This article aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools to effectively leverage these functionalities for improved governance and compliance in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations.
Let's get started.
CONTENT Introduction Audit Trail Audit Workbench Key Differences Conclusion |
Introduction
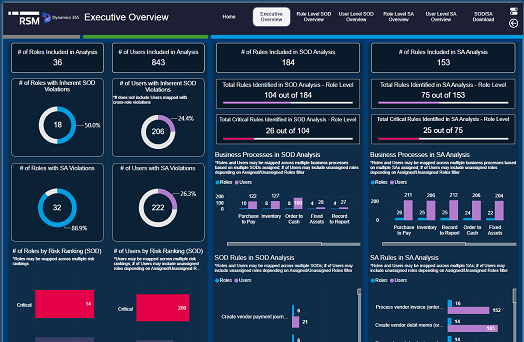
Audit and compliance play a crucial role in managing business processes, especially in industries that need to meet regulatory requirements like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX). In Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations (D365FO), Microsoft provides a range of tools to support businesses in achieving these goals. Two such tools, the Audit Trail and Audit Workbench, are often used for tracking and managing compliance-related activities, but their functions and purposes are quite distinct.
The Audit Trail focuses on tracking changes to key data, enabling you to maintain a record of who changed what and when—an essential feature for organizations that need detailed data accountability. On the other hand, the Audit Workbench is designed for a broader approach, allowing businesses to define and monitor specific audit processes, such as reviewing user activity or evaluating system configurations against predefined compliance standards.
This article dives into the details of these two tools, explaining how they work, their individual strengths, and the scenarios where they are most useful. By the end, you'll have a better understanding of how the Audit Trail and Audit Workbench can be leveraged to support your organization's compliance strategy. Whether you're new to these features or looking to enhance your use of D365FO for regulatory purposes, this guide aims to provide clarity and practical insights.
Audit Trail
In Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations (D365FO), the Audit Trail button on vouchers provides detailed tracking information, such as type, description, creator, and creation date and time. This feature supports regulatory compliance, including SOX, by maintaining a comprehensive record of changes for audit purposes.
The Audit Trail function, accessible from the Voucher transaction inquiry page, retrieves financial transaction entries posted to the general ledger. It opens the Audit Trail Inquiry page, displaying details such as who posted the transaction, when it occurred, and the document type. Additionally, the creation date and time reflect when the transaction was posted. The page also allows users to view associated voucher transactions.
Navigate to the Audit trail form using the following menu path:
General ledger >> Inquiries and reports >> Audit trail
This button takes you to original voucher as shown below:
Investigating a user who created a voucher: If you're viewing a voucher and want to investigate who created it, click the Audit trail button.
The system will take you to the Audit Trail form, where you can see details of the posted transaction, including:
- Transaction type
- Date of posting
- User who posted the transaction
While the Audit Trail provides detailed insights into individual transactions and their origin, the Audit Workbench in D365FO offers a centralized platform to manage, review, and analyze audit policies and rule violations across the system, enabling a broader scope of compliance and monitoring.
Audit Workbench
The Audit Workbench in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations (D365FO) provides organizations with a centralized framework to monitor, review, and analyze compliance-related activities. Its purpose is to help users manage audit policies, track potential violations, and ensure transactions align with internal controls and regulatory requirements.
Key Functionalities
➡️ Audit Policy Configuration: Users can configure audit policies to monitor specific scenarios, such as duplicate invoices, unusual transactions, or modifications to master data.
➡️ Rule Violations and Alerts: The system automatically evaluates transactional data against defined policies and flags any rule violations. Violations are consolidated in the workbench for further review, making it easier to assess the impact and determine corrective actions.
➡️ Exception Review and Follow-up: The workbench provides a structured approach to reviewing flagged exceptions. Users can document findings, assign tasks to team members, and track resolution efforts, ensuring accountability throughout the process.
➡️ Integrated Data Analysis: Audit Workbench allows users to drill down into transactional and master data directly from flagged violations, providing full visibility into the root cause.
➡️ Compliance Reporting: The tool includes capabilities for generating reports on policy violations and exceptions, helping organizations assess trends and compliance risks. These reports can be used for internal evaluations or shared with external auditors to demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards.
Practical Use
For example, if an organization wants to ensure there are no duplicate vendor payments, the Audit Workbench can flag any cases where multiple invoices with the same reference number are processed. Users can then investigate these cases and take appropriate corrective actions, all within the same tool.
Consultant’s Perspective:
From a consultant's point of view, the Audit Workbench is a practical feature that bridges the gap between transactional data and compliance management. It is especially useful for organizations aiming to maintain SOX compliance or other regulatory requirements. By leveraging this functionality, users can standardize the audit process, reduce manual intervention, and ensure audit trails are well-documented for future reference.
This functionality is not a standalone solution but a key component that complements other D365FO features, such as security roles and financial controls. It allows organizations to embed compliance management into their day-to-day operations, making it easier to manage risks proactively.
Conclusion
Both the Audit Trail and Audit Workbench play critical roles in supporting compliance and audit objectives within D365FO. While the Audit Trail ensures comprehensive data change tracking for accountability, the Audit Workbench proactively identifies and resolves anomalies to safeguard against risks. When used together, these tools provide a robust framework for maintaining compliance, enhancing audit readiness, and meeting regulatory requirements such as SOX.
Understanding the distinction and interplay between these functionalities is essential for maximizing their value and ensuring a secure and compliant ERP environment.