Facts you should know about a sinus infection (sinusitis)

- The majority of sinus infections are not considered contagious
- Symptoms of sinus infections may include:
- A yellowish-greenish nasal discharge that may have an odor
- bad breath
- Puffiness around the eyes
- Headaches
- Pressure in the sinuses
- Coughing
- Fatigue
- Earaches
- Sore throat
- Acute sinusitis lasts about 3 weeks.
- Chronic sinusitis lasts about 8 weeks or longer.
- Usually, sinus infections are caused by viruses or bacteria that inhabit a person’s body.
- Acute sinusitis goes away after about 3 weeks.
- Chronic sinusitis usually lasts 8 weeks or more and can be recurrent.
- Usually, acute sinusitis is self-limiting.
- Chronic sinusitis may require more complex treatments.
- Treatments to help relieve signs and symptoms and cure a sinus infection include:
- Decongestants
- Saline water nasal sprays
- Humidified air and less frequently
- Antibiotics for bacterial sinus infections
- Surgery (for example, nasal polyp removal)
- Natural home remedies
- Contact your doctor if you have signs and symptoms of:
- Severe headaches
- A swollen face and/or eyes
- Short of breath
- Stiff neck
- Confusion
Can you catch a sinus infection from someone?
Experts disagree about the contagiousness of sinus infections (also termed sinusitis and rhinosinusitis).
- Because bacteria and viruses (and occasionally, fungi) are the cause of most sinus infections, some experts say that the bacteria, viruses, or fungi can be transferred from person-to–person, and occasionally cause sinus infections.
- Other experts say that sinus infections, although caused by bacteria and viruses, occur because the conditions in the individual's sinuses are optimal for infection. Moreover, the infection can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that are already present in a person so person-to-person transfer is not required for them to develop.
However, the majority of doctors think that most people do not transmit sinus infections except in rare instances, and conclude that sinus infections are not contagious.
Still, there is widespread agreement that bacteria, fungi and/or viruses are transmitted from person-to-person (contagious) even if the disease, sinusitis, is not. It's recommended that individuals with sinus infections avoid direct contact (for example, through kissing) with those who are more prone to infection, for example: infants, the elderly, and those who have weakened immune systems to reduce the chance of transferring bacteria, fungi, and viruses to other people as they may cause problems other than sinus infections.
Viral or bacterial organisms that reside in the person's body are major causes of sinusitis.
Since the majority of doctors consider sinus infections to be non-contagious, the only spread of sinusitis would consist of the bacteria to the various sinuses within each person.

