Does Cytotec (misoprostol) cause side effects?
Cytotec (misoprostol) is a synthetic (man-made) prostaglandin used to reduce the risk of stomach ulcers in patients treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, for example, aspirin, ibuprofen, etc.) for pain and various inflammatory conditions, for example, arthritis.
Cytotec is used primarily in patients at high risk for stomach ulcers when treated with NSAIDs, such as the elderly, patients with concomitant debilitating diseases, and patients with a history of ulcers.
Prostaglandins are chemicals that are made within many organs of the body including the stomach. In the stomach, prostaglandins are believed to protect the inner lining of the stomach from the ulcer-producing effects of NSAIDs.
Scientists now believe that NSAIDs produce ulceration by preventing the production of prostaglandins in the stomach. Synthetic prostaglandins such as Cytotec given orally "replace" the prostaglandins whose production is inhibited by NSAIDs and have been shown to protect the lining of the stomach from NSAID-induced ulcers.
Common side effects of Cytotec include
Less common side effects of Cytotec include
- headache,
- menstrual cramps,
- nausea, and
- gas (flatulence).
Allergic reactions have also been reported.
Serious side effects of Cytotec include
Cytotec has no clinically important drug interactions.
Cytotec should never be used during pregnancy since it can cause abortion, premature birth, or birth defects. Uterine rupture has been reported when Cytotec was administered to pregnant women to induce labor or to induce abortion beyond the eighth week of pregnancy.
It is unknown if Cytotec is excreted in human breast milk; however, it should not be administered to breastfeeding mothers because it could cause significant diarrhea in nursing infants.
What are the important side effects of Cytotec (misoprostol)?
Common side effects include
Diarrhea is more common with higher doses and usually resolves with continued administration. Rarely, profound and persistent diarrhea necessitates stopping the drug.
Less common side effects include
- headache,
- menstrual cramps,
- nausea, and
- flatulence.
Allergic reactions have also been reported.
Cytotec (misoprostol) side effects list for healthcare professionals
The following have been reported as adverse events in subjects receiving Cytotec:
Gastrointestinal
- In subjects receiving Cytotec 400 or 800 mcg daily in clinical trials, the most frequent gastrointestinal adverse events were diarrhea and abdominal pain.
- The incidence of diarrhea at 800 mcg in controlled trials in patients on NSAIDs ranged from 14-40% and in all studies (over 5,000 patients) averaged 13%.
- Abdominal pain occurred in 13-20% of patients in NSAID trials and about 7% in all studies, but there was no consistent difference from placebo.
- Diarrhea was dose related and usually developed early in the course of therapy (after 13 days), usually was self-limiting (often resolving after 8 days), but sometimes required discontinuation of Cytotec (2% of the patients).
- Rare instances of profound diarrhea leading to severe dehydration have been reported.
- Patients with an underlying condition such as inflammatory bowel disease, or those in whom dehydration, were it to occur, would be dangerous, should be monitored carefully if Cytotec is prescribed.
- The incidence of diarrhea can be minimized by administering after meals and at bedtime, and by avoiding coadministration of Cytotec with magnesium-containing antacids.
Gynecological
- Women who received Cytotec during clinical trials reported the following gynecological disorders:
- spotting (0.7%),
- cramps (0.6%),
- hypermenorrhea (0.5%),
- menstrual disorder (0.3%) and
- dysmenorrhea (0.1%).
- Postmenopausal vaginal bleeding may be related to Cytotec administration. If it occurs, diagnostic workup should be undertaken to rule out gynecological pathology.
Elderly
- There were no significant differences in the safety profile of Cytotec in approximately 500 ulcer patients who were 65 years of age or older compared with younger patients.
- Additional adverse events which were reported are categorized as follows.
Incidence Greater Than 1%
- In clinical trials, the following adverse reactions were reported by more than 1% of the subjects receiving Cytotec and may be causally related to the drug:
- nausea (3.2%),
- flatulence (2.9%),
- headache (2.4%),
- dyspepsia (2.0%),
- vomiting (1.3%), and
- constipation (1.1%).
- However, there were no significant differences between the incidences of these events for Cytotec and placebo.
Causal Relationship Unknown
The following adverse events were infrequently reported. Causal relationships between Cytotec and these events have not been established but cannot be excluded:
Body as a whole: aches/pains, asthenia, fatigue, fever, chills, rigors, weight changes.
Skin: rash, dermatitis, alopecia, pallor, breast pain.
Special senses: abnormal taste, abnormal vision, conjunctivitis, deafness, tinnitus, earache.
Respiratory: upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, bronchospasm, dyspnea, pneumonia, epistaxis.
Cardiovascular: chest pain, edema, diaphoresis, hypotension, hypertension, arrhythmia, phlebitis, increased cardiac enzymes, syncope, myocardial infarction (some fatal), thromboembolic events (e.g., pulmonary embolism, arterial thrombosis, and CVA).
Gastrointestinal: GI bleeding, GI inflammation/infection, rectal disorder, abnormal hepatobiliary function, gingivitis, reflux, dysphagia, amylase increase.
Hypersensitivity: anaphylactic reaction
Metabolic: glycosuria, gout, increased nitrogen, increased alkaline phosphatase.
Genitourinary: polyuria, dysuria, hematuria, urinary tract infection.
Nervous system/Psychiatric: anxiety, change in appetite, depression, drowsiness, dizziness, thirst, impotence, loss of libido, sweating increase, neuropathy, neurosis, confusion.
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, myalgia, muscle cramps, stiffness, back pain.
Blood/Coagulation: anemia, abnormal differential, thrombocytopenia, purpura, ESR increased.
What drugs interact with Cytotec (misoprostol)?
Cytotec has not been shown to interfere with the beneficial effects of aspirin on signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Cytotec does not exert clinically significant effects on the absorption, blood levels, and antiplatelet effects of therapeutic doses of aspirin. Cytotec has no clinically significant effect on the kinetics of diclofenac or ibuprofen.
Prostaglandins such as Cytotec may augment the activity of oxytocic agents, especially when given less than 4 hours prior to initiating oxytocin treatment. Concomitant use is not recommended.
Summary
Cytotec (misoprostol) is a synthetic (man-made) prostaglandin used to reduce the risk of stomach ulcers in patients treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, for example, aspirin, ibuprofen, etc.) for pain and various inflammatory conditions, for example, arthritis. Common side effects of Cytotec include diarrhea and abdominal pain. Less common side effects of Cytotec include headache, menstrual cramps, nausea, and gas (flatulence). Allergic reactions have also been reported. Cytotec should never be used during pregnancy since it can cause abortion, premature birth, birth defects, or uterine rupture. It should not be administered to breastfeeding mothers.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
-

