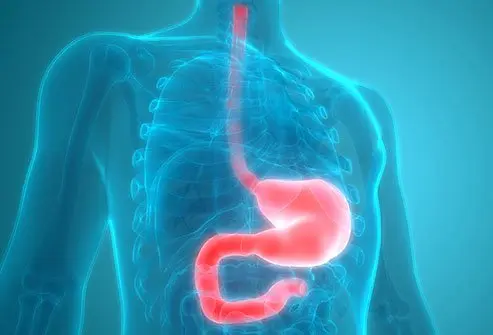
The pylorus is the lowermost part of the stomach, where it connects to the beginning of the small intestine (duodenum). Pyloroplasty is a surgical procedure to widen the pylorus by cutting and relaxing the pyloric sphincter muscle of the stomach.
The pyloric opening is controlled by the pyloric sphincter muscle, which acts as a valve. The pyloric sphincter relaxes to allow the food flow into the duodenum and contracts to prevent it from flowing back into the stomach.
What are the types of pyloroplasty?
Pyloroplasty may be performed using one of three techniques:
- Heineke-Mikulicz pyloroplasty: The pylorus is cut lengthwise to make it wider and then sutured across. This is the most commonly performed pyloroplasty procedure.
- Jaboulay pyloroplasty: The stomach is directly connected to the duodenum (gastroduodenostomy), but the pylorus is not incised.
- Finney pyloroplasty: A gastroduodenostomy is performed along with an incision of the pylorus. This method is rarely used.
Alternatives to pyloroplasty are:
- Chemical pyloroplasty: Botulinum toxin is injected into the pylorus making it relax.
- Pyloromyotomy: the muscle surrounding the pylorus is cut lengthwise. The pyloric tract becomes wider because it bulges through the opening in the muscle.
- Pyloric dilatation: the pylorus is dilated with a balloon passed through a flexible tube (endoscope) through the nose and upper digestive tract or through a tiny incision in the stomach wall (gastrotomy).
Why is pyloroplasty performed?
Pyloroplasty is performed when normal function of the pylorus is affected due to disease, or as an adjunct to certain other gastric surgeries. Pyloroplasty is most commonly performed as a gastric drainage procedure along with a vagotomy (surgical severing of the part of the vagus nerve controlling the digestive system). A vagotomy is performed as treatment for peptic ulcers.
In addition, a pyloroplasty may be performed to treat other conditions that affect the digestive system such as
- Bleeding or perforated bleeding ulcers in the duodenum.
- Abnormally narrow pylorus (pyloric stenosis)
- Obstruction in the pylorus
- Pyloric atresia (congenital condition causing pyloric stenosis)
- Helicobacter pylori infection
- Vagus nerve damage
- Delayed emptying of stomach contents (gastroparesis)
- Diabetes

QUESTION
Pancreatitis is inflammation of an organ in the abdomen called the pancreas. See AnswerWhat is the surgical procedure for pyloroplasty?
A general surgeon usually performs a pyloroplasty under general anesthesia. It may be performed as an open surgery with a large incision in the abdomen or a laparoscopic surgery, which is less invasive with several smaller incisions.
Preparation
- Prior to a pyloroplasty a patient
- Undergoes blood, urine and imaging tests.
- Must avoid eating or drinking 8 hours prior to the procedure.
- Check with the doctor before taking any regular medications.
- Inform the doctor of any allergies.
- May undergo stomach pumping (gastric lavage) to clear residual gastric contents
Procedure
- An anesthesiologist administers anesthesia and monitors the patient’s vital functions during the procedure.
- The patient will be intubated to provide oxygen.
- The surgeon makes one or more incisions in the abdomen depending on the type of surgery.
- The surgeon makes a 5 cm-long incision lengthwise starting from the lower stomach (antrum), along the pylorus up to the top part of the duodenum.
- The incision is stretched into a diamond shape to widen the pylorus.
- Part or all of the pyloric sphincter muscle may be removed.
- The pyloric incision is closed with sutures.
- The abdominal muscles and the incision are sutured.
Post-procedure
- The patient is brought out of anesthesia and administered painkillers for post-surgical pain.
- The patient is monitored in the recovery room for a few hours.
- Most people will be able to go home after three to six days in the hospital, depending on the underlying conditions.
- Complete recovery may take up to six weeks, during which the patient must avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities.
Health News
- More of America's Pets Are Overdosing on Stray Coke, Meth
- GLP-1 Zepbound Is Approved As First Drug For Sleep Apnea
- Feeling Appreciated by Partner is Critical for Caregiver's Mental Health
- Tips for Spending Holiday Time With Family Members Who Live with Dementia
- The Most Therapeutic Kind of Me-Time
 More Health News »
More Health News »
What are the risks and complications of pyloroplasty?