IMAGES
Is a Sinus Infection Contagious? See a medical illustration of the sinuses plus our entire medical gallery of human anatomy and physiology See ImagesHow to tell the difference between a cold and sinus infection
Sinus infections usually begin with the symptoms of a cold (for example, a runny nose, occasional cough, and/or mild fever), and then develop into pain and pressure in the sinus cavities. About 7 to 10 days after initial cold-like symptoms other symptoms develop that suggest you may have a sinus infection.
Sinus infection symptoms include:
- A yellowish-greenish nasal discharge that may have an odor
- Bad breath
- Puffiness around the eyes
- Sinus headaches
- Pressure in the sinuses
- Coughing
Many people with a sinus infection or sinusitis may develop signs and symptoms that include:
- Fatigue
- Earaches
- Sore throat
Definitive diagnosis of a sinus infection is based on the patient's history, physical exam, and evidence of sinus inflammation that may be seen with X-rays or CT scans of the sinuses.
What are the stages of sinus infection?
A sinus infection can be broken down into several stages. These stages vary in severity and length depending on their cause and other factors.
The four most common stages of sinus infection include:
- Acute sinusitis or sinus infections symptoms and signs last about three weeks if the signs and symptoms go away.
- Subacute sinusitis usually lasts 4-12 weeks with symptoms that may become less severe but are more persistent.
- Chronic sinusitis or sinus infections usually last about eight weeks or longer.
- Recurrent sinusitis is acute sinusitis that occurs several times over one year and may develop into chronic sinusitis.
Will a sinus infection go away without antibiotics?
A person may be "cured" of a sinus infection when the symptoms stop, usually after about 3 weeks. However, a "cure" often is temporary in some people that either have chronic or recurrent sinus infections. Bacterial sinus infections may benefit from antibiotics (sometimes long-term antibiotic treatment is required before the patient is "cured" of a bacterial sinusitis), but there is no antibiotic treatment for viral sinusitis.
What meds are best for sinus infection?
Pain relievers to manage pain and other symptoms of sinus infections or sinusitis include:
- acetaminophen (Tylenol and others) and
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (for example, ibuprofen [Advil and Motrin] and naproxen [Aleve]).
Some people have sinus infections because of other conditions or diseases. For example, people with asthma have airway narrowing and are at a higher risk of developing sinusitis.
Prescription medications to reduce asthma symptoms may reduce the tendency to develop sinusitis.
Surgery for sinusitis and sinus infections
Some people may need to have surgery or other procedures to open up narrowed or obstructed nasal or sinus passages in people with the following conditions:
- Nasal polyps
- A deviated septum
- Chronic sinus infections or sinusitis
- A deviated septum in the nose to relieve sinusitis
When should I be worried about a sinus infection?
If you develop persistent fever or have a history of recurrent or chronic sinusitis or if you have sinus symptoms that don't improve or get worse, you should contact your doctor.
Seek medical care immediately if you develop:
- Severe headaches
- Swellings in the forehead and/or eyes
- Shortness of breath
- Stiff neck
- Confusion
Subscribe to MedicineNet's Daily Health News Newsletter
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet's Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet's subscriptions at any time.
Top Is a Sinus Infection Contagious Related Articles

CT Scan (Computerized Tomography)
A CT scan is an X-ray procedure that combines many X-ray images with the aid of a computer to generate cross-sectional and three-dimensional images of internal organs and structures of the body. A CT scan is a low-risk procedure. Contrast material may be injected into a vein or the spinal fluid to enhance the scan.
Cold, Fever and Flu Symptoms in Children: Medications and Home Remedies
How long does a cold last? How long is a cold contagious? Colds and fevers are some of the most common ailments in children. Learn common cold symptoms, treatment options, over the counter (OTC) medicines for cold and fever, home remedies, and how to relieve a sore throat.
Chronic Rhinitis
Chronic rhinitis (non-allergic rhinitis) causes runny nose, sneezing, nasal itching, and congestion. Post-nasal drip is the drainage of mucus from the sinuses into the throat. Treatment includes over-the-counter (OTC) medications.
Cold & Flu Quiz
Aches? Pain? Fever? This Cold & Flu Quiz tests your knowledge on the difference between coming down with the common cold and sickness from influenza virus.
Common Cold Quiz
Take this quiz to learn the truth behind the infectious, contagious, uncomfortable disease known as the common cold. Test your knowledge of colds; get prevention tips, and learn what you may want to avoid when treating a cold!
Common Medical Abbreviations & Terms
Doctors, pharmacists, and other health-care professionals use abbreviations, acronyms, and other terminology for instructions and information in regard to a patient's health condition, prescription drugs they are to take, or medical procedures that have been ordered. There is no approved this list of common medical abbreviations, acronyms, and terminology used by doctors and other health- care professionals. You can use this list of medical abbreviations and acronyms written by our doctors the next time you can't understand what is on your prescription package, blood test results, or medical procedure orders. Examples include:
- ANED: Alive no evidence of disease. The patient arrived in the ER alive with no evidence of disease.
- ARF: Acute renal (kidney) failure
- cap: Capsule.
- CPAP: Continuous positive airway pressure. A treatment for sleep apnea.
- DJD: Degenerative joint disease. Another term for osteoarthritis.
- DM: Diabetes mellitus. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- HA: Headache
- IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease. A name for two disorders of the gastrointestinal (BI) tract, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
- JT: Joint
- N/V: Nausea or vomiting.
- p.o.: By mouth. From the Latin terminology per os.
- q.i.d.: Four times daily. As in taking a medicine four times daily.
- RA: Rheumatoid arthritis
- SOB: Shortness of breath.
- T: Temperature. Temperature is recorded as part of the physical examination. It is one of the "vital signs."