What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)? Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? Learn about treatment, diagnosis, and the symptoms of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Discover...
-

Osteoarthritis (OA): Treatment, Symptoms, Diagnosis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease most often affecting major joints such as knees, hands, back, or hips....
-

Digestive Disorders: Visual Guide to Stomach Ulcers
Learn about the causes and symptoms of stomach ulcers, and find out which kinds of treatment can help.
-

Osteoarthritis Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
How does osteoarthritis differ from other types of arthritis? Learn about osteoarthritis with this quiz.
-

Rheumatoid Arthritis Quiz: What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
How is rheumatoid arthritis different from other forms of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis and gout? Take the Rheumatoid...
-

Rheumatoid Arthritis Exercises: Joint-Friendly Workouts
Regular exercise boosts fitness and helps reverse joint stiffness for people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). WebMD demonstrates...
-

Exercises for Knee Osteoarthritis and Joint Pain
Learn about osteoarthritis and exercises that relieve knee osteoarthritis pain, stiffness and strengthen the knee joint and...
-
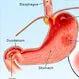
Picture of Peptic Ulcer
A hole in the lining of the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus. See a picture of Peptic Ulcer and learn more about the health topic.
-
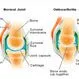
Picture of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that is caused by the breakdown and eventual loss of the cartilage of one or more...
-
Arthritis: Causes and Treatment for Joint Stiffness and Pain
Arthritis and injuries can leave your joints swollen, tender, and damaged. Discover treatments for morning stiffness, sore...
-

Osteoarthritis: 15 Tips to Improve Daily Living With OA
Have arthritis in the knee? Osteoarthritis joint pain can make it hard to carry out activities of daily living. Cartilage...
-

Arthritis: 16 Bad Habits That Cause Joint Pain
Being overweight, wearing uncomfortable shoes, or carrying a heavy purse can make joint pain and arthritis symptoms worse. Some...
-

Tips for Healthy Joints: Exercise, Nutrition, & More
Dealing with joint pain and arthritis? Learn why weight matters--and why NOT to stretch before exercise. See these solutions for...
-

Fun With Kids? Don't Let Arthritis Stop You
You can still have lots of fun with children despite arthritis. Our experts uncover ways to spend time with your kids or...
-

Active Living with Osteoarthritis
Check out this slideshow on Active Living From Day to Night with Osteoarthritis. Even with arthritis you can keep your active...
Related Disease Conditions
-

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints, the tissue around the joints, as well as other organs in the body.
-

Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints. When joints are inflamed they can develop stiffness, warmth, swelling, redness and pain. There are over 100 types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout.
-
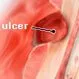
Peptic Ulcer
Peptic or stomach ulcers are ulcers in the lining of the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus. Learn about symptoms, causes, diet, and treatment.
-

Rheumatoid Arthritis vs. Arthritis
Arthritis is a general term used to describe joint disease. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing chronic inflammation.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis vs. Lupus: Differences and Similarities
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and lupus are two varieties of autoimmune diseases that cause flare-ups. While RA attacks the immune system on the joints, lupus involves many other parts of the body besides the joints. Common RA symptoms involve warm, swollen, and painful joints; morning stiffness in the joints or stiffness after inactivity, joint deformity, fever, fatigue, etc. Lupus symptoms include Malar rash (butterfly-shaped rash involving the cheeks and bridge of the nose), fever, joint pain in the absence of joint deformity, etc.
Treatment & Diagnosis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis FAQs
- Osteoarthritis FAQs
- What if I get COVID-19 with Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- Are Corticosteroids Safe for Pregnant and Nursing Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- 5 Surprising Facts About Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Ulcers May Be Caused By Your Cat
- Arava Approved For Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Arthritis - Whether Weather Affects Arthritis
- Arthritis Medications
- Ulcers: What Causes Ulcers?
- What Kind of Joint Injections Treat Osteoarthritis?
- Can Milk Allergy Cause Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- How Is Arthritis Diagnosed?
Medications & Supplements

Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Professional side effects and drug interactions sections courtesy of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.