As is common with any surgical procedure, pyloroplasty carries certain risks and complications, which include:
- Anesthetic side effects such as
- Surgical risks such as
- Wound infection
- Hemorrhage
- Blood clots
- Injury to nearby organs, blood vessels or nerves
- Pneumonia
- Incisional hernia
Complications of associated surgeries such as vagotomy or gastrectomy (removal of part of the stomach)
Gastric dumping syndrome due to the stomach contents emptying too fast into the intestine
Bile reflux and gastritis
Bowel blockage
Inflammation of the stomach lining (peritonitis)
Weight loss and fatigue
Infection and sepsis
Recurrence of gastric ulcers
Diarrhea and malnutrition
Top What Is the Surgical Procedure for Pyloroplasty Related Articles

atracurium
Atracurium is a medication used in addition to general anesthesia to produce skeletal muscle relaxation during surgical procedures, and endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation. Common side effects of atracurium include skin flush, redness (erythema), rash, hives (urticaria), wheals, itching (pruritus), injection site reaction, wheezing, increased bronchial secretions, changes in mean arterial pressure, and changes in heart rate. Atracurium can cause fetal harm if used during pregnancy.
Electrogastrogram
An electrogastrogram is a test that measures the electrical signals that measure how the muscles of the stomach contract.
Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is a procedure that creates a small stomach pouch to restrict food intake and constructs bypasses of the duodenum and parts of the small intestine to decrease one's ability to absorb nutrients from food. There are two types of gastric bypass operations: Roux-en-Y and extensive gastric bypass. Patients who undergo gastric bypass surgery will need to take nutrition supplements due to limited absorption of certain vitamins and minerals.
Gastric Cancer Quiz
What are the main risk factors for gastric cancer? Where does gastric cancer occur? Take this quiz to learn about this different type of cancer.
Gastric Emptying Study
A gastric emptying study is a procedure that is done by nuclear medicine physicians using radioactive chemicals that measures the speed with which food empties from the stomach and enters the small intestine. A gastric emptying study often is used when there is a possibility of an abnormal delay in food emptying from the stomach. Medically, this is called delayed gastric emptying. The two most common causes of delayed gastric emptying are gastric outlet obstruction and gastroparesis.
Gastritis
Gastritis (acute and chronic) is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach Some people have no gastritis symptoms, but when they do occur they may include bloating, belching, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. H. pylori infection and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the two main causes of gastritis. Alcohol, caffeine, and high-fat foods also can cause gastritis. Fried, fatty, and spicy foods and alcohol aggravate gastritis symptoms. Other stomach lining irritants that aggravate symptoms include cigarette smoking, acidic juices, caffeine, tomato products, peppers, and chili powder. Foods that soothe gastritis symptoms, and that help reduce and stop H. pylori infection growth in the stomach includes apples, onions, garlic, teas, green leafy vegetables, coconut water, and wheat bran. Gastritis is diagnosed with endoscopy, blood tests, or stool tests. Some people get relief from gastritis symptoms with prescription and non-prescription antacids, histamine blockers like famotidine (Pepcid AC) or ranitidine (Zantac 75), or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) like omeprazole (Prilosec) and esomeprazole (Nexium). These drugs will not cure gastritis. Complications of gastritis include gastric cancers, MALT lymphoma, renal problems, and death.
GERD Picture
The stomach contents regurgitate and back up (reflux) into the esophagus The food in the stomach is partially digested by stomach acid and enzymes. See a picture of Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD) and learn more about the health topic.
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis is a medical condition in which the muscle of the stomach is paralyzed by a disease of either the stomach muscle itself or the nerves controlling the muscle. As a consequence, food and secretions do not empty normally from the stomach. Gastroparesis symptoms are nausea and vomiting; abdominal bloating, and pain can result.
GERD Quiz
Who is at risk for developing GERD? Are you? Take this quiz to learn what GERD is, if you're at risk, and what you can do about it.
How Long Does It Take to Recover from A Gastrojejunostomy Procedure?
A gastrojejunostomy is a surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia by a gastrointestinal surgeon. The surgeon produces a direct connection (anastomosis) between the stomach and the jejunum, part of the small intestine. Recovery time is generally about six weeks, but you can be home from the hospital in as little as three days if you have a laparoscopic procedure.
Lap Band Surgery
Lap band (gastric banding) surgery, also referred to as laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) is a surgical procedure in which an adjustable belt is placed around the upper portion of the stomach. Candidates for lap band surgery are generally individuals with a body mass index over 40 kg/m2, or are more than 45 kilograms over their ideal body weight. Side effects, risks, and complications from lap band surgery should be discussed with a surgeon or physician before the operation.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is a surgical procedure used on patients who have difficulty swallowing. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is generally performed in an outpatient facility or hospital. Possible complications with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) include infection or leakage of the liquid diet fed through the tube.
propofol
Propofol is an intravenous anesthetic drug used for general anesthesia and sedation during surgical procedures. Common side effects of propofol include injection site burning, stinging or pain; low blood pressure (hypotension), reduced cardiac output, elevated blood pressure (hypertension), pause in breathing (apnea), lung impairment (respiratory acidosis), impaired movement, high level of emulsified fats in the blood (hyperlipidemia), and high triglyceride level in blood (hypertriglyceridemia). Abuse of propofol can cause death and other injuries.
What Is Gastric (Stomach) Cancer? Signs, Symptoms, Causes
What are the common signs and symptoms of stomach cancer? Learn about gastric cancer diagnosis, treatment, and their risks, how Heliobacter pylori affects the stomach, what the risk factors are, and how clinical trials have helped determine cancer risks. Guard your gastrointestinal health with reliable medical information.
What Is a Gastrojejunostomy Procedure?
Gastrojejunostomy is a surgical procedure to create a direct connection (anastomosis) from the stomach to the middle part of the small intestine (jejunum), bypassing or removing the beginning part of the small intestine (duodenum).