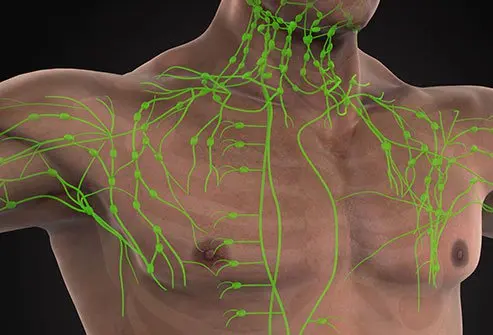
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that can spread to the surrounding organs and cause death. A sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is done in patients with melanoma to investigate the spread of the disease.
SLNB is generally performed for melanoma when one or more of the following are true:
- Melanoma is equal to or greater than 1 mm in depth
- Presence of an ulcerated tumor of any thickness
- Invasion of cancer cells to the lymphatic channels or blood vessels
- Margins taken during biopsy reveals melanoma
However, SLNB should not be considered during the following conditions:
- The size of melanoma is less than 0.76 mm and presents no risk factors
- If melanoma extended to lymph node is in stage III
- The melanoma has spread to distant organs (stage IV)
What is a sentinel lymph node biopsy?
A sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is a specialized procedure to identify, remove, or examine any cancer cells present in the sentinel lymph nodes. It is usually performed in people diagnosed with melanoma cancer. If melanoma spreads, it will first extend to the nearest lymph node, that is, the sentinel lymph node.
Melanoma first extends to a group of lymph nodes known as the sentinel lymph nodes. Most of the individuals usually have between one and five sentinel lymph nodes.
A positive SLNB indicates that cancer has spread to the sentinel lymph nodes or other nearby lymph nodes. It also helps the physician to determine the exact stage of cancer and develop an appropriate treatment plan for the same.
Enlarged, irregular, firm, and palpable nodes may require a fine needle aspiration biopsy rather than SLNB.
How is a sentinel lymph node biopsy performed?
A sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) has two parts:
- Lymphatic mapping
- Surgical procedure
Lymphatic mapping or lymphoscintigram usually involves injecting radioactive dye in the skin around the site of the original melanoma. The physician then with the help of a special camera locates the radioactive material as it travels from the original melanoma site to the sentinel lymph nodes.
After the completion of lymphatic mapping, the physician injects a second blue dye to visualize the lymph nodes already located by the specialized camera. The physician removes the sentinel lymph nodes and sends it for examination.
Another procedure for a biopsy includes wide local excision. In this, the physician removes the melanoma along with the biopsy tissue and some normal tissue surrounding it.
What are the outcomes of a sentinel lymph node biopsy?
After examination of the biopsied tissue, the sentinel lymph node may show evidence of melanoma in them. If the sentinel lymph nodes don’t show any evidence of melanoma, it is improbable that cancer has spread to the remaining lymph nodes, and no further surgery is needed. Completion lymph node dissection (CLND) is the complete removal of the affected sentinel lymph nodes and remaining lymph nodes in that area and is useful if one or more of the sentinel lymph nodes is positive for melanoma.
What are the complications of a sentinel lymph node biopsy?
The complications of a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) include:

QUESTION
What causes dry eyes? See AnswerTop Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Melanoma Related Articles

aldesleukin (Proleukin)
Aldesleukin is an interleukin injection drug prescribed to treat wide-spread cancer of the kidney and skin (melanoma). Aldesleukin causes side effects in almost every organ, so review side effects of this drug prior to treatment.
Bavencio (avelumab)
Bavencio is a prescription medicine used to treat a type of skin cancer called Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) in adults and children 12 years of age and older, a type of cancer in the bladder or urinary tract called urothelial carcinoma (UC), and a type of kidney cancer called renal cell carcinoma (RCC). The most common side effects of Bavencio include feeling tired, muscle and bone pain, diarrhea, nausea, chills, fever, back pain, rash, decreased appetite, and more, depending upon the patient's condition.
binimetinib
Binimetinib is an anticancer (antineoplastic) medication used in combination with encorafenib in the treatment of adults with melanoma, a type of skin cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Common side effects of binimetinib with encorafenib include fatigue, fever (pyrexia), swelling of extremities (peripheral edema), musculoskeletal pain, generalized edema, localized edema, facial edema, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, and others.
cobimetinib
Cobimetinib is used in the treatment of melanoma, a type of skin cancer, and histiocytic neoplasms, a rare group of tumors that are caused by uncontrolled proliferation of certain types of immune cells known as histiocytes, which include monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells. Common side effects of cobimetinib include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, indigestion (dyspepsia), oral inflammation (stomatitis), dry mouth (xerostomia), oral pain, increase in serum creatinine, increase in creatine phosphokinase (CPK), muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), and others. Cobimetinib may cause fetal harm.
dabrafenib
Dabrafenib is an anticancer (antineoplastic) medication used in the treatment of certain types of melanoma skin cancer, lung and thyroid cancers, and solid tumors. Common side effects of dabrafenib include thickening of skin (hyperkeratosis), hair loss (alopecia), hand-foot syndrome (palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome/PPES), rash, dry skin, acneiform dermatitis, high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia), electrolyte disturbances, and others. Dabrafenib can cause fetal harm if used during pregnancy.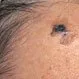
Desmoplastic Melanoma Picture
Desmoplastic melanoma is a rare and invasive form of skin cancer that represents about 4 percent of all skin melanomas. The malignant cells are within the dermis and are surrounded by fibrous tissue so they may look like a scar in texture and appearance. It is usually found in older individuals who have sun damaged skin and is most often found on areas of the skin exposed to the sun such as the face, neck, scalp, legs, and arms.
How Can You Tell the Difference Between Melanoma and Seborrheic Keratosis?
Learn the difference between melanoma and seborrheic keratosis and how to treat each condition.
encorafenib
Encorafenib is an anticancer (antineoplastic) medication used in the treatment of certain types of cancers in adults, including metastatic melanoma, colorectal cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In combination with either binimetinib or cetuximab, encorafenib is used to control cancer growth and resistance to treatment. Side effects of encorafenib vary, depending on which drug it is used in combination with for cancer treatment.
Klisyri (tirbanibulin)
Klisyri is a prescription cream used on the skin to treat actinic keratosis on the face or scalp. Typically caused by years of sun damage, actinic keratosis can later turn into skin cancer if left untreated. The most common side effects of Klisyri include itching or pain in the treatment area.
Melanoma (Skin Cancer)
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer which begins in skin cells called melanocytes and affects more than 53,600 people in the United States each year. These melanocytes can grow together to form benign moles which, after a change in size, shape, or color can be a sign of melanoma. Caused by sun exposure, early detection becomes extremely important to avoid a spread to other areas of the body. Diagnosis is confirmed through a biopsy of the abnormal skin and treatment depends on the extent and characteristics of the patient. Metastatic melanoma is melanoma that has spread to various organs.
pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab is a medication used to treat many cancers as a targeted therapy that does not directly kill cancer cells but alters a specific cell mechanism that promotes cancer growth and spread. Common side effects of pembrolizumab include fatigue, fever, pain, headache, peripheral nerve damage (neuropathy), musculoskeletal pain, joint pain (arthralgia), muscle pain (myalgia), back pain, weakness (asthenia), neck pain, muscle inflammation (myositis), joint inflammation (arthritis), decreased appetite, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, swallowing difficulties (dysphagia), colon inflammation (colitis), and others. Do not take if pregnant or breastfeeding.
Picato (ingenol mebutate)
Picato gel, 0.015% is a prescription medicine used on the skin to treat actinic keratosis on the face or scalp. Picato gel, 0.05% is a prescription medicine used on the skin to treat actinic keratosis on the body or arms and legs. Serious side effects of Picato gel include Eye problems can happen if Picato gel gets in your eyes, serious allergic reactions, and local skin reactions.
Skin Cancer Quiz
What causes skin cancer? Take our Skin Cancer Quiz to learn about the risks, symptoms, causes, and treatments for this common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
Skin Cancer Slideshow
Discover the causes, types, and treatments of skin cancer. Learn how to prevent skin cancer and how to check for melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Also, find out how to spot the early signs of skin cancer.
Sty (Stye)
A sty is a bump that forms on the eyelid as a result of a blocked gland. Styes may be caused by infections, burns, or trauma to the eyelid. Most styes resolve on their own. The application of warm compresses can speed healing. In some cases, steroid injection or incision and drainage may be necessary. Keeping the area clean and consuming a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids may help prevent the formation of styes.
technetium Tc 99m tilmanocept
Technetium Tc 99m tilmanocept is a radioactive diagnostic imaging agent used for mapping lymphatic system and guiding sentinel lymph node biopsy for detection and staging of cancer and planning treatment. Common side effects of technetium Tc 99m tilmanocept include injection site irritation, pain, and hypersensitivity reactions. Report immediately to your physician if you experience hypersensitivity reactions such as rash, difficulty breathing or other allergic reactions following the administration of technetium Tc 99m tilmanocept injection.
Tolak (fluorouracil) Cream
Tolak (fluorouracil) is a prescription cream used to treat skin lesions on the face, ears, or scalp called actinic keratosis caused by sun damage on the skin. Serious side effects of Tolak Cream include skin reactions, possible allergic reactions, and eye problems when the eyes are exposed to the cream.