CT Scan vs. MRI
CT or computerized tomography scan uses X-rays that take images of cross-sections of the bones or other parts of the body to diagnose tumors or lesions in the abdomen, blood clots, and lung conditions like emphysema or pneumonia. MRI or magnetic resonance imaging uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to make images of the organs, cartilage, tendons, and other soft tissues of the body. MRI costs more than CT, while CT is a quicker and more comfortable test for the patient.
Headaches Quiz
If you're plagued with headaches, our Headaches Quiz may help you identify causes, triggers, symptoms, and treatments for headache pain caused by different types of headaches such as migraines, sinus, cluster, tension, or stress.
Cough: 19 Tips on How to Stop a Cough
Learn how to stop coughing attacks without medicine at night and at other times naturally. Learn about 19 tips to stop nighttime and persistent cough. Causes of excessive coughing include prescription medications, allergies, cigarette smoke, heart disease, and infections. Home remedies include natural herbs and supplements like ginger, honey, turmeric, and mint.
How to Get Rid of a Cold: Natural Remedies
What home remedies work to get rid of a cold fast? Many claim cold symptoms and flu symptoms can be relieved with Echinacea, zinc, neti pots, garlic, vitamin C, saltwater gargles, nasal strips, or bed rest. Find out what cold and flu treatments work the natural way, and what doesn't.
Sinus Infection Dos and Don'ts
Is it OK to fly when you've got sinusitis? How about going to work? WebMD helps you decide what's right and wrong when you're all stuffed up.
Sinus Surgery (Endoscopic) Procedure
Sinus surgery involves the precise removal of diseased sinus tissue with the improvement in the natural drainage channels by the creation of a pathway for infected material to drain from the sinus cavities. The sinus surgery information is provided to help you prepare for sinus surgery and to help you understand more clearly the associated benefits, risks, and complications.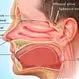
Sinuses Picture
The sinuses are an air-filled cavity in a dense portion of a skull bone. See a picture of the Sinuses and learn more about the health topic.
Sinusitis
Sinus infection (sinusitis) is caused by allergies, infection, and chemicals or other irritants of sinuses. Signs and symptoms include headache, fever, and facial tenderness, pressure, or pain. Treatments of sinus infections are generally with antibiotics and at times, home remedies.
Sinusitis Slideshow
Sinus infection (sinusitis) symptoms can include headaches, a sore throat, and toothaches. Antibiotics and home remedies can relieve sinus infection symptoms.
Sore Throat
Sore throat (throat pain) usually is described as pain or discomfort in the throat area. A sore throat may be caused by bacterial infections, viral infections, toxins, irritants, trauma, or injury to the throat area. Common symptoms of a sore throat include a fever, cough, runny nose, hoarseness, earaches, sneezing, and body aches. Home remedies for a sore throat include warm soothing liquids and throat lozenges. OTC remedies for a sore throat include OTC pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Antibiotics may be necessary for some cases of sore throat.

Sore Throat Home Remedies
Natural and home remedies for sore throat symptoms and pain relief include essential oils, licorice gargles, slippery elm leaves, raw garlic, Throat Coat tea, sage, and acupuncture. Typical symptoms of a sore throat include throat pain, coughing, sneezing, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Sore throats are caused by viral (common cold, flu, mumps), bacterial (tonsillitis, some STDs), toxins, allergens, trauma or injury, or "mechanical causes" (breathing through the mouth).
Upper Respiratory Infection (URI)
An upper respiratory infection is a contagious infection of the structures of the upper respiratory tract, which includes the sinuses, nasal passages, pharynx, and larynx. Common causes of an upper respiratory infection include bacteria and viruses such as rhinoviruses, group A streptococci, influenza, respiratory syncytial, whooping cough, diphtheria, and Epstein-Barr. Examples of symptoms of upper respiratory infection include sneezing, sore throat, cough, fever, and nasal congestion. Treatment of upper respiratory infections are based upon the cause. Generally, viral infections are treated symptomatically with over-the-counter (OTC) medication and home remedies.