Does Allegra (fexofenadine) cause side effects?
Allegra (fexofenadine) is an oral, "second generation" antihistamine used to treat seasonal allergies in patients 2 years of age and older and chronic urticaria (hives, itching) in patients 6 months of age and older.
Histamine is a chemical that is responsible for many of the signs and symptoms of allergic reactions, for example, swelling of the lining of the nose, sneezing, and itchy eyes. Histamine is released from histamine-storing cells (mast cells) and then attaches to other cells that have receptors for histamine.
The attachment of the histamine to the receptors causes the cells to be "activated," releasing other chemicals that produce the effects that we associate with allergy (for example, sneezing). Allegra blocks one type of receptor for histamine (the H1 receptor) and thus prevents activation of H1 receptor-containing cells by histamine.
Unlike the first-generation antihistamines, Allegra and other second-generation antihistamines do not readily enter the brain from the blood. Therefore, they cause less drowsiness and are called non-sedating antihistamines.
Common side effects of Allegra include
Other important side effects of Allegra include
Drug interactions of Allegra include aluminum-containing antacids (for example, Maalox), which reduce the absorption of Allegra when administered 15 minutes apart.
- Therefore, aluminum-containing antacids and Allegra should not be administered together. Fruit juices (apple, orange, grapefruit) may reduce the absorption of Allegra.
- Allegra should only be administered with water.
Allegra has not been adequately studied in pregnant women. Allegra has not been adequately studied in women who are breastfeeding. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
What are the important side effects of Allegra (fexofenadine)?
The most common side effects of fexofenadine are:
Other important side effects include:
Summary
Allegra (fexofenadine) is an oral, "second generation" antihistamine used to treat seasonal allergies in patients 2 years of age and older and chronic urticaria (hives, itching) in patients 6 months of age and older. Common side effects of Allegra include headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, weakness, sleepiness, and dizziness. Allegra has not been adequately studied in pregnant women. Allegra has not been adequately studied in women who are breastfeeding.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
-

Allergies: 10 Ways to Reduce Mold Allergies
WebMD shows you 10 ways to fight the fungus and reduce mold allergy symptoms from dust masks to bottles of bleach.
-

The Most Common Food Allergies for Kids and Adults
What common food allergens cause the most problems for adults and children? See this list of common food allergies and learn to...
-

Allergies Quiz: Symptoms & Home Remedies
What are the causes of allergies? This online quiz challenges your knowledge of common food and household allergens,...
-

10 Signs Your Allergies Are Out of Control
Learn 10 signs your allergies are out of control. See these surprising allergy symptoms and find out how to get relief for...
-

10 Worst Cities for Spring Allergies
See pictures of the top 10 "spring allergy capitals", according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (AAFA). From...
-
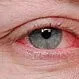
Picture of Eye Allergies
Severe allergic eye symptoms can be very distressing and are a common reason for visits to the allergist or ophthalmologist. See...
-

When Animal (Allergies) Attack: Pet Allergy Symptoms, Treatment
How do you control and relieve pet allergies? How do you prevent pet allergies? Learn dog and cat allergy symptoms, the cause of...
-

Allergies: Common Plants and Trees That Trigger Allergies
Find out more about which plants and trees might be producing pollen that is causing your itchy eyes and a runny nose.
-

Allergies: Myths and Facts About Seasonal Allergies
Seasonal allergy symptoms are hard. Do deserts prevent allergies? What can allergies do to your body? What is an allergen? Adult...
-
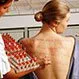
Dangerous Allergies: Anaphylaxis and Life-Threatening Allergy Triggers
Common allergy triggers may provoke anaphylaxis. Hives, tongue swelling, face swelling, rashes, low blood pressure, rapid and...
-

Preparing for Severe Allergies at School
Help your child manage and prepare for severe allergies at school. Protect your child from food allergies, insect stings, and...
-

Itchy Eyes? Top 13 Ways to Tame Eye Allergies
Do you need eye drops? Eye allergies, or allergic conjunctivitis, cause itchy eyes and other allergic symptoms. Avoiding...
Related Disease Conditions
-

Allergy
An allergy refers to a misguided reaction by our immune system in response to bodily contact with certain foreign substances. When these allergens come in contact with the body, it causes the immune system to develop an allergic reaction in people who are allergic to it. It is estimated that 50 million North Americans are affected by allergic conditions. The parts of the body that are prone to react to allergies include the eyes, nose, lungs, skin, and stomach. Common allergic disorders include hay fever, asthma, allergic eyes, allergic eczema, hives, and allergic shock.
-

Cosmetic Allergies
Fragrances and preservatives in cosmetics may cause allergic reactions in some people. Symptoms include redness, itching, and swelling after the product comes in contact with the person's skin. Treatment typically involves the use of over-the-counter cortisone creams.
-

Sinus Infection vs. Allergies
Both sinus infections and allergies (allergic rhinitis) cause symptoms such as runny or stuffy nose and fatigue. Sinus infection (known as sinusitis) is inflammation of the sinuses, caused by infection from bacteria, viruses, and/or fungi (molds). Allergic rhinitis occurs when certain allergies cause nasal symptoms. When a person with allergies breathes in an allergen, such as pollen, dust, or animal dander, symptoms such as runny or stuffy nose, itching, sneezing, and fatigue occur.
-

Insect Sting Allergies
The majority of stinging insects in the United States are from bees, yellow jackets, hornets, wasps, and fire ants. The severity of reactions to stings varies greatly. Avoidance and prompt treatment are essential. In selected cases, allergy injection therapy is highly effective.
-

COVID-19 vs. Allergies
Though there is some overlap in allergy and COVID-19 signs and symptoms there are also significant differences. Symptoms that they have in common include headache, fatigue, tiredness, shortness of breath, wheezing, and sore throat. Fever does not occur with allergies but is one of the defining symptoms of COVID-19 infections.
-
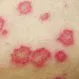
Drug Allergy
Drug or medication allergies are caused when the immune system mistakenly creates an immune response to a medication. Symptoms of a drug allergic reaction include hives, rash, itchy skin or eyes, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, fainting, and anxiety. The most common drugs that people are allergic to include penicillins and penicillin type drugs, sulfa drugs, insulin, and iodine. Treatment may involve antihistamines or corticosteroids. An EpiPen may be used for life-threatening anaphylactic symptoms.
Treatment & Diagnosis
Medications & Supplements

Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Professional side effects and drug interactions sections courtesy of